Description
- Every candidate can place exactly one poster on the wall.
- All posters are of the same height equal to the height of the wall; the width of a poster can be any integer number of bytes (byte is the unit of length in Bytetown).
- The wall is divided into segments and the width of each segment is one byte.
- Each poster must completely cover a contiguous number of wall segments.
They have built a wall 10000000 bytes long (such that there is enough place for all candidates). When the electoral campaign was restarted, the candidates were placing their posters on the wall and their posters differed widely in width. Moreover, the candidates started placing their posters on wall segments already occupied by other posters. Everyone in Bytetown was curious whose posters will be visible (entirely or in part) on the last day before elections.
Your task is to find the number of visible posters when all the posters are placed given the information about posters' size, their place and order of placement on the electoral wall.
Input
Output
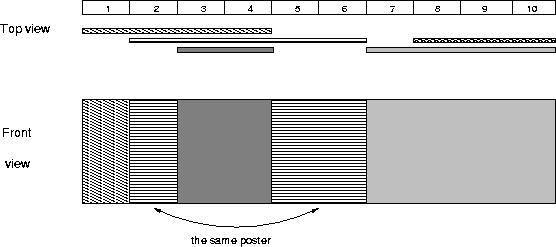
The picture below illustrates the case of the sample input.
这题n太大,如果直接去建立线段树,内存一定会不够,所以要离散化
离散化是指,把所有坐标从小到大排序,然后用其序号代替值,这样,压缩了值,但是覆盖关系没变,我们用一个结构体数组去存边和点
其他的:
本题相当于区间染色,问你最后可以看到几种颜色,那么我们把线段离散化好了后,一个个加入到线段树里,压缩了以后坐标最大也只有20000+
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10000+10
struct node
{
int l,r,color;
}tree[maxn<<2];
bool flag[maxn<<1];
int cnt;
struct node2
{
int edge,p;
}edges[maxn<<2];
int mat[maxn<<1][2];
int cmp(node2 a,node2 b)
{
return a.p<b.p;
}
void build(int p,int l,int r)
{
tree[p].l=l;
tree[p].r=r;
tree[p].color=0;//0表示没有颜色
if(l==r)
return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(p<<1,l,mid);
build(p<<1|1,mid+1,r);
}
void update(int p,int l,int r,int m)
{
if(l==tree[p].l && r==tree[p].r)//找到区间后,更新
{
tree[p].color=m;
return ;
}
int mid=(tree[p].l + tree[p].r)>>1;
if(tree[p].color>0)//当前节点有色,也就是更新过了,那么就要去更新子节点,然后把当前节点标记为无色,相当于lazy标记
{
tree[p<<1].color=tree[p].color;
tree[p<<1|1].color=tree[p].color;
tree[p].color=0;
}
if(l>mid)
update(p<<1|1,l,r,m);
else if(r<=mid)
update(p<<1,l,r,m);
else
{
update(p<<1,l,mid,m);
update(p<<1|1,mid+1,r,m);
}
}
void query(int p)
{
if(tree[p].color)//假如p节点是有色的,那么他的左右儿子是被他包含的,也就是p节点下的节点都是被覆盖的,看不到{
if(!flag[tree[p].color])//如果没出现这个颜色
{
cnt++;
flag[tree[p].color]=1;
}
return ;
}
query(p<<1);
query(p<<1|1);
}
int main()
{
int c,n;
while(~scanf("%d",&c))
{
while(c--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&mat[i][0],&mat[i][1]);
edges[2*i].p=mat[i][0];
edges[2*i].edge=-(i+1);负号表示左边端点
edges[2*i|1].p=mat[i][1];
edges[2*i|1].edge=(i+1);
}
sort(edges,edges+2*n,cmp);//排序
int ans=1;
int temp=edges[0].p;
for(int i=0;i<2*n;i++)
{
if(temp!=edges[i].p)//防止相同端点映射到不同的点
{
ans++;
temp=edges[i].p;
}
if(edges[i].edge<0) //左边
mat[-edges[i].edge-1][0]=ans;
else
mat[edges[i].edge-1][1]=ans;
}
build(1,1,ans);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
update(1,mat[i][0],mat[i][1],i+1);
cnt=0;
memset(flag,0,sizeof(flag));
query(1);
printf("%d\n",cnt );
}
}
return 0;
}





















 516
516

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








