1. 元素尺寸与位置
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>元素的尺寸和位置</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.father {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
padding: 5px;
border: 10px solid red;
margin: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
.son {
width: 100px;
background-color: purple;
}
.box {
background-color: aqua;
margin: 100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">
里面包含一些文字
里面包含一些文字
里面包含一些文字
</div>
</div>
<div class="box">11</div>
<!-- 元素尺寸与位置:获得元素的尺寸大小和页面中的位置 -->
<script>
/*
1. 大小
⚫ offsetWidth 和 offsetHeight
⚫ 获取元素的自身宽高、包含元素自身设置的宽高、padding、border
⚫ 返回的是数字不带单位,并且是只读属性
*/
const father = document.querySelector('.father')
const box = document.querySelector('.box')
console.log(father.offsetWidth, father.offsetHeight) // 有边框 328 328
console.log(father.clientWidth, father.clientHeight) // 无边框 310 310
box.style.width = father.offsetWidth + 'px'
/*
2. 位置
⚫ offsetLeft 和 offsetTop
⚫ 获取元素距离自己定位父级元素的左、上距离,跟绝对定位类似
⚫ 如果父级都没有定位则以浏览器文档为准
⚫ 返回的是数字不带单位,并且是只读属性
*/
const son = document.querySelector('.son')
console.log(son.offsetLeft, son.offsetTop) // 5 5(父级内边距)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. 节点操作
2.1 DOM节点
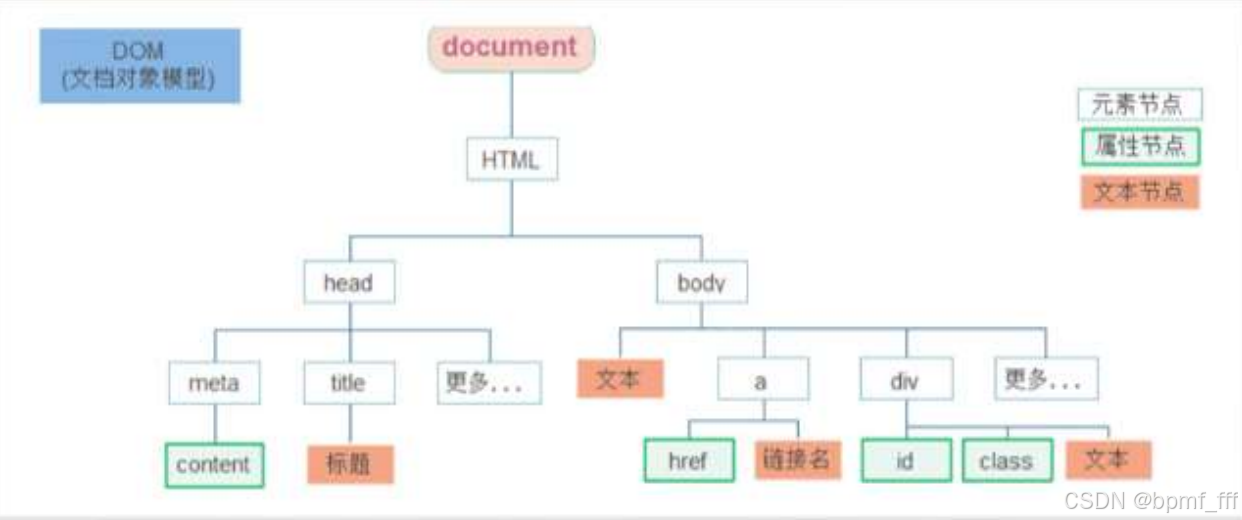
<script>
/*
DOM节点
⚫ DOM树:DOM 将 HTML文档以树状结构直观的表现出来,我们称之为 DOM 树 或者 节点树
⚫ 节点(Node)是DOM树(节点树)中的单个点。包括文档本身、元素、文本以及注释都属于是节点。
➢ 元素节点(重点): 所有的标签 比如 body、 div; html 是根节点
➢ 属性节点: 所有的属性 比如 class属性、href
➢ 文本节点: 所有的文本
利用节点关系可以更好的操作元素(比如查询更方便)
*/
</script>
2.2 查找节点
2.2.1 查找父节点 parentNode
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>王者荣耀关闭登录案例</title>
<style>
.pop {
display: block;
visibility: visible;
position: fixed;
z-index: 9999;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
width: 530px;
height: 254px;
margin-top: -127px;
margin-left: -265px;
background: url(./images/login.webp) no-repeat;
}
.close {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
width: 40px;
height: 40px;
}
@keyframes slideUp {
to {
height: 0;
}
}
@keyframes hidden {
to {
display: none;
}
}
.hide {
animation: slideUp .3s linear forwards, hidden .3s .3s forwards;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="pop">
<a href="javascript:;" class="close"></a>
</div>
<!-- 查找节点:利用节点关系查找节点,返回的都是对象,找不到返回null -->
<!-- 需求:点击关闭按钮,关闭弹窗 ==> 点击关闭按钮,关闭父元素 -->
<script>
const closeBtn = document.querySelector('.close')
closeBtn.addEventListener('click', function () {
// closeBtn.parentNode.classList.add('hide')
// xx.parentNode 返回最近一级的父节点对象,找不到返回为 null
this.parentNode.classList.add('hide')
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.2.2 查找子节点 children
