一、类图说明
- 实现Future和CompletionStage
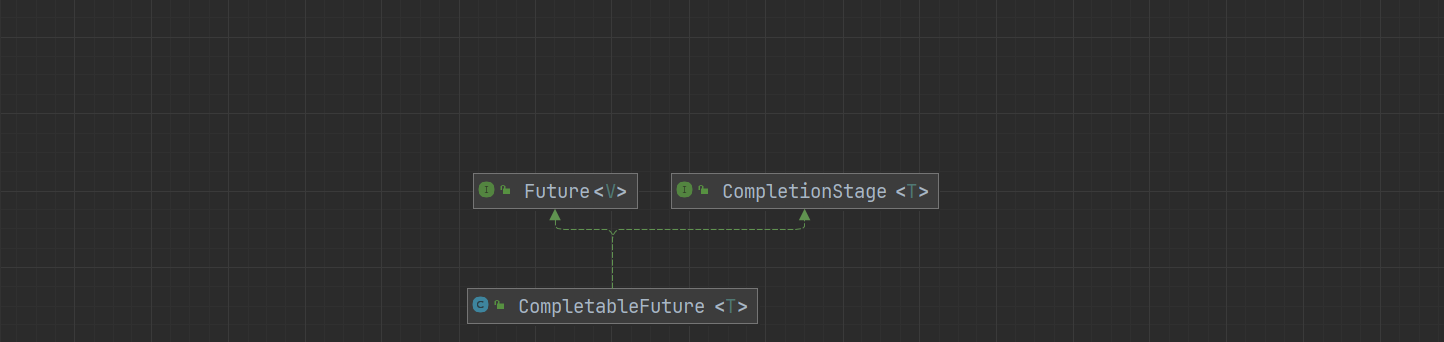
二、核心方法使用
-
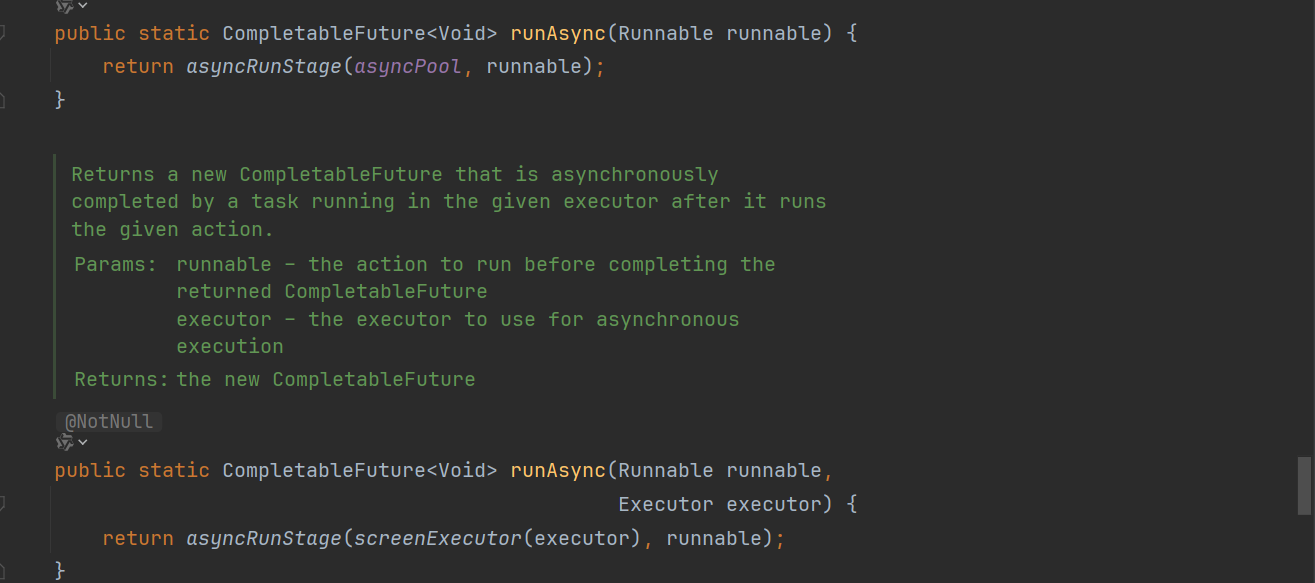
runAsync : 无返回值
// 无返回值+默认线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
// 无返回值+自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,
Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
}
测试代码如下:
/**
* 测试无返回值+使用默认线程池
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForRunAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("test CompletableFuture run Async");
System.out.println("execute thread name"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
System.out.println("结果->"+runAsync.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
/**
* 测试无返回值+使用自定义线程池
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForRunAsyncForThreadPool() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("test CompletableFuture run Async");
System.out.println("execute thread name"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
},executorService);
System.out.println("结果->"+runAsync.get());
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
测试结果如下:

-
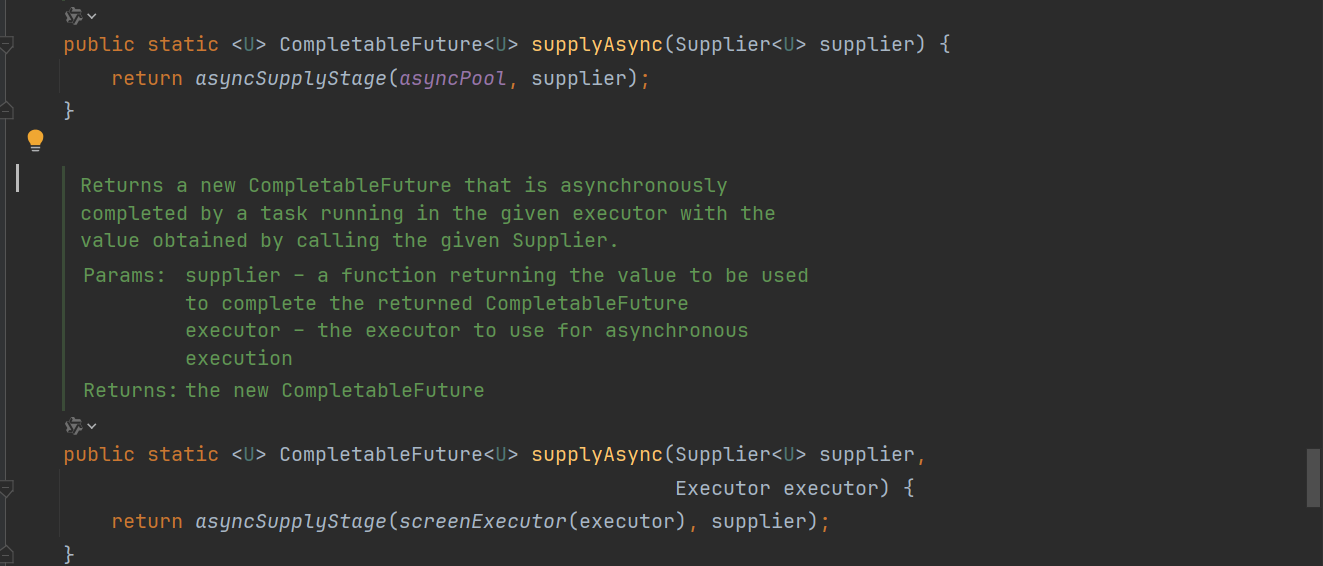
supplyAsync:有返回值
// 有返回值+默认线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
// 有返回值+自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}
测试代码如下:
/**
* 测试有返回值+使用默认线程池
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForSupplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("test CompletableFuture supply Async");
System.out.println("execute thread name"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "result";
});
System.out.println("结果->"+supplyAsync.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
/**
* 测试有返回值+使用自定义线程池
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForSupplyAsyncForThreadPool() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("test CompletableFuture supply Async");
