Our vulnerability-scanning system at PeckShield has so far discovered several dangerous smart contract vulnerabilities ( batchOverflow[1], proxyOverflow[2], transferFlaw[3],ownerAnyone[4], multiOverflow[5], burnOverflow[6], ceoAnyone[7], allowAnyone[8],allowFlaw[9]), tradeTrap[10]). Some of them could be used by attackers to generate tokens out of nowhere or steal tokens from legitimate holders, while others can be used to take over the ownership from legitimate contract owner (or administrator).
In this blog, we disclose a new type of vulnerability named evilReflex. By exploiting this bug, the attacker can transfer an arbitrary amount of tokens owned by a vulnerable smart contract to any address. Specifically, whenever a smart contract has non-zero token balance, those tokens could be swept out by an attacker.
Credit: https://gdblogs.shu.ac.uk/b5023021/2017/02/22/self-reflection/
In Figure 1, we show the vulnerable approveAndCallcode() function of an evilReflex-affected smart contract. The issue is in line 135, where _spender.call() is invoked with the user-controllable parameter _extraData. By design, the intended use of this callback function is to send out related notification while finishing an approve() operation. However, by tweaking the _extraData, an attacker can completely hijack the callback to do something unintended by the original design.
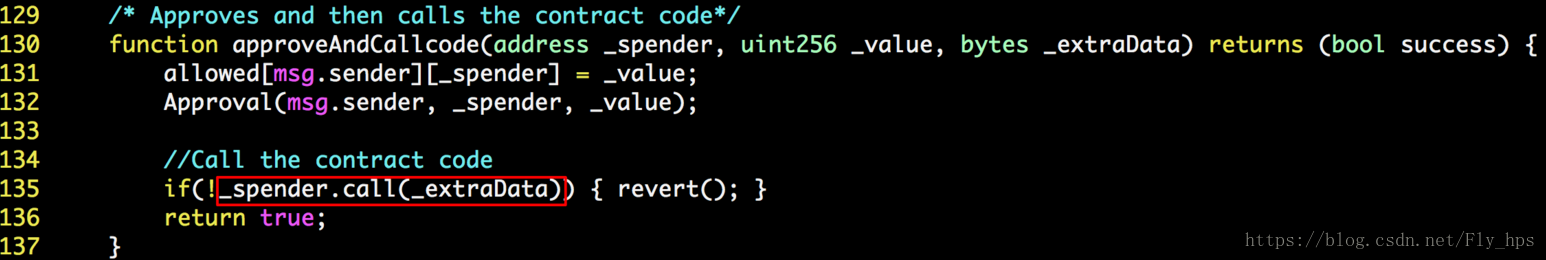
In other words, such vulnerability will essentially allow an attacker to call any contract address from a vulnerable contract, with arbitrary parameters! One thing she immediately obtains would be the privileges of the victim contract. In some smart contracts, the contract address itself might be used for authorization purposes so that certain privileged operations will only be issued from the contract itself.
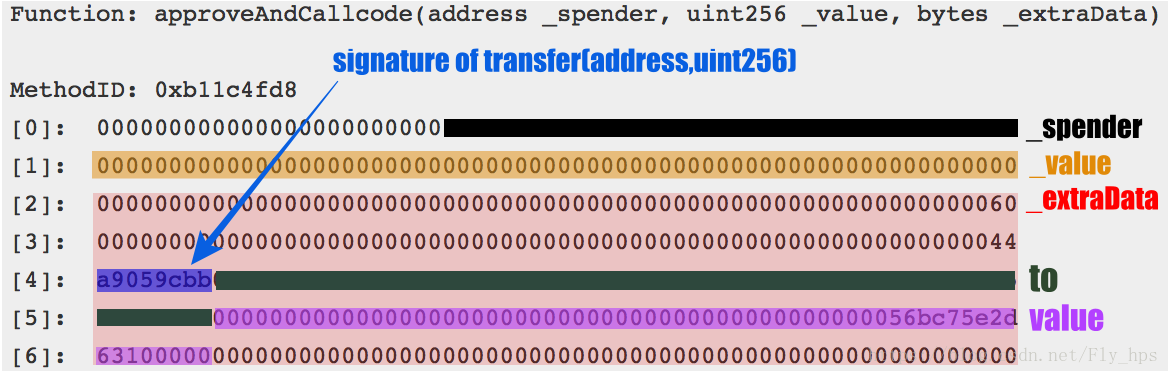
From another perspective, if the vulnerable contract happens to own certain tokens, which are likely the case for the contract to receive ETH payments or distribute certain ERC20 tokens, an attacker might easily steal these crypto assets. How to do that? The attacker can exploit the evilReflex bug by making the contract to call the transfer() function of itself. Specifically, she can simply set _spender as the contract address with a tweaked_extraData. And the tweaked _extraData starts from the signature of transfer() followed by the two parameters to and value. This way, the contract issues a transfer() call which could transfer all of its tokens out. Figure 2 illustrates a tweaked _extraData we observed in an “in-the-wild” attack.
So far, our system has found at least 28 vulnerable smart contracts which are affected by this bug. And several of them are tradable on top cryptocurrency exchanges. Furthermore, one of the tradable ERC20 tokens had been attacked in the wild with at least 100 tokens stolen. As for this writing, we are still in the process of contacting related project teams behind these tokens and affected cryptocurrency exchanges [11] to remedy this issue. Please contact us if we can be of any help regarding evilReflex.
We would like to point out that we internally discovered this vulnerability about a month ago. However, due to the severity of affected tokens and tradable facts in related exchanges, we chose not to disclose the vulnerability until today – after the coordinated response with major exchanges [11]. In the meantime, some researchers have independently discussed the mechanism of such vulnerability in the same nature, though in a different ERC223 context [12].







 本文披露了一种名为邪恶反射的新类型智能合约漏洞,该漏洞允许攻击者从易受攻击的智能合约中转移任意数量的代币到任意地址。通过操纵回调函数,攻击者可以完全劫持合约行为,从而窃取加密资产。
本文披露了一种名为邪恶反射的新类型智能合约漏洞,该漏洞允许攻击者从易受攻击的智能合约中转移任意数量的代币到任意地址。通过操纵回调函数,攻击者可以完全劫持合约行为,从而窃取加密资产。
















 1114
1114

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








