刷LeetCode二叉树题目,简单明了,保证一看就懂的代码。
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回 它的 中序 遍历 。递归实现【左->根->右】
import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
inorder(root, res);
return res;
}
// 递归实现中序遍历
public void inorder(TreeNode root, List<Integer> res) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
inorder(root.left, res);
res.add(root.val);
inorder(root.right, res);
}
}104. 二叉树的最大深度【递归实现】
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
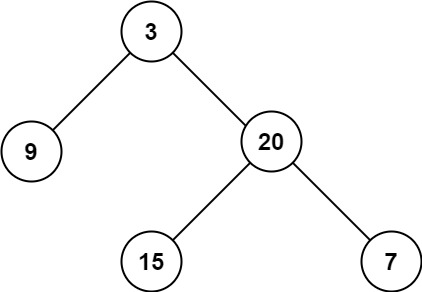
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2] 输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
// 递归计算二叉树的高度
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
// 最大高度即为最大深度
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}简化版写法:
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
public static int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
//如果左子树等于空,我们返回右子树的最小高度+1
if (root.left == null)
return minDepth(root.right) + 1;
//如果右子树等于空,我们返回左子树的最小高度+1
if (root.right == null)
return minDepth(root.left) + 1;
//如果左右子树都不为空,我们返回左右子树深度最小的那个+1
return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}226. 翻转二叉树【递归算法,根->左->右】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(Objects.isNull(root)){
return null;
}
TreeNode tmp=root.right;
root.right=root.left;
root.left=tmp;
// 递归最子树节点
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
return root;
}
}101. 对称二叉树 【递归的前序遍历】
**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
}
// 二叉树的前序遍历实现
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) {
return true;
}
if (p == null || q == null) {
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
}
}543. 二叉树的直径【递归的前序遍历】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int maxd=0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
depth(root);
return maxd;
}
public int depth(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return 0;
}
int Left = depth(node.left);
int Right = depth(node.right);
// 将每个节点最大直径(左子树深度+右子树深度)当前最大值比较并取大者
maxd=Math.max(Left+Right,maxd);
// 所以求直径(即求路径长度的最大值)等效于求路径经过节点数的最大值减,已该节点为起点的加一
return Math.max(Left,Right)+1;
}
}import java.util.*;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
if (root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
List<Integer> level = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int currentLevelSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 1; i <= currentLevelSize; ++i) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
level.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
ret.add(level);
}
return ret;
}
}108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树【递归的前序实现】
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
// 总是选择中间位置左边的数字作为根节点,二叉搜索树特点:根节点大于左节点,小于右节点,那么类似二叉搜索树的中序遍历
int mid = left+(right-left)/2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
// 递归实现
root.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
root.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
return root;
}
}/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNod




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 293
293

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










