FFT:快速傅里叶变换--DFT快速模式
DFT:离散傅里叶变换
DCT:离散余弦变换
一、介绍
快速傅里叶变换 (fast Fourier transform), 即利用计算机计算离散傅里叶变换(DFT)的高效、快速计算方法的统称,简称FFT。

离散傅里叶变换DFT公式:
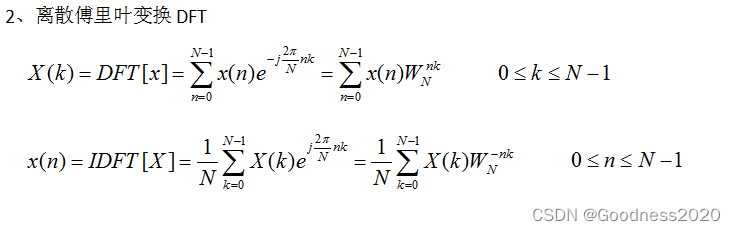
离散余弦变换DCT公式:
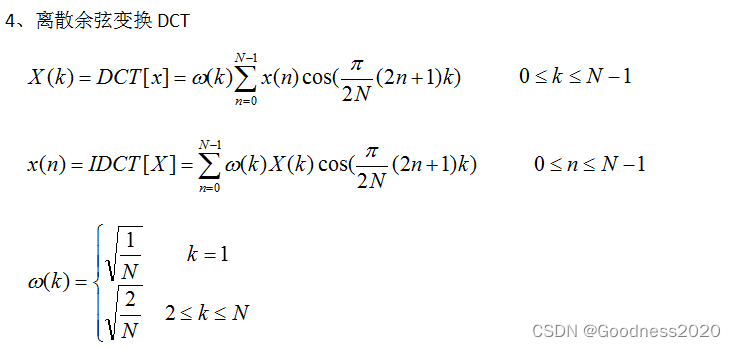
二、公式推导
参考:快速傅里叶变换(FFT)的推导过程(DIT)__hxh的博客-优快云博客_快速傅里叶变换推导
三、FFT应用
参考:快速傅里叶变换 - MATLAB fft- MathWorks 中国
1、构造一个信号
Fs = 1000; % Sampling frequency
T = 1/Fs; % Sampling period
L = 1500; % Length of signal
t = (0:L-1)*T; % Time vector,1.5 s
% 构造一个信号,包含幅值为0.7的50Hz正弦量和幅值为1的120Hz正弦量
S = 0.7*sin(2*pi*50*t) + sin(2*pi*120*t); % 周期T = 100ms
figure; plot(1000*t(1:200), S(1:200)) % 画2个周期
title('Signal without Noise')
xlabel('t (milliseconds)'); ylabel('X(t)');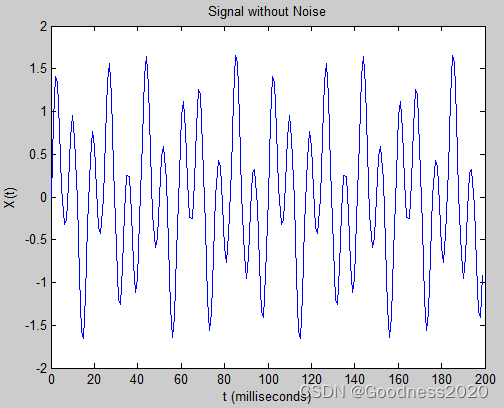
2、构造带有噪声的信号
X = S + 2*randn(size(t)); % 用均值为0方差为4的白噪声扰乱该信号
figure; plot(1000*t(1:200), X(1:200)) % 在时域中绘制含噪信号
title('Signal Corrupted with Zero-Mean Random Noise')
xlabel('t (milliseconds)'); ylabel('X(t)'); 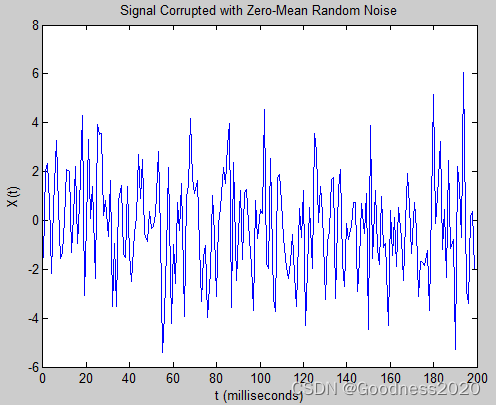
3、带有噪声信号的FFT
Y = fft(X); % 计算信号的傅里叶变换
