1.负载因子
负载因子=已有元素数组长度\frac{已有元素}{数组长度}数组长度已有元素
2.哈希函数
[1] 除余法h(x) = x % M
[2] 乘余取整法 h(x) = floor(n * (A * x的小数部分))
[3] 平方取中法 先平方,然后取中间几位
[4] 基数转换法 换成其他进制,然后取其中几位
[5] ELFhash字符串
2种哈希算法
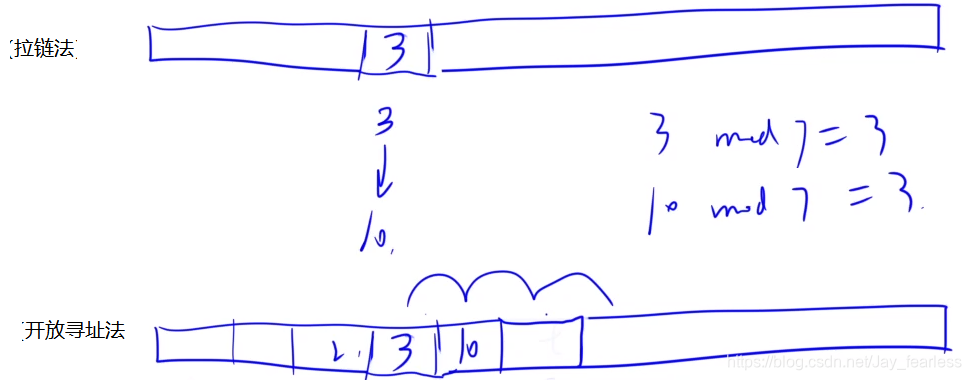
1.开散列方法(拉链法)
2.闭散列方法(开放寻址法)
聚集和二级聚集
a. 线性探查法 d(i) = (d(0) + i * c) % M。易产生聚集问题。
b. 二次探查法。易产生二级聚集问题。
d(2i - 1) = (d(0) + i^2) % M
d(2i) = (d(0) - d ^2) % M
c. 随机探查法。易产生二级聚集问题。
d. 双散列探查法
拉链法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5+3;
int n,x,idx;
char op[2];
int h[N],e[N],ne[N];
void add(int a, int b)
{
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ;
}
bool check(int t,int x)
{
for(int i=h[t];~i;i=ne[i])
{
if(e[i]==x) return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",op);
if(*op=='I'){
scanf("%d",&x);
int t=(x%N+N)%N;
if(!check(t,x))
add(t,x);
}
else{
scanf("%d",&x);
int t=(x%N+N)%N;
if(check(t,x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}
开放寻址法
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5+3,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,x,idx;
char op[2];
int h[N];
int find(int x)
{
int t=(x%N+N)%N;
while(h[t]!=INF && h[t]!=x)
t=(t+1)%N;
return t;
}
int main()
{
memset(h,0x3f,sizeof h);
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s%d",op,&x);
if(*op=='I')
{
h[find(x)]=x;
}
else{
if(h[find(x)]==INF) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
return 0;
}
3.KMP算法
ne[i]:前i个字母构成的字符串中,最长的前缀相等的后缀长度

KMP算法代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 1000010;
int n, m;
char p[N], s[M];
int ne[N];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%s", &n, p + 1);
scanf("%d%s", &m, s + 1);
//求ne数组
for (int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i ++ )
{
while (j && p[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (p[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
//求匹配情况
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i ++ )
{
while (j && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == n) printf("%d ", i - n);
}
return 0;
}
散列表中解决冲突的两种方法是(开放地址法)和(链地址法)。





 本文深入探讨了哈希表中的负载因子概念,介绍了多种哈希函数的实现,如除余法、乘余取整法等,并详细阐述了开散列(拉链法)和闭散列(开放寻址法)解决冲突的策略,包括线性探查、二次探查和随机探查。同时,提到了KMP算法在字符串匹配中的应用,讨论了其如何利用最长公共前后缀避免不必要的比较。最后,总结了散列表中解决冲突的两种主要方法:开放地址法和链地址法。
本文深入探讨了哈希表中的负载因子概念,介绍了多种哈希函数的实现,如除余法、乘余取整法等,并详细阐述了开散列(拉链法)和闭散列(开放寻址法)解决冲突的策略,包括线性探查、二次探查和随机探查。同时,提到了KMP算法在字符串匹配中的应用,讨论了其如何利用最长公共前后缀避免不必要的比较。最后,总结了散列表中解决冲突的两种主要方法:开放地址法和链地址法。

















 899
899

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










