论文名称:
Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning
发表期刊:
Cell,2018
主要工作:
提出基于深度学习(CNN)和迁移学习(Transform Learning)的诊断模型,将其用于眼底疾病的分类,并验证该模型在儿童肺炎的诊断上的泛化性能
数据:
- 训练集:108312张OCT图片,其中37206张新生血管(choroidal neovascularization),11349张糖尿病性黄斑水肿(diabetic macular edema),8617张脉络膜小疣(drusen)和51140张正常无病变(normal)图像。这些数据来源于4686例病人
- 测试集:1000张图片(每类250张),来源于633例病人
模型:
普通的卷积神经网络+迁移学习
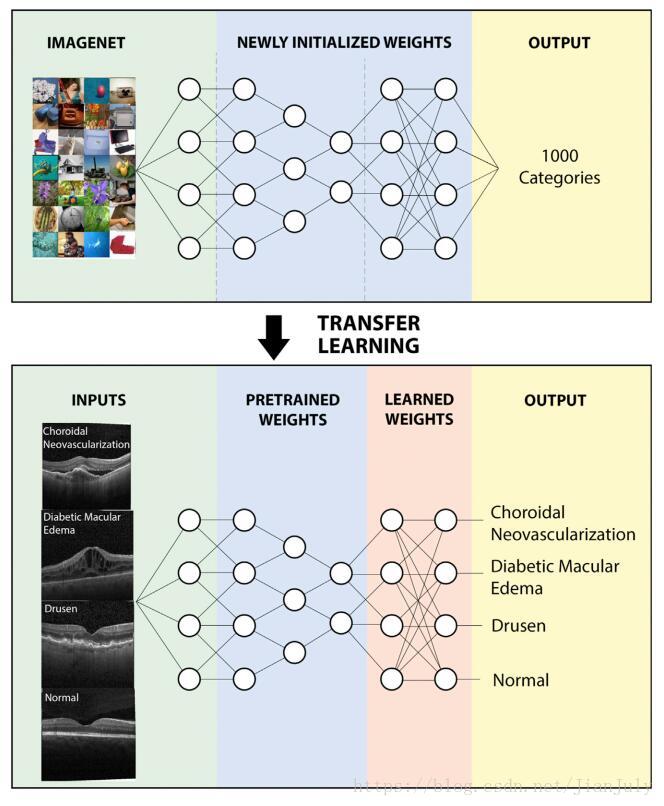
实验一:
将新生血管(choroidal neovascularization)和糖尿病性黄斑水肿(diabetic macular edema)病人视为紧急病人(urgent referrals);将脉络膜小疣(drusen)视为常规病人(routine referrals);将正常无病变图像作为对照组(observation)。进行多分类的测试实验。
实验结果: achieved an accuracy of 96.6%, with a sensitivity of 97.8%, a specificity of 97.4%, and a weighted error of 6.6%.
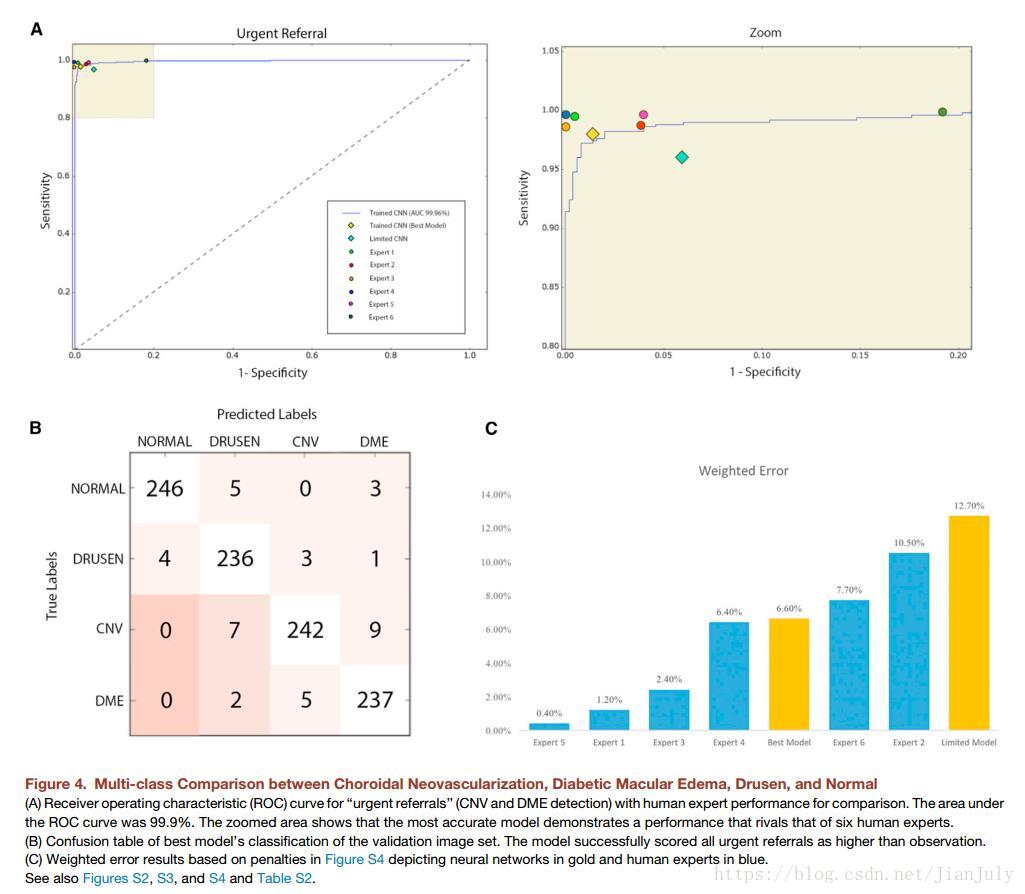
实验二:
训练了一个 “limited model”,只使用了1000张图片作为训练集。
实验结果: achieved an accuracy of 93.4%, with a sensitivity of 96.6%, a
specificity of 94.0%, and a weighted error of 12.7%.
