Link:点击打开链接
Problem:
胜利大逃亡
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 25781 Accepted Submission(s): 9836
魔王住在一个城堡里,城堡是一个A*B*C的立方体,可以被表示成A个B*C的矩阵,刚开始Ignatius被关在(0,0,0)的位置,离开城堡的门在(A-1,B-1,C-1)的位置,现在知道魔王将在T分钟后回到城堡,Ignatius每分钟能从一个坐标走到相邻的六个坐标中的其中一个.现在给你城堡的地图,请你计算出Ignatius能否在魔王回来前离开城堡(只要走到出口就算离开城堡,如果走到出口的时候魔王刚好回来也算逃亡成功),如果可以请输出需要多少分钟才能离开,如果不能则输出-1.
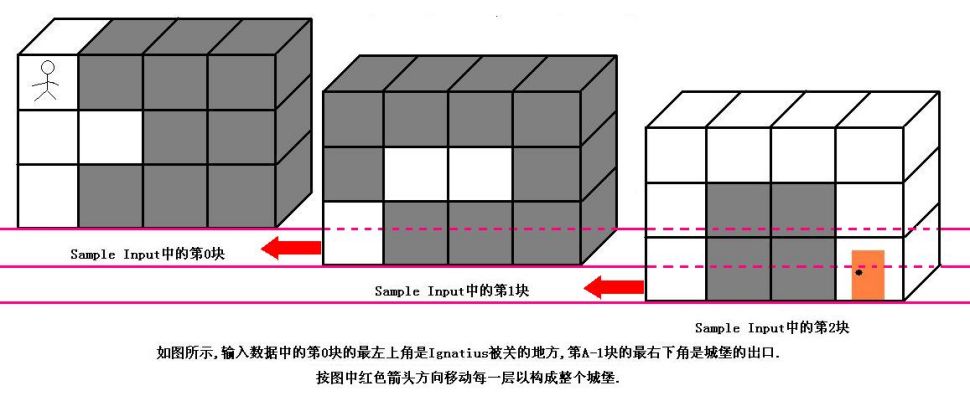
特别注意:本题的测试数据非常大,请使用scanf输入,我不能保证使用cin能不超时.在本OJ上请使用Visual C++提交.
1 3 3 4 20 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
11
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int map[51][51][51];
int d[6][3]={{1,0,0},{0,1,0},{0,0,1},{-1,0,0},{0,-1,0},{0,0,-1}};
int T,a,b,c;
struct node
{
int x;
int y;
int z;
int t;
};
int bfs()
{
queue<node>Q;
int i,xi,yi,zi;
node now,next;
now.x=0;
now.y=0;
now.z=0;
now.t=0;
Q.push(now);
map[0][0][0]=1;
while(!Q.empty())
{
now=Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(now.x==a-1&&now.y==b-1&&now.z==c-1)
{
if(now.t<=T)
return now.t;
}
for(i=0;i<6;i++)
{
xi=d[i][0]+now.x;
yi=d[i][1]+now.y;
zi=d[i][2]+now.z;
if(xi>=0&&xi<a&&yi>=0&&yi<b&&zi>=0&&zi<c&&map[xi][yi][zi]==0)
{
next.t=now.t+1;
next.x=xi;
next.y=yi;
next.z=zi;
Q.push(next);
map[xi][yi][zi]=1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k,cas;
while(scanf("%d",&cas)!=EOF)
{
while(cas--)
{
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&T);
for(i=0;i<a;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<b;j++)
{
for(k=0;k<c;k++)
{
scanf("%d",&map[i][j][k]);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",bfs());
}
}
return 0;
}
 胜利大逃亡迷宫问题
胜利大逃亡迷宫问题

























 4535
4535

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