System.out.println("execute thread name"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "thread pool result";
},executorService);
System.out.println("结果->"+supplyAsync.get());
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
测试结果如下:

-
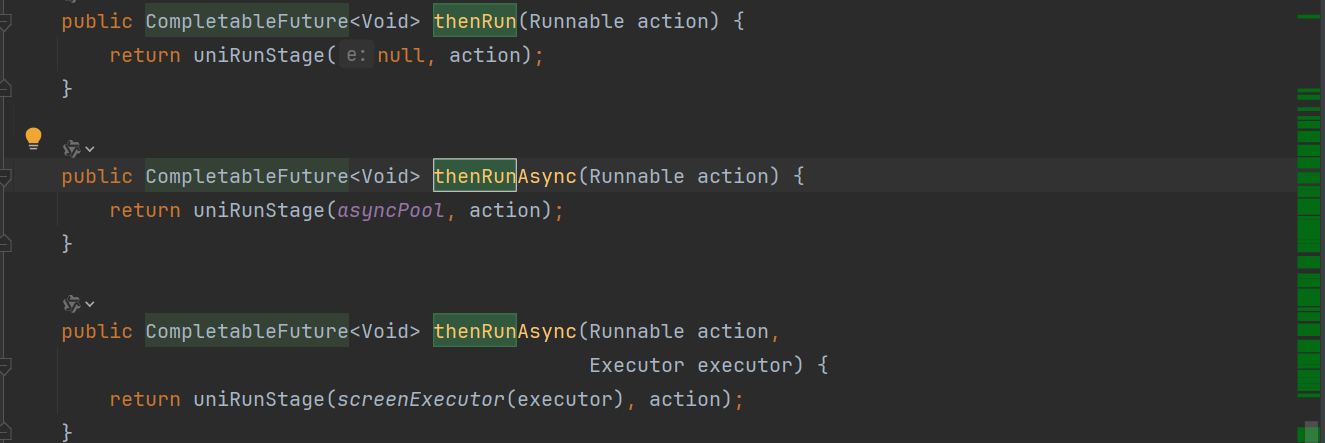
thenApply:表示某个任务执行完成后执行的动作,即回调方法,会将该任务的执行结果即方法返回值作为入参传递到回调方法中,带有返回值。
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(null, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action) {
return uniRunStage(asyncPool, action);
}
public CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action,
Executor executor) {
return uniRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), action);
}
测试代码如下:
/**
* 测试thenApply
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
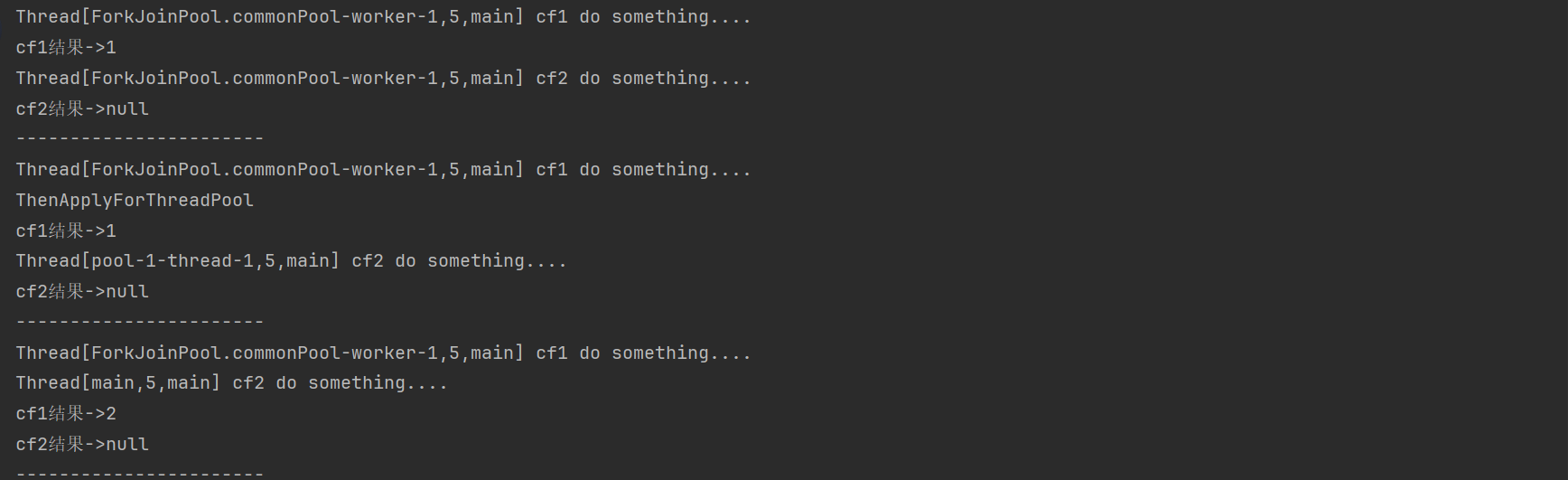
public static void testCompletableFutureForThenApply() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync = supplyAsync1.thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + supplyAsync1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + thenRunAsync.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
/**
* 测试thenRunAsync
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForThenApplyForThreadPool() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 1;
});
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRunAsync = supplyAsync1.thenRunAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
},executorService);
System.out.println("ThenApplyForThreadPool");
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + supplyAsync1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + thenRunAsync.get());
executorService.shutdown();
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
/**
* 测试thenRunAsync
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public static void testCompletableFutureForThenApplyAsync() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Integer> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf1 do something....");
