目录
概要
2025年9月24日,阿里在云栖大会上宣布开源其最新一代视觉语言模型Qwen3-VL(Visual+Language)。在32项核心指标上超过了闭源模型Gemini2.5 Pro和GPT-5。
Qwen3-VL的核心突破之一是其强大的视觉智能体(Visual Agent)能力,这使其能够像人类一样理解并操作计算机和移动设备的用户界面(GUI)。该模型可以识别界面上的元素,理解按钮的功能,调用相应的工具,并最终完成复杂的任务 。这一能力为日常任务的自动化提供了可能,例如,它可以自动打开应用程序、点击特定按钮或填写在线表单。
Dense模型代码结构
整体来说,模型由三部分组成:Visual Encoder->Embedding Replace->Language Decoder:
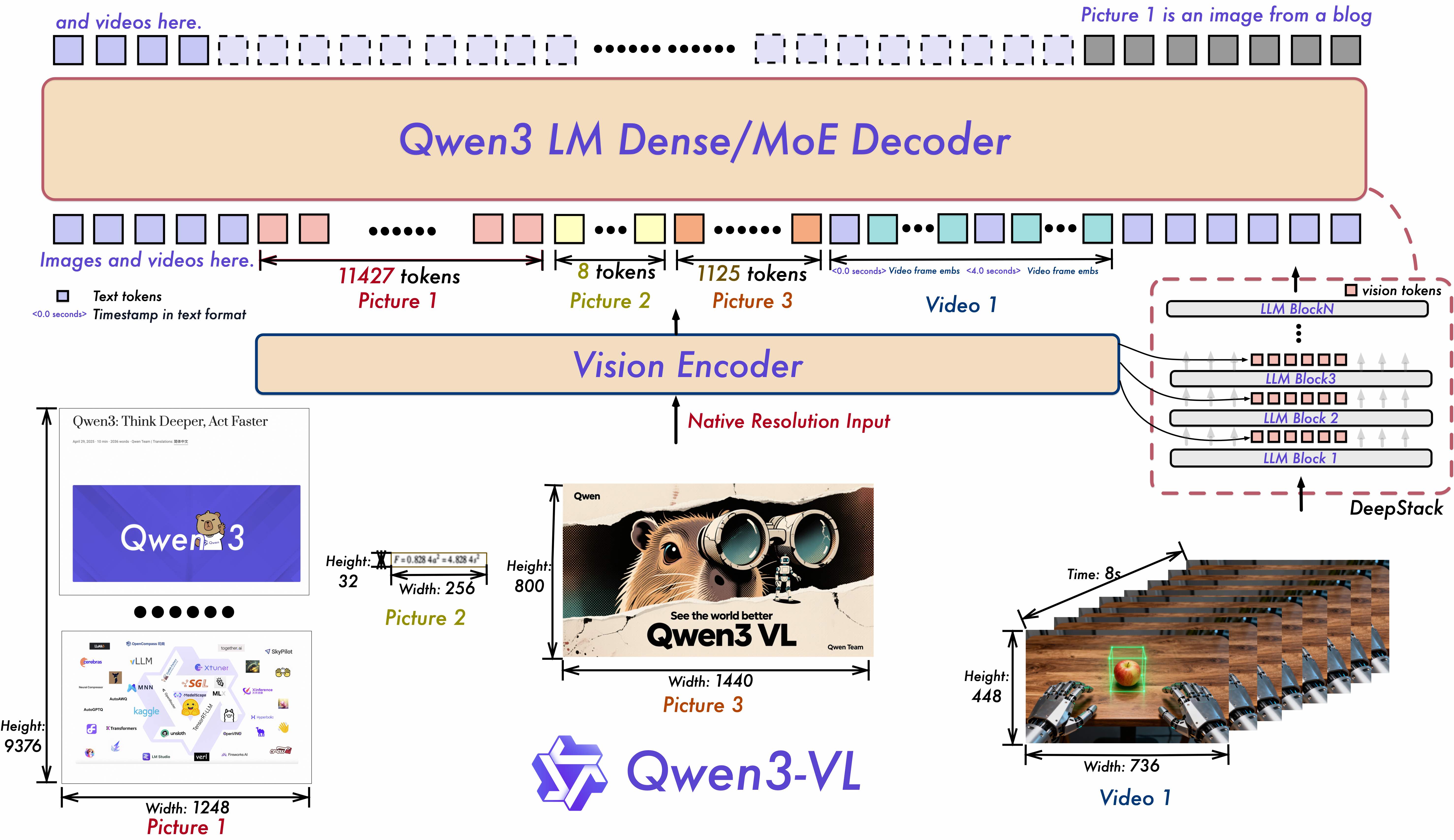
Qwen3VLModel
在模型中,可以选择任意输入文本数据,视频数据和图片数据,那么就需要确定究竟输入的数据是哪些。这里支持多张图片和多段视频作为输入,所以中间有一步torch.cat,将多个视频或者多张图片拼接在一起。图片是只有一帧的视频,视频是有时间轴的图片,所以在模型中,图片的时间轴默认为1。
if inputs_embeds is None:
inputs_embeds = self.get_input_embeddings()(input_ids)
if pixel_values is not None:
image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds = self.get_image_features(pixel_values, image_grid_thw)
image_embeds = torch.cat(image_embeds, dim=0).to(inputs_embeds.device, inputs_embeds.dtype)
image_mask, _ = self.get_placeholder_mask(
input_ids, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, image_features=image_embeds
)
inputs_embeds = inputs_embeds.masked_scatter(image_mask, image_embeds)
if pixel_values_videos is not None:
video_embeds, deepstack_video_embeds = self.get_video_features(pixel_values_videos, video_grid_thw)
video_embeds = torch.cat(video_embeds, dim=0).to(inputs_embeds.device, inputs_embeds.dtype)
_, video_mask = self.get_placeholder_mask(
input_ids, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds, video_features=video_embeds
)
inputs_embeds = inputs_embeds.masked_scatter(video_mask, video_embeds)
通过inputs_embeds.masked_scatter函数将图片占位符<image>替换为图片tokens,将视频占位符<video>替换为视频tokens。
在get_video_features函数中,直接调用的get_image_features函数:
def get_video_features(
self, pixel_values_videos: torch.FloatTensor, video_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None
):
# Same implementation as for images
return self.get_image_features(pixel_values_videos, video_grid_thw)
def get_image_features(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, image_grid_thw: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None):
pixel_values = pixel_values.type(self.visual.dtype)
image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds = self.visual(pixel_values, grid_thw=image_grid_thw)
split_sizes = (image_grid_thw.prod(-1) // self.visual.spatial_merge_size**2).tolist()
image_embeds = torch.split(image_embeds, split_sizes)
return image_embeds, deepstack_image_embeds
其中self.visual是Qwen3VLVisionModel。可以发现模型使用了deepstack技术,参考论文DeepStack,将视觉模型中某些层(取决于配置参数)的隐藏层取出,传入LLM。
Qwen3VLVisionModel
Qwen3VLVisionModel
hidden_states = self.patch_embed(hidden_states)->Qwen3VLVisionPatchEmbed
pos_embeds = self.fast_pos_embed_interpolate(grid_thw)->函数
rotary_pos_emb = self.rot_pos_emb(grid_thw)->函数
for layer_num, blk in enumerate(self.blocks):->循环block
