文章目录
往期文章目录链接
Relation Extraction (RE)
Relation Extraction (RE): The extraction of relations between named entities in text.

Relation Extraction is an important task of NLP. Most existing works focus on intra-sentence RE. In fact, in real-world scenarios, a large amount of relations are expressed across sentences. The task of identifying these relations is named inter-sentence RE.
Typically, inter-sentence relations occur in textual snippets with several sentences, such as documents. In these snippets, each entity is usually repeated with the same phrases or aliases, the occurrences of which are often named entity mentions and regarded as instances of the entity.
The multiple mentions of the target entities in different sentences can be useful for the identification of inter-sentential relations, as these relations may depend on the interactions of their mentions with other entities in the same document. The figure above is an good example of identifying the relationship between “ethambutol”, “isoniazid” and “scotoma”, where they all interact with the green colored entity (and its alias).
document-level RE
-
In concept, document-level RE the input is considered an annotated document. The annotations include concept-level entities as well as multiple occurrences of each entity under the same phrase of alias, i.e., entity mentions.
-
Objective: the objective of the task is given an annotated document, to identify all the related concept-level pairs in that document.
Document-level RE is not common in the general domain, as the entity types of interest can often be found in the same sentence. On the contrary, in the biomedical domain, document-level relations are particularly important given the numerous aliases that biomedical entities can have (as shown in the figure above).
Intuition
Graph-based neural approaches have proven useful in encoding long distance, inter-sentential information. These models interpret words as nodes and connections between them as edges. They typically perform on the nodes by updating the representations during training.
This paper: However, a relation between two entities depends on different contexts. It could thus be better expressed with an edge connection that is unique for the pair. A straightforward way to address this is to create graph-based models that rely on edge representations rather focusing on node representations, which are shared between multiple entity pairs.
Contribution
- We propose a novel edge-oriented graph neural model for document-level relation extraction, which encodes information into edge representations rather than node representations.
- Analysis indicates that the document-level graph can effectively encode document-level dependencies.
- we show that inter-sentence associations can be beneficial for the detection of intra-sentence relations.
Overview of Proposed Model
We presented a novel edge-oriented graph neural model (EoG) for document-level relation extraction using multi-instance learning. The proposed model constructs a document-level graph with heterogeneous types of nodes and edges, modelling intra- and inter-sentence pairs simultaneously with an iterative algorithm over the graph edges.
Here is an illustration of the abstract architecture of the proposed approach.
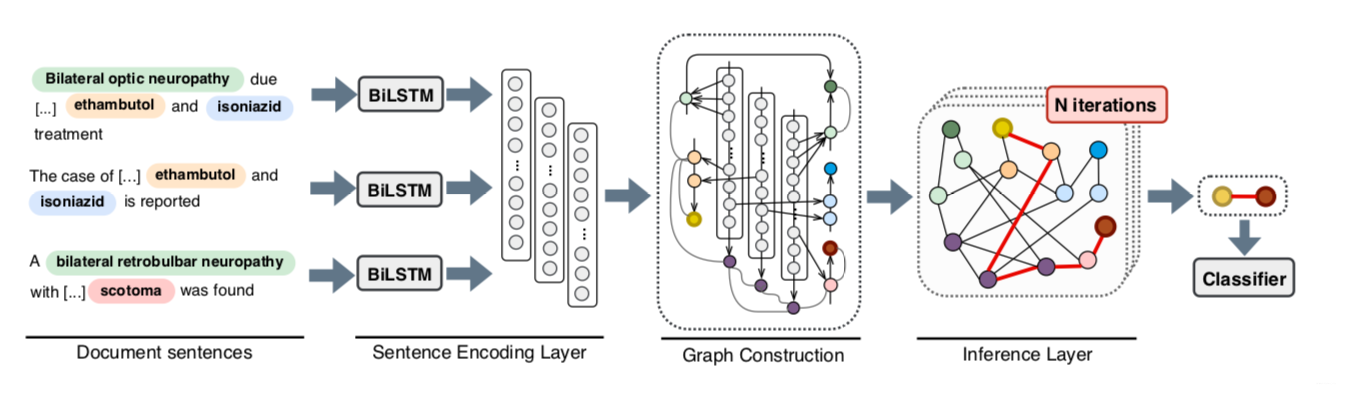
Proposed Model
The proposed model consists of four layers: sentence encoding, graph construction, inference and classification layers. The model receives a document (with identified concept-level entities and their textual mentions) and encodes each sentence separately. A document-level graph is constructed and fed into an iterative algorithm to generate edge representations between the target entity nodes.
Sentence Encoding Layer
We use a Bi-LSTM to encode each sentence and then get a contextualized word representations of the input sentence. The contextualized word representations from the encoder are then used to construct a document-level graph structure.
Graph construction Layer
Graph construction consists of Node Construction and Edge Construction.
Node Construction
They form three distinct types of nodes in the graph:
- Mention nodes (M) n m n_m nm. Mention nodes correspond to different mentions of entities in the input document. The representation of a mention node is formed as the average of the words ( w w w) that the mention contains, i.e. avg w i ∈ m ( w i ) \operatorname{avg}_{w_{i} \in m}\left(\mathbf{w}_{i}\right) avgwi∈m(wi).
- Entity nodes (E) n e n_e ne. Entity nodes represent unique entity concepts. The representation of an entity node is computed as the average of the mention ( m m m) representations associated with the entity, i.e. avg m i ∈ e ( m i ) \operatorname{avg}_{m_{i} \in e}\left(\mathbf{m}_{i}\right) avgmi∈e(mi).
- Sentence nodes (S) n s n_s ns. Sentence nodes correspond to sentences. A sentence node is represented as the average of the word representations in the sentence, i.e. avg w i ∈ s ( w i ) \operatorname{avg}_{w_{i} \in s}\left(\mathbf{w}_{i}\right) avgwi∈s(wi).
To distinguish different node types in the graph, they concatenate a node type ( t t t) embedding to each node representation. The final node representations are then estimated as n m = [ avg w i ∈ m ( w i ) ; t m ] , n e = \mathbf{n}_{m}=[\operatorname{avg}_{w_{i} \in m}\left(\mathbf{w}_{i}\right) ; \mathbf{t}_{m}], \mathbf{n}_{e}= nm=[avgwi∈m(wi);tm],ne= [ avg m i ∈ e ( m i ) ; t e ] , n s = [ avg w i ∈ s ( w i ) ; t s ] [\operatorname{avg}_{m_{i} \in e}\left(\mathbf{m}_{i}\right) ; \mathbf{t}_{e}], \mathbf{n}_{s}=[\operatorname{avg}_{w_{i} \in s}\left(\mathbf{w}_{i}\right) ; \mathbf{t}_{s}] [avgmi∈e(mi





 本文介绍了如何使用边导向图神经模型进行文档级的关系抽取,重点在于利用边表示不同实体对的独特上下文,从而提高跨句子关系识别的准确性。模型包括句子编码、图构建、推理和分类层,实验表明该模型在提取文档级和句子级关系时表现出优越性能。
本文介绍了如何使用边导向图神经模型进行文档级的关系抽取,重点在于利用边表示不同实体对的独特上下文,从而提高跨句子关系识别的准确性。模型包括句子编码、图构建、推理和分类层,实验表明该模型在提取文档级和句子级关系时表现出优越性能。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1750
1750

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








