文章目录
往期文章链接目录
Information Extraction v.s. Relation Extraction
Information Extraction: Information extraction is the task of automatically extracting structured information from unstructured and/or semi-structured machine-readable documents and other electronically represented sources.
Relation extraction (RE) is an important task in IE. It focuses on extracting relations between entities. A complete relation RE system consists of
- a named entity recognizer to identify named entities from text.
- an entity linker to link entities to existing knowledge graphs.
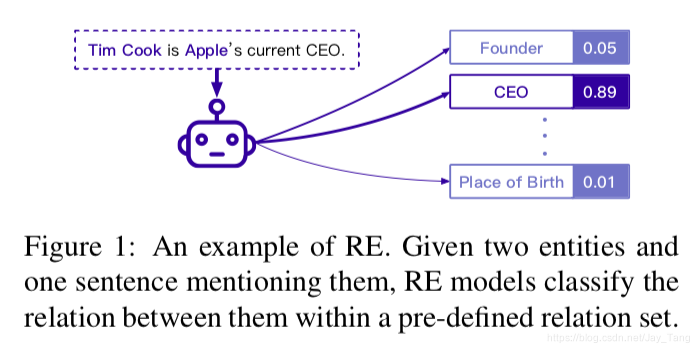
- a relational classifier to determine relations between entities by given context (most difficult and important).
Existing Works of RE
RE methods follows the typical supervised setting, from early pattern-based methods, statistical approaches, to recent neural models.
Pattern-based Methods
The early methods use sentence analysis tools to identify syntactic elements in text, then automatically construct pattern rules from these elements. Later work involves larger corpora, more formats of patterns and more efficient ways of extraction.
Statistical Relation Extraction Models
Statistical Methods requires less human efforts so that statistical relation extraction (SRE) has been extensively studied. Approaches includes:
- feature-based methods which design lexical, syntactic and semantic features for entity pairs and their corresponding context (hard to design features).
- kernel-based methods measures the similarities between relation representations and textual instances (hard to design kernel functions).
- Graphical methods abstract the dependencies between entities, text and relations in the form of directed acyclic graphs, and then use inference models to identify the correct relations (still limited model capacities)





 本文探讨了关系抽取的重要性和发展历程,从早期的模式匹配方法到现代的神经网络模型,包括递归神经网络、卷积神经网络、循环神经网络和注意力机制。未来的研究方向集中在利用更多数据、进行更有效的学习以及处理复杂上下文,以应对现实世界的挑战,如远程监督、少样本学习和开放域关系抽取。
本文探讨了关系抽取的重要性和发展历程,从早期的模式匹配方法到现代的神经网络模型,包括递归神经网络、卷积神经网络、循环神经网络和注意力机制。未来的研究方向集中在利用更多数据、进行更有效的学习以及处理复杂上下文,以应对现实世界的挑战,如远程监督、少样本学习和开放域关系抽取。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