实验三:
二分类模型。分别测试了模型区分choroidal neovascularization / diabetic macular edema / drusen 与normal的性能。
实验结果:
- choroidal neovascularization / normal: achieved an accuracy of 100.0%, with a sensitivity of 100.0% and specificity of 100.0%.
- diabetic macular edema / normal: achieved an accuracy of 98.2%, with a sensitivity of 96.8% and specificity of 99.6%.
- drusen / normal: achieved an accuracy of 99.0%, with a sensitivity of 98.0%
and specificity of 99.2%.
与人类专家比较:
模型的weighted error 为6.6%, 五位人类专家的weighted error 为 0.4% to 10.5%,平均为4.8%。
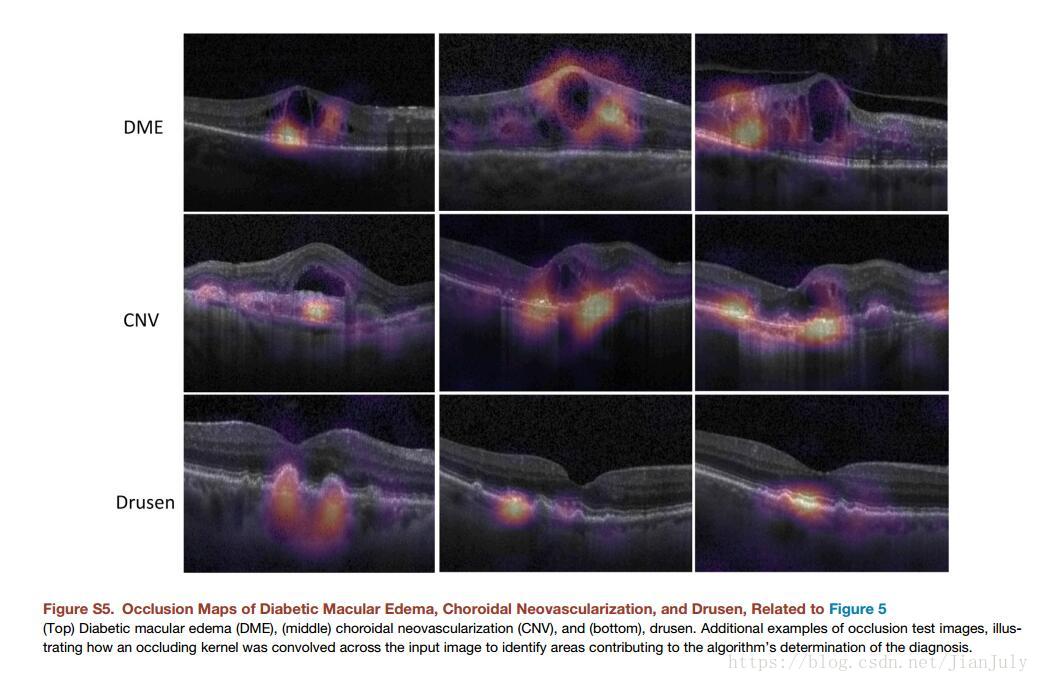
Occlusion Testing:
通过Occlusion Testing来绘制关于模型决策的heatmap。heatmap值大的像素代表该像素对于模型决策的贡献度高,反之亦然。
将模型应用于儿童肺炎检测:
- 用于测试模型的泛化性能
- 细菌性肺炎和病毒性肺炎二分类,achieved an accuracy of 92.8%, with a sensitivity of 93.2% and a specificity of 90.1%





 研究利用深度学习技术,特别是卷积神经网络和迁移学习,实现了对眼底疾病的准确分类,包括新生血管、糖尿病性黄斑水肿等。此外,还评估了模型在儿童肺炎诊断中的泛化能力。
研究利用深度学习技术,特别是卷积神经网络和迁移学习,实现了对眼底疾病的准确分类,包括新生血管、糖尿病性黄斑水肿等。此外,还评估了模型在儿童肺炎诊断中的泛化能力。
















 1307
1307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