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>第1个li</li>
<li>第2个li</li>
<li>第3个li</li>
<li>第4个li</li>
<li>第5个li</li>
</ul>
<ol></ol>
<!--
子节点查找:children(重点)
获得所有子元素节点,返回的是一个伪数组
节点对象.children
-->
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector('ul')
const ol = document.querySelector('ol')
// 节点对象.children 找到返回伪数组,找不到返回空数组
console.log(ul.children) // HTMLCollection(5) [li, 1i, li, 1i, 1i]
console.log(ol.children) // HTMLCollection []
// 节点对象.children[index] 找到返回元素节点,找不到返回undefined
console.log(ul.children[0]) // <li>第1个li</li>
console.log(ul.children[5]) // undefined
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.2.3 查找兄弟节点
nextElementSibling
previousElementSibling
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<h4>1</h4>
<p class="p">2</p>
<span>3</span>
<!-- 兄弟节点查找 -->
<script>
const h4 = document.querySelector('h4')
const p = document.querySelector('.p')
const span = document.querySelector('span')
// 1. 下一个兄弟 节点对象.nextElementSibling
console.log(p.nextElementSibling) // <span>3</span>
console.log(span.nextElementSibling) // <script>...< / script >
// 2. 上一个兄弟 节点对象.previousElementSibling
console.log(p.previousElementSibling) // <h4>1</h4>
console.log(h4.previousElementSibling) // null
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.3 增加节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>我是默认的li</li>
</ul>
<!--
增加节点
➢ 创建一个新的节点 document.createElement('标签名')
➢ 把创建的新的节点放入到指定的元素内部
父元素最后一个子节点之后,插入节点元素 element.append()
父元素第一个子元素的之前,插入节点元素 element.prepend()
-->
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector('ul')
// 1. 创建节点
// 创建后直接填充内容(错误) 其返回值 newLi1 会是一个字符串而不是 DOM 元素
const newLi1 = document.createElement('li').innerHTML = '新增的li1 直接填充内容'
// 先创建后填充内容(正确)
const newLi2 = document.createElement('li')
newLi2.innerHTML = '新增的li2 先创建后填充内容'
// 2. 添加节点
// 2.1 最后面添加节点
ul.append(newLi2)
// 2.2 最前面添加节点
ul.prepend(newLi2)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.4 删除节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="remove">这是要删除的 div</div>
<div class="hide">这是要隐藏的 div</div>
<!--
删除节点:若一个节点在页面中已不需要时,可以删除它
element.remove()
➢ 把对象从它所属的 DOM 树中删除
➢ 删除节点和隐藏节点(display:none)有区别的:
隐藏节点还是存在的,但是删除,则从DOM树中删除
一个标签一会显示一会隐藏 -- 来回切换的,用display或透明度 -- 性能好
-->
<script>
const removeEl = document.querySelector('.remove')
const hideEl = document.querySelector('.hide')
// 删除节点
removeEl.remove()
// 隐藏节点
hideEl.style.display = 'none'
// hideEl.style.opacity = 0
</script>
</body>
</html>
3. 阶段案例-智慧园区























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