hidden_states = blk(hidden_states)->Qwen3VLVisionBlock
if layer_num in self.deepstack_visual_indexes:->如果当前层需要收集deepstack_feature
deepstack_feature = self.deepstack_merger_list[self.deepstack_visual_indexes.index(layer_num)](hidden_states)->Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger
hidden_states = self.merger(hidden_states)->Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger
fast_pos_embed_interpolate:为了训练不同规格大小的图像,对图像进行差值,让图像适应训练网络固定的分辨率。
rot_pos_emb:旋转位置编码。
deepstack_merger_list和merger的区别是Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger中的use_postshuffle_norm是否为True,deepstack_merger_list为True,merger为False。
Qwen3VLVisionPatchEmbed
通过nn.Conv3d处理图片后直接将图片reshape成一个向量,这个向量就是该图片或者视频的tokens。
Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger
通过use_postshuffle_norm控制输出大小。
class Qwen3VLVisionPatchMerger(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3VLVisionConfig, use_postshuffle_norm=False) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size * (config.spatial_merge_size**2)
self.use_postshuffle_norm = use_postshuffle_norm
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(self.hidden_size if use_postshuffle_norm else config.hidden_size, eps=1e-6)
self.linear_fc1 = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size)
self.act_fn = nn.GELU()
self.linear_fc2 = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, config.out_hidden_size)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.norm(x.view(-1, self.hidden_size) if self.use_postshuffle_norm else x).view(-1, self.hidden_size)
x = self.linear_fc2(self.act_fn(self.linear_fc1(x)))
return x
Qwen3VLVisionBlock
Qwen3VLVisionBlock
hidden_states = hidden_states + self.attn(self.norm1(hidden_states))->Qwen3VLVisionAttention
hidden_states = hidden_states + self.mlp(self.norm2(hidden_states))->Qwen3VLVisionMLP
norm均为nn.LayerNorm。
Qwen3VLVisionAttention
query_states, key_states, value_states = self.qkv(hidden_states)->nn.Linear
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb_vision(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)->旋转位置编码
attn_output, _ = attention_interface(query_states, key_states, value_states)
attn_output = self.proj(attn_output)->nn.Linear
class Qwen3VLVisionMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size
self.linear_fc1 = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=True)
self.linear_fc2 = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=True)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
def forward(self, hidden_state):
return self.linear_fc2(self.act_fn(self.linear_fc1(hidden_state)))
config.hidden_act为gelu_pytorch_tanh。
Qwen3VLTextModel
Qwen3VLTextModel
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)->Qwen3VLTextRotaryEmbedding旋转位置编码