P2 = abs(Y/L); % 计算双侧频谱P2 对称的
P1 = P2(1:L/2+1); % 单侧频谱P1
P1(2:end-1) = 2*P1(2:end-1);
f = Fs*(0:(L/2))/L; % 定义频域f
figure; plot(f, P1) % 绘制单侧幅值频谱P1
title('Single-Sided Amplitude Spectrum of X(t)')
xlabel('f (Hz)'); ylabel('|P1(f)|'); 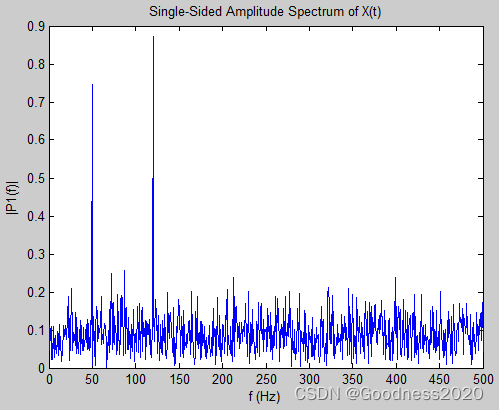
4、不带噪声信号的FFT
Y = fft(S); % 采用原始未破坏的信号做傅里叶变换
P2 = abs(Y/L); % 计算双侧频谱P2 对称的
P1 = P2(1:L/2+1); % 单侧频谱P1
P1(2:end-1) = 2*P1(2:end-1);
figure; plot(f, P1)
title('Single-Sided Amplitude Spectrum of S(t)')
xlabel('f (Hz)'); ylabel('|P1(f)|');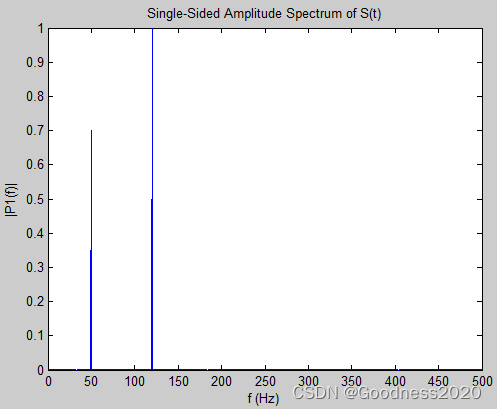
四、DCT应用
DCT可以用于数据压缩。
clear all
clc
% 利用DCT做数据压缩
x = (1:100) + 50*cos((1:100)*2*pi/40);
X = dct(x);
[XX, ind] = sort(abs(X), 'descend');
i = 1;
while norm(X(ind(1:i))) / norm(X) < 0.99
i = i + 1;
end
Needed = i;
X(ind(Needed+1:end)) = 0;
xx = idct(X);
plot([x;xx]')
legend('',['Reconstructed, N = ' int2str(Needed)],'Location','SouthEast')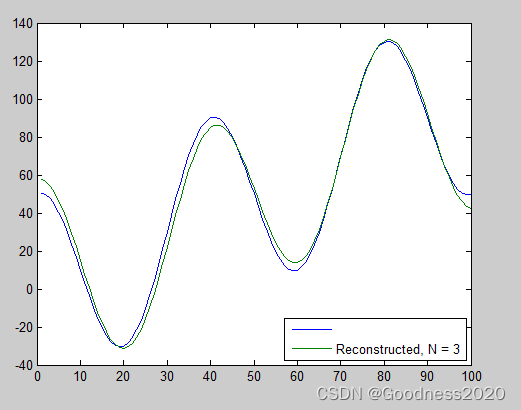























 1115
1115

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