return 2;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun = supplyAsync1.thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " cf2 do something....");
});
//等待任务1执行完成
System.out.println("cf1结果->" + supplyAsync1.get());
//等待任务2执行完成
System.out.println("cf2结果->" + thenRun.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
测试结果如下:
-
allof 聚合任务(任意任务完成)
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return andTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}

测试代码如下:
/**
* 测试allOf
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
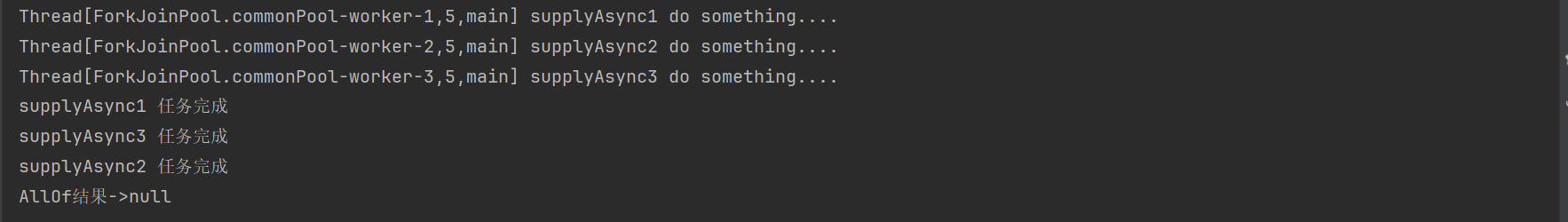
public static void testCompletableFutureForallOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync1 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync2 do something....");
// int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync2 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync3 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync3 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync3 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> supplyAllOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(supplyAsync1, supplyAsync2, supplyAsync3);
System.out.println("AllOf结果->" + supplyAllOf.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
测试结果如下:
测试代码如下:
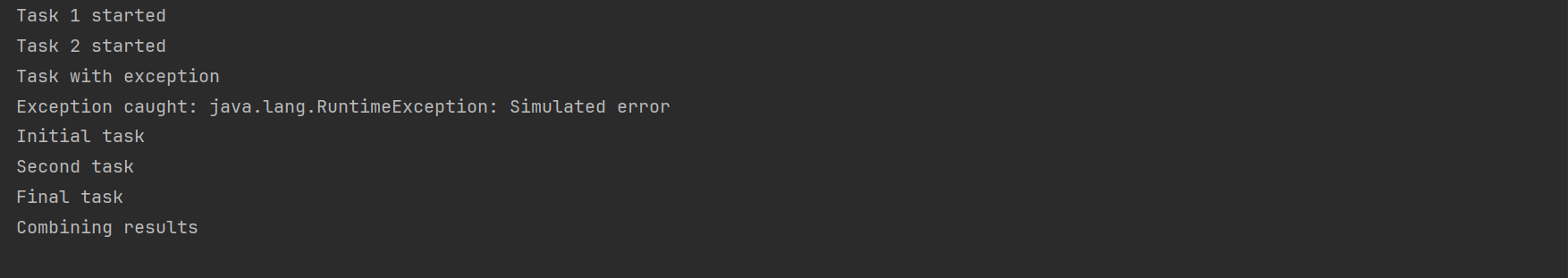
// 1. 异步任务组合
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Task 1 started");
try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
return 10;
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Task 2 started");
try { Thread.sleep(300); } catch (InterruptedException e) {}
return 20;
});
// 2. 并行组合任务结果
CompletableFuture<Integer> combined = future1.thenCombine(future2, (a, b) -> {
System.out.println("Combining results");
return a + b;
});