for layer_idx, decoder_layer in enumerate(self.layers):->循环block
layer_outputs = decoder_layer(hidden_states)->Qwen3VLTextDecoderLayer
if deepstack_visual_embeds is not None and layer_idx in range(len(deepstack_visual_embeds)):
hidden_states = self._deepstack_process(hidden_states, visual_pos_masks, deepstack_visual_embeds[layer_idx])->通过_deepstack_process函数,将deepstack技术加入语言模型
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)->Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm
Qwen3VLTextDecoderLayer和原始的大语言模型完全一样,在这里不再赘述,代码放在了文末附录。
_deepstack_process:一个函数,将隐藏层和视觉层特征进行融合。
def _deepstack_process(
self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, visual_pos_masks: torch.Tensor, visual_embeds: torch.Tensor
):
visual_pos_masks = visual_pos_masks.to(hidden_states.device)
visual_embeds = visual_embeds.to(hidden_states.device, hidden_states.dtype)
hidden_states = hidden_states.clone()
local_this = hidden_states[visual_pos_masks, :] + visual_embeds
hidden_states[visual_pos_masks, :] = local_this
return hidden_states
Moe模型代码结构
Qwen3VLMoeModel
代码和Qwen3VLModel完全一样,除了里面的模型名称改成带有Moe的模型:
Qwen3VLVisionModel->Qwen3VLMoeVisionModel
Qwen3VLTextModel->Qwen3VLMoeTextModel
Qwen3VLMoeVisionModel和Qwen3VLVisionModel完全相同。
Qwen3VLMoeTextModel
Moe的体现在Qwen3VLMoeTextModel中,在Qwen3MoeDecoderLayer的__init__中,有一段代码:
if (layer_idx not in config.mlp_only_layers) and (
config.num_experts > 0 and (layer_idx + 1) % config.decoder_sparse_step == 0
):
self.mlp = Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock(config)
else:
self.mlp = Qwen3MoeMLP(config, intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size)
当前层触发了Qwen3MoeSparseMoeBlock的调用:
class Qwen3VLMoeTextSparseMoeBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.num_experts = config.num_experts
self.top_k = config.num_experts_per_tok
self.gate = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_experts, bias=False)
self.experts = Qwen3VLMoeTextExperts(config)
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
batch_size = hidden_states.shape[0]
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(-1, self.hidden_size)
router_logits = self.gate(hidden_states)
routing_weights = torch.nn.functional.softmax(router_logits, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float)
routing_weights, router_indices = torch.topk(routing_weights, self.top_k, dim=-1)
routing_weights = routing_weights / routing_weights.sum(dim=-1, keepdim=True)
routing_weights = routing_weights.to(router_logits.dtype)
router_weights = torch.zeros_like(router_logits).scatter_(1, router_indices, routing_weights)
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(batch_size, -1, self.hidden_size)
routed_out = self.experts(hidden_states, router_weights, router_indices)
return routed_out
