#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a, b;
int process(int n);
int main()
{
int n;
while(1)
{
cin>>a>>b>>n;
if(a==0 && b ==0 && n==0)
break;
else
cout<<process(n);
}
return 0;
}
int process(int n)
{
if(n!=1 && n!=2)
return ((a*process(n-1)+b*process(n-2))%7);
else
return 1;
}
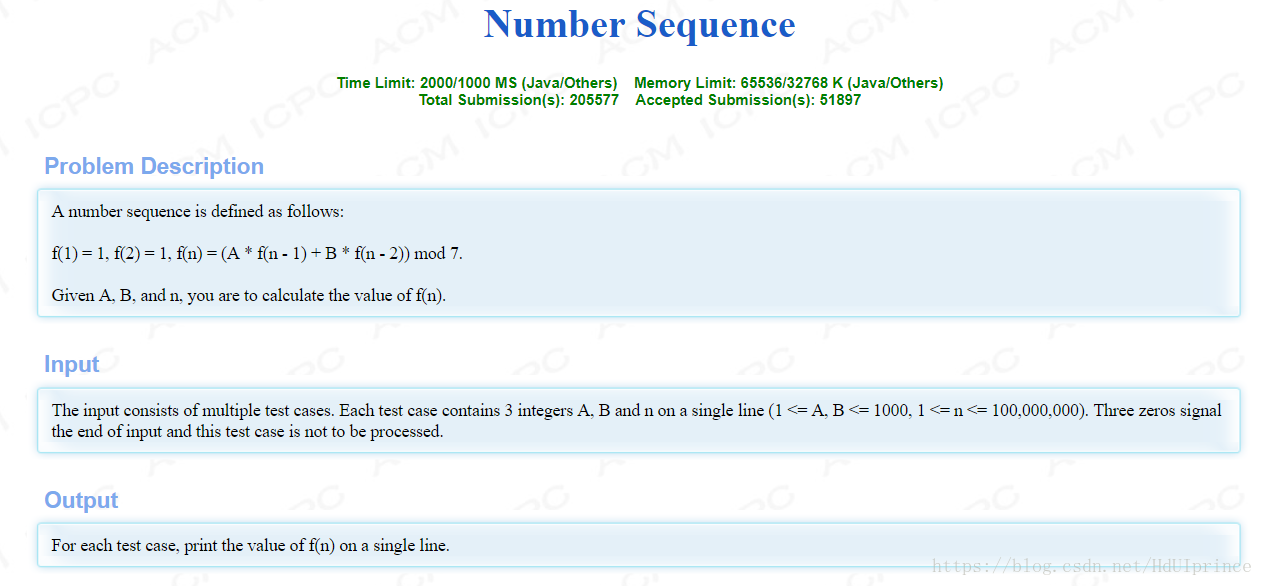
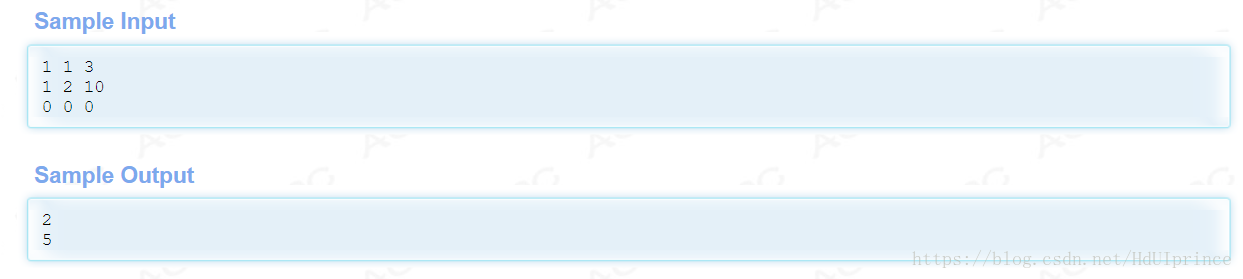
递归法:Memory Limit Exceeded
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a, b, n;
while(cin>>a>>b>>n)
{
int arr[50] = {0};
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 1;
if (a==0 && b==0 && n==0)
break;
for(int i=3; i<50; i++)
{
arr[i] = (a*arr[i-1] + b*arr[i-2])%7;
}
int t = n%49;
cout<<arr[t]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}





 本文通过一个具体的数学问题,介绍了两种不同的算法实现方式——递归法与迭代法,并对比了它们在内存使用上的差异。通过对递归法中出现的Memory Limit Exceeded错误进行分析,进而提出了一种优化方案,即采用迭代法来解决问题,有效避免了内存溢出的情况。
本文通过一个具体的数学问题,介绍了两种不同的算法实现方式——递归法与迭代法,并对比了它们在内存使用上的差异。通过对递归法中出现的Memory Limit Exceeded错误进行分析,进而提出了一种优化方案,即采用迭代法来解决问题,有效避免了内存溢出的情况。
















 804
804

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








