
机器学习核心问题:过拟合 vs 欠拟合
图示作者:Chris Albon
1. 什么是拟合(Fit)?
拟合(Fit)是指模型对数据的学习效果。
理想目标:
在训练集上效果好
在测试集上效果也好
不复杂、不简单,恰到好处
2. 什么是过拟合(Overfitting)?
定义
过拟合是指模型在训练集上表现很好,但在测试集或新数据上效果很差。模型学到了“噪声”或“异常值”的特征。
特征
| 特征 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| 方差很大 | 对数据过度敏感 |
| 决策边界复杂 | 曲折、震荡 |
| 泛化能力差 | 新数据易失败 |
图示(来自图片左侧)
特征2 ↑
● ○ ○
○ ○
○ ● ● ○ ← 决策边界很曲折
特征1 →
3. 什么是欠拟合(Underfitting)?
定义
欠拟合是指模型太简单,无法捕捉数据的有效规律,无论在训练集还是测试集上效果都不好。
特征
| 特征 | 表现 |
|---|---|
| 偏差很大 | 无法拟合数据规律 |
| 决策边界简单 | 接近直线 |
| 泛化能力弱 | 无法有效学习 |
图示(来自图片右侧)
特征2 ↑
● ○ ○
○ ○
○ ● ● ○ ← 决策边界几乎是直线
特征1 →
4. 理想拟合(Best Fit)
状态
-
偏差(Bias)适中
-
方差(Variance)适中
-
决策边界恰好捕捉规律
-
泛化能力强
图示(图片中间)
特征2 ↑
● ○ ○
○ ○
○ ● ● ○ ← 决策边界几乎是直线
特征1 →
5. 数学公式:偏差-方差分解(Bias-Variance Tradeoff)
理论公式
机器学习期望误差可以分解为:
| 名称 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Bias | 偏差,模型简单 |
| Variance | 方差,模型敏感 |
| Irreducible Error | 无法消除的随机误差 |
6. Python实操示例
构造数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 真实函数
def true_func(x):
return np.sin(2 * np.pi * x)
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.sort(np.random.rand(30))
y = true_func(x) + np.random.normal(scale=0.3, size=x.shape)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3)
欠拟合(低阶多项式)
poly1 = PolynomialFeatures(degree=1)
x1_train = poly1.fit_transform(x_train.reshape(-1, 1))
x1_test = poly1.transform(x_test.reshape(-1, 1))
model1 = LinearRegression().fit(x1_train, y_train)
print('欠拟合 MSE:', mean_squared_error(y_test, model1.predict(x1_test)))
欠拟合 MSE: 0.418206083278207
过拟合(高阶多项式)
poly15 = PolynomialFeatures(degree=15)
x15_train = poly15.fit_transform(x_train.reshape(-1, 1))
x15_test = poly15.transform(x_test.reshape(-1, 1))
model15 = LinearRegression().fit(x15_train, y_train)
print('过拟合 MSE:', mean_squared_error(y_test, model15.predict(x15_test)))过拟合 MSE: 2.732472745353921
理想情况(适中阶)
poly4 = PolynomialFeatures(degree=4)
x4_train = poly4.fit_transform(x_train.reshape(-1, 1))
x4_test = poly4.transform(x_test.reshape(-1, 1))
model4 = LinearRegression().fit(x4_train, y_train)
print('理想拟合 MSE:', mean_squared_error(y_test, model4.predict(x4_test)))
理想拟合 MSE: 0.1546713133312227
7. 如何避免过拟合与欠拟合?
| 问题类型 | 解决思路 |
|---|---|
| 过拟合 | - 降低模型复杂度 - 增加正则化(L1/L2) - 增加数据量 - Dropout - 提前停止 |
| 欠拟合 | - 增加特征 - 增强模型复杂度 - 降低正则化 - 使用更强模型 |
8. 可视化偏差-方差关系(效果示意)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# 真实函数
def true_func(x):
return np.sin(2 * np.pi * x)
np.random.seed(0)
x = np.sort(np.random.rand(30))
y = true_func(x) + np.random.normal(scale=0.3, size=x.shape)
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.3)
complexity = np.arange(1, 15)
train_errors = []
test_errors = []
for d in complexity:
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=d)
x_tr = poly.fit_transform(x_train.reshape(-1, 1))
x_te = poly.transform(x_test.reshape(-1, 1))
model = LinearRegression().fit(x_tr, y_train)
train_errors.append(mean_squared_error(y_train, model.predict(x_tr)))
test_errors.append(mean_squared_error(y_test, model.predict(x_te)))
plt.plot(complexity, train_errors, label='Train Error')
plt.plot(complexity, test_errors, label='Test Error')
plt.xlabel('Model Complexity (degree)')
plt.ylabel('MSE')
plt.legend()
plt.show()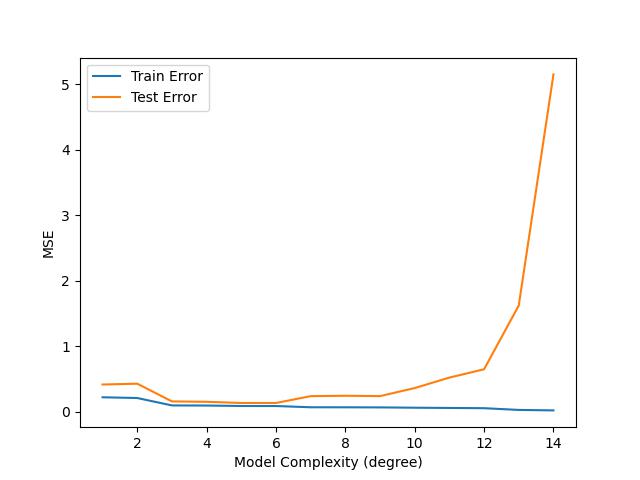
9. 总结
| 项目 | 过拟合 | 欠拟合 |
|---|---|---|
| 决策边界 | 复杂 | 简单 |
| 偏差Bias | 低 | 高 |
| 方差Variance | 高 | 低 |
| 表现 | 训练好,测试差 | 训练差,测试差 |
10. 最佳实践
寻找偏差和方差的平衡,是机器学习调参的艺术。
合理的特征工程 + 模型复杂度控制 + 正则化技术,是最佳组合。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