// 3. 异常处理
CompletableFuture<Integer> exceptionHandling = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Task with exception");
if (true) throw new RuntimeException("Simulated error");
return 100;
}).exceptionally(ex -> {
System.out.println("Exception caught: " + ex.getMessage());
return 0;
});
// 4. 链式回调
CompletableFuture<Void> chain = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("Initial task");
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("Second task");
}).thenRun(() -> {
System.out.println("Final task");
});
// 5. 等待所有任务完成
CompletableFuture<Void> allDone = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, combined, exceptionHandling, chain);
allDone.get(); // 等待所有任务完成
测试结果如下:
-
anyof聚合任务(任意任务完成)
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {
return orTree(cfs, 0, cfs.length - 1);
}

测试代码如下:
/**
* 测试anyOf
* @throws ExecutionException
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
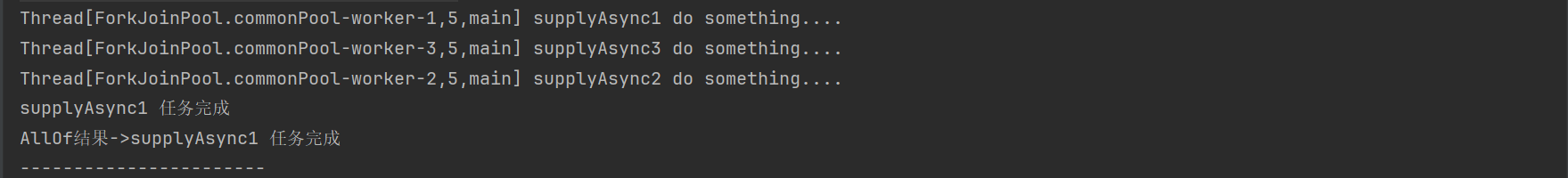
public static void testCompletableFutureForanyOf() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync1 do something....");
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync1 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync1 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync2 do something....");
// int a = 1/0;
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync2 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync2 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsync3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " supplyAsync3 do something....");
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("supplyAsync3 任务完成");
return "supplyAsync3 任务完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> supplyAllOf = CompletableFuture.anyOf(supplyAsync1, supplyAsync2, supplyAsync3);
System.out.println("AllOf结果->" + supplyAllOf.get());