class Qwen3VLMoeTextExperts(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.num_experts = config.num_experts
self.intermediate_size = config.moe_intermediate_size
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.expert_dim = self.intermediate_size
self.gate_up_proj = nn.Parameter(torch.empty(self.num_experts, self.hidden_size, 2 * self.expert_dim))
self.down_proj = nn.Parameter(torch.empty((self.num_experts, self.expert_dim, self.hidden_size)))
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
def forward(
self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, routing_weights: torch.Tensor, router_indices: torch.Tensor
) -> torch.Tensor:
"""
When training it is more efficient to just loop over the experts and compute the output for each expert
as otherwise the memory would explode.
For inference we can sacrifice some memory and compute the output for all experts at once. By repeating the inputs.
Args:
hidden_states (torch.Tensor): (batch_size * token_num, hidden_size)
routing_weights (torch.Tensor): (batch_size * token_num, num_experts)
router_indices (torch.Tensor): (batch_size * token_num, top_k)
Returns:
torch.Tensor
"""
batch_size = hidden_states.shape[0]
hidden_states = hidden_states.reshape(-1, self.hidden_size) # (num_tokens, hidden_size)
if self.training:
next_states = torch.zeros_like(hidden_states, dtype=hidden_states.dtype, device=hidden_states.device)
with torch.no_grad():
expert_mask = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(router_indices, num_classes=self.num_experts)
expert_mask = expert_mask.permute(2, 1, 0)
# we sum on the top_k and on the sequence length to get which experts
# are hit this time around
expert_hit = torch.greater(expert_mask.sum(dim=(-1, -2)), 0).nonzero()
for expert_idx in expert_hit[:]:
with torch.no_grad():
_, token_idx = torch.where(expert_mask[expert_idx[0]])
current_state = hidden_states[token_idx]
gate_up = current_state @ self.gate_up_proj[expert_idx]
gate, up = gate_up.chunk(2, dim=-1)
gated_output = up * self.act_fn(gate)
out = gated_output @ self.down_proj[expert_idx]
weighted_output = out[0] * routing_weights[token_idx, expert_idx, None]
next_states.index_add_(0, token_idx, weighted_output.to(hidden_states.dtype))
next_states = next_states.view(batch_size, -1, self.hidden_size)
else:
hidden_states = hidden_states.repeat(self.num_experts, 1)
hidden_states = hidden_states.view(self.num_experts, -1, self.hidden_size)
gate_up = torch.bmm(hidden_states, self.gate_up_proj)
gate, up = gate_up.chunk(2, dim=-1) # not supported for DTensors
next_states = torch.bmm((up * self.act_fn(gate)), self.down_proj)
next_states = next_states.reshape(self.num_experts, batch_size, -1, self.hidden_size)
next_states = (
next_states * routing_weights.transpose(0, 1).view(self.num_experts, batch_size, -1)[..., None]
