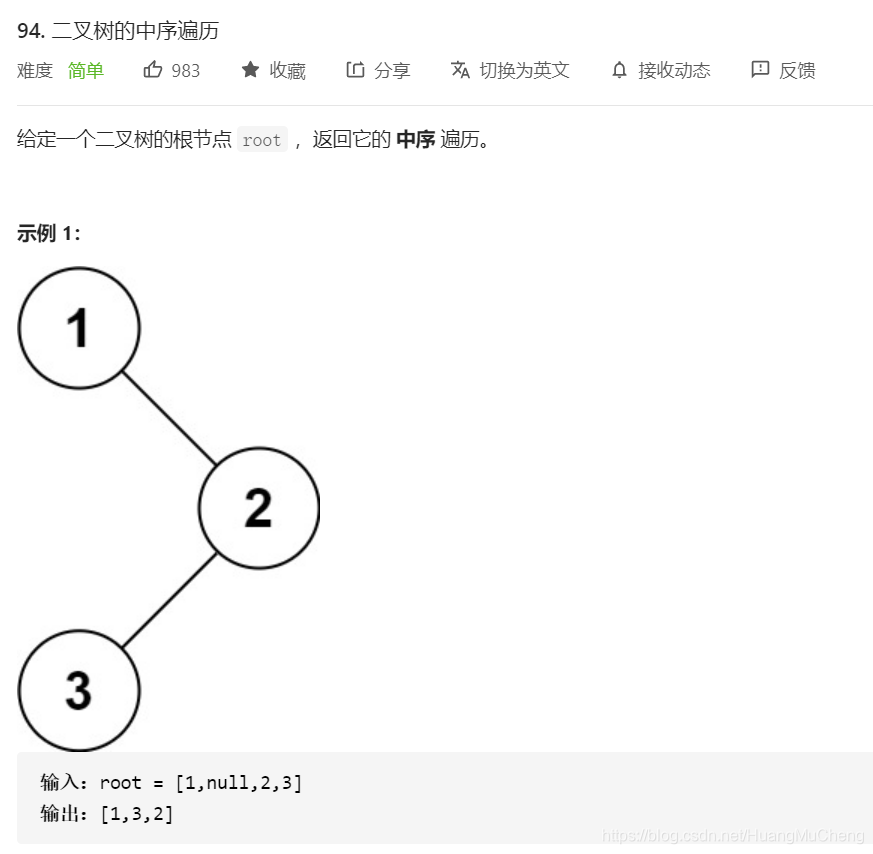
LeetCode-094-二叉树的中序遍历
思路
参考 迭代解法,时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n) - 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
二叉树有三种常用的遍历方式,分别为先(根 -> 左 -> 右),中(左 ->根-> 右),后(左 ->右-> 根)
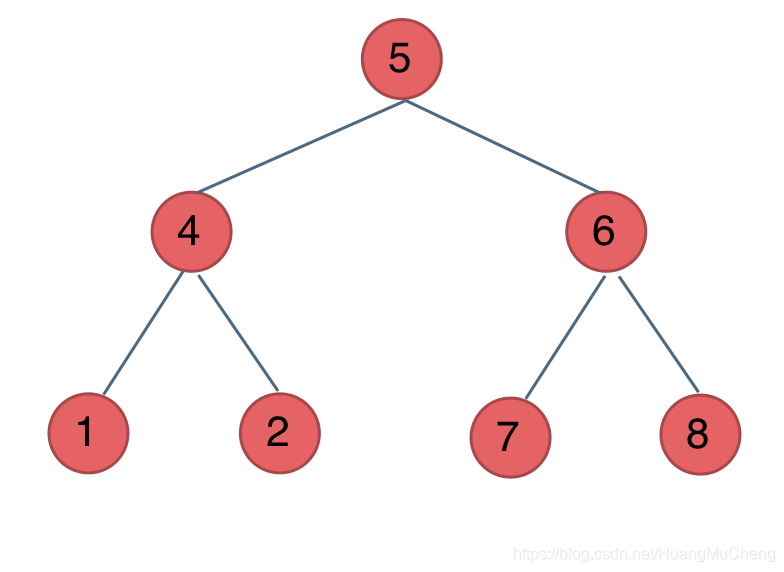
前中后序遍历顺序如下:
前序遍历(中左右):5 4 1 2 6 7 8
中序遍历(左中右):1 4 2 5 7 6 8
后序遍历(左右中):1 2 4 7 8 6 5
这里顺便总结一下二叉树的三种遍历的递归和非递归写法
参考:
帮你对二叉树不再迷茫,彻底吃透前中后序递归法(递归三部曲)和迭代法(不统一写法与统一写法) - 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
迭代解法,时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n) - 二叉树的后序遍历 - 力扣(LeetCode) (leetcode-cn.com)
1.递归:
1.1先序遍历
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
visit(root);
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
}
1.2中序遍历
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
visit(root);
dfs(root.right);
}
1.3 后序遍历
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
visit(root);
}
2.非递归
2.1先序遍历
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root!=null){
if(root!=null){
res.add(root.val);
stack.push(root.right);
root = root.left;
}
else {
root = stack.pop();
}
}
return res;
}
2.2中序遍历
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null)return res;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty()||root!=null){
if(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}
else {
root=stack.pop();
res.add(root.val);
root=root.right;
}
}
return res;
}
2.3后序遍历
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(!stack.isEmpty() || root!=null){
if(root!=null){
res.add(0,root.val);//头插,使得中左右->右左中
//先左后右,使得右左中->左右中
stack.push(root.left);
root = root.right;
}
else {
root = stack.pop();
}
}
return res;
}
3.层次遍历
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ans=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return ans;
Queue<TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
int n=queue.size();
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
while(n>0){
TreeNode node=queue.poll();
list.add(node.val);
if(node.left!=null)queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right!=null)queue.add(node.right);
n--;
}
ans.add(list);
}
return ans;
}





 本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历的递归与非递归方法,包括代码实现,并给出了层次遍历的解决方案。通过对不同遍历方式的解析,帮助读者深入理解二叉树操作。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的前序、中序、后序遍历的递归与非递归方法,包括代码实现,并给出了层次遍历的解决方案。通过对不同遍历方式的解析,帮助读者深入理解二叉树操作。
















 715
715

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