System.out.println("-----------------------");
}
测试结果如下:
-
thenCombine 合并任务
thenCombine 会把 两个 CompletionStage 的任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果一块交给 thenCombine 来处理。
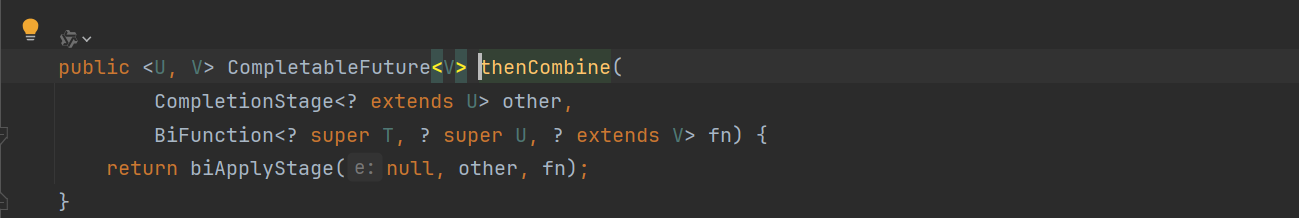
public <U,V> CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(
CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn) {
return biApplyStage(null, other, fn);
}
private static void thenCombine() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
return "then";
}
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<String>() {
@Override
public String get() {
return "combine";
}
});
CompletableFuture<String> result = future1.thenCombine(future2, new BiFunction<String, String, String>() {
@Override
public String apply(String t, String u) {
return t+" "+u;
}
});
System.out.println(result.get());
}
-
acceptEither
两个CompletionStage,谁执行返回的结果快,就用那个CompletionStage的结果进行下一步的消耗操作。返回是Consumer<T>接口
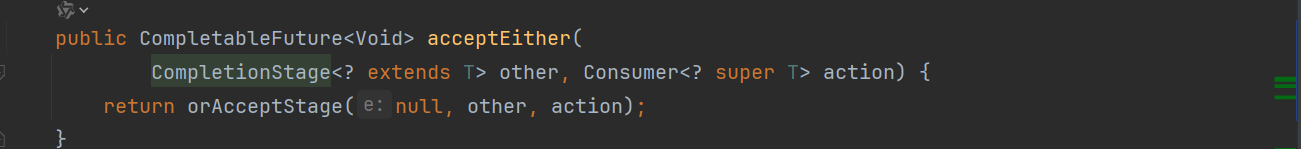
public CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(
CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Consumer<? super T> action) {
return orAcceptStage(null, other, action);
}
private static void acceptEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1="+value);
return value;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("f2="+value);
return value;
}
});
Void unused = future1.acceptEither(future2, new Consumer<Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer t) {
System.out.println(t);
}
}).get();
}
测试结构如下:

-
applyToEither
两个CompletionStage,谁执行返回的结果快,我就用那个CompletionStage的结果进行下一步的转化操作。返回值是
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> applyToEither(
CompletionStage<? extends T> other, Function<? super T, U> fn) {
return orApplyStage(null, other, fn);
}
private static void applyToEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1="+value);