)
next_states = next_states.sum(dim=0)
return next_states
实际上,Experts和Qwen3-Moe是等价的,对于Qwen3-VL-235B-A22B-Instruct,这里是128个专家,每一个token选择8个专家。通过torch.bmm(batch matmul)一次性计算多个matmul提升运行性能,而在训练的是后则逐一拆开,遍历被选中的专家expert_hit,每个专家计算得到结果。
load_balancing_loss_func函数
相比于非Moe模型,Moe模型有一个问题是专家负载均衡,需要通过损失函数让每一个专家选到的概率尽可能的相同:
def load_balancing_loss_func
concatenated_gate_logits = torch.cat([layer_gate for layer_gate in gate_logits], dim=0)
routing_weights = torch.nn.functional.softmax(concatenated_gate_logits, dim=-1)
_, selected_experts = torch.topk(routing_weights, top_k, dim=-1)
expert_mask = torch.nn.functional.one_hot(selected_experts, num_experts)
# Compute the percentage of tokens routed to each experts
tokens_per_expert = torch.mean(expert_mask.float(), dim=0)
# Compute the average probability of routing to these experts
router_prob_per_expert = torch.mean(routing_weights, dim=0)
overall_loss = torch.sum(tokens_per_expert * router_prob_per_expert.unsqueeze(0))
return overall_loss * num_experts
实现论文,可以看到前半部分是在模拟路由过程,和Qwen3VLMoeTextExperts中类似,后4行代码实现论文中的算法(论文中的公式4到6,在论文中的第7页)。
一个batch有
T
T
T个token,总共
N
N
N个专家,专家从
i
=
1
i=1
i=1开始计算一直到
N
N
N,那么损失函数为:
l
o
s
s
=
α
⋅
N
⋅
∑
i
=
1
N
(
f
i
⋅
P
i
)
loss=\alpha\cdot N\cdot\sum_{i=1}^{N}(f_i\cdot P_i)
loss=α⋅N⋅i=1∑N(fi⋅Pi)
其中
f
i
f_i
fi为分配给专家
i
i
i的token比例,在代码中为tokens_per_expert,而
P
i
P_i
Pi为分配给专家
i
i
i的路由权重,在代码中为router_prob_per_expert,那么
∑
i
=
1
N
(
f
i
⋅
P
i
)
\sum_{i=1}^{N}(f_i\cdot P_i)
∑i=1N(fi⋅Pi)就是overall_loss,含义是路由了多少个token给专家
i
i
i,每个token又实际分配给该专家多少权重。
在均匀的情况下,每个专家被分到的token概率为 1 N \frac{1}{N} N1,并且该专家被分配的权重也为 1 N \frac{1}{N} N1,那么 ∑ i = 1 N ( f i ⋅ P i ) = ∑ i = 1 N ( 1 N ⋅ 1 N ) = 1 N \sum_{i=1}^{N}(f_i\cdot P_i)=\sum_{i=1}^{N}(\frac{1}{N}\cdot\frac{1}{N})=\frac{1}{N} ∑i=1N(fi⋅Pi)=∑i=1N(N1⋅N1)=N1,未来让损失不随着专家个数的变化而变化,就要再乘以 N N N,再乘以学习率,就得到了最终的loss函数。
总结
token在大模型的世界中相当于物理世界的原子,是一个数字,Qwen3-VL将图像和文本处理成token后训练模型,通过deepstack技术抽取不同层次的视觉特征,动态注入到语言模型中,这算是一种独特的skip connect,和SDXL使用的U-Net和Refiner模型异曲同工。
非Moe模型可以理解为特殊的单专家的Moe模型,整个Qwen3-VL-Moe模型可以看做Qwen3-Moe模型与一个Vision模型(ViT)相结合的产物。
附录
@use_kernel_forward_from_hub("RMSNorm")
class Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps: float = 1e-6) -> None:
"""
Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm
"""
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size))
self.variance_epsilon = eps
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32)
variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon)
return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)
def extra_repr(self):
return f"{tuple(self.weight.shape)}, eps={self.variance_epsilon}"
def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, position_ids=None, unsqueeze_dim=1):
"""Applies Rotary Position Embedding to the query and key tensors.