return value;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2="+value);
return value;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> result = future1.applyToEither(future2, new Function<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer t) {
System.out.println(t);
return t * 2;
}
});
System.out.println(result.get());
}
测试结果如下:

-
thenAcceptBoth
当两个CompletionStage都执行完成后,把结果一块交给thenAcceptBoth来进行消耗。返回值是:BiConsumer
private static void thenAcceptBoth() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1="+value);
return value;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2="+value);
return value;
}
});
future1.thenAcceptBoth(future2, new BiConsumer<Integer, Integer>() {
@Override
public void accept(Integer t, Integer u) {
int result = t+u;
System.out.println("future1="+t+";future2="+u+";");
System.out.println("result="+result);
}
}).get();
}
测试结果如下:

-
runAfterEither
两个CompletionStage,任何一个完成了都会执行下一步的操作(Runnable)
public CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other,
Runnable action) {
return orRunStage(null, other, action);
}
测试代码如下:
private static void runAfterEither() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<Integer> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1="+value);
return value;
}
});
CompletableFuture<Integer> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(new Supplier<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer get() {
int value = new Random().nextInt(10);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(value);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2="+value);
return value;
}
});
future1.runAfterEither(future2, new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("两个任务任意一个已经完成了");
}
}).get();
}
测试结果如下:

三、通用总结
区分返回值、不同的函数式接口如Runnable、Consumer、Function、BiConsumer、是否自定义线程池,根据入参和返回具体使用。






















 169万+
169万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