Args:
q (`torch.Tensor`): The query tensor.
k (`torch.Tensor`): The key tensor.
cos (`torch.Tensor`): The cosine part of the rotary embedding.
sin (`torch.Tensor`): The sine part of the rotary embedding.
position_ids (`torch.Tensor`, *optional*):
Deprecated and unused.
unsqueeze_dim (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
The 'unsqueeze_dim' argument specifies the dimension along which to unsqueeze cos[position_ids] and
sin[position_ids] so that they can be properly broadcasted to the dimensions of q and k. For example, note
that cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] have the shape [batch_size, seq_len, head_dim]. Then, if q and
k have the shape [batch_size, heads, seq_len, head_dim], then setting unsqueeze_dim=1 makes
cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] broadcastable to the shapes of q and k. Similarly, if q and k have
the shape [batch_size, seq_len, heads, head_dim], then set unsqueeze_dim=2.
Returns:
`tuple(torch.Tensor)` comprising of the query and key tensors rotated using the Rotary Position Embedding.
"""
cos = cos.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
sin = sin.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)
k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
return q_embed, k_embed
class Qwen3VLTextAttention(nn.Module):
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3VLTextConfig, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.layer_type = config.layer_types[layer_idx] if hasattr(config, "layer_types") else None
self.config = config
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads)
self.num_key_value_groups = config.num_attention_heads // config.num_key_value_heads
self.scaling = self.head_dim**-0.5
self.attention_dropout = config.attention_dropout
self.is_causal = True
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(
config.hidden_size, config.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(
config.num_attention_heads * self.head_dim, config.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias
)
self.q_norm = Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm(self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps) # unlike olmo, only on the head dim!
self.k_norm = Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm(
self.head_dim, eps=config.rms_norm_eps
) # thus post q_norm does not need reshape
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor],
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
) -> tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
input_shape = hidden_states.shape[:-1]
hidden_shape = (*input_shape, -1, self.head_dim)
query_states = self.q_norm(self.q_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
key_states = self.k_norm(self.k_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape)).transpose(1, 2)
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states).view(hidden_shape).transpose(1, 2)
cos, sin = position_embeddings
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
if past_key_values is not None:
# sin and cos are specific to RoPE models; cache_position needed for the static cache
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
key_states, value_states = past_key_values.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
attention_interface: Callable = eager_attention_forward
if self.config._attn_implementation != "eager":
attention_interface = ALL_ATTENTION_FUNCTIONS[self.config._attn_implementation]
attn_output, attn_weights = attention_interface(
self,
query_states,
key_states,
value_states,
attention_mask,
dropout=0.0 if not self.training else self.attention_dropout,
scaling=self.scaling,
**kwargs,
)
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(*input_shape, -1).contiguous()
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
return attn_output, attn_weights
class Qwen3VLTextMLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__()
self.config = config
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=False)
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=False)
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
def forward(self, x):
down_proj = self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x))
return down_proj
class Qwen3VLTextDecoderLayer(GradientCheckpointingLayer):
def __init__(self, config: Qwen3VLTextConfig, layer_idx: int):
super().__init__()
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
self.self_attn = Qwen3VLTextAttention(config=config, layer_idx=layer_idx)
self.mlp = Qwen3VLTextMLP(config)
self.input_layernorm = Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
self.post_attention_layernorm = Qwen3VLTextRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
def forward(
self,
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
position_embeddings: tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor],
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
past_key_values: Optional[Cache] = None,
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
**kwargs: Unpack[TransformersKwargs],
) -> torch.Tensor:
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
# Self Attention
hidden_states, _ = self.self_attn(
hidden_states=hidden_states,
attention_mask=attention_mask,
position_ids=position_ids,
past_key_values=past_key_values,
use_cache=use_cache,
cache_position=cache_position,
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
**kwargs,
)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
# Fully Connected
residual = hidden_states
hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states)
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
return hidden_states






















 100
100

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










