本博客对C++中的vector进行梳理
一、vector的使用
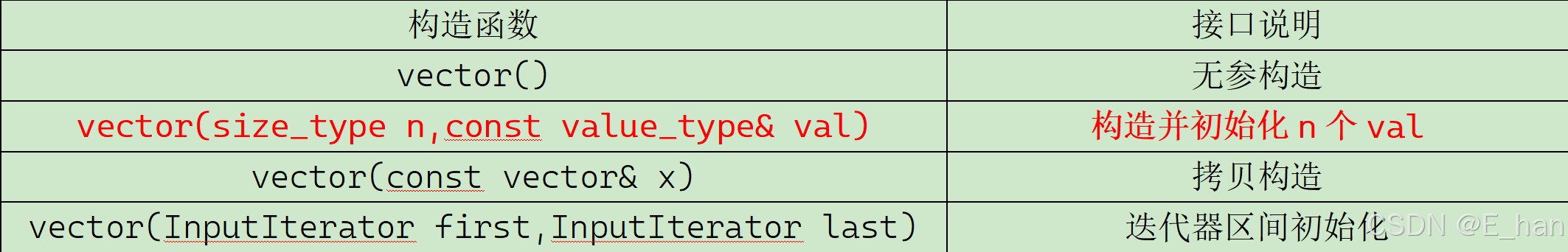
1.vector的构造函数
2.迭代器
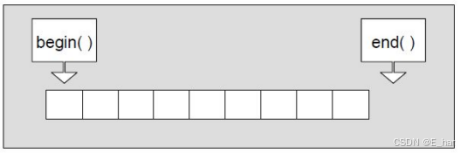
本质就是指向数组头部和尾部下一个位置的原生指针
3.空间增长问题
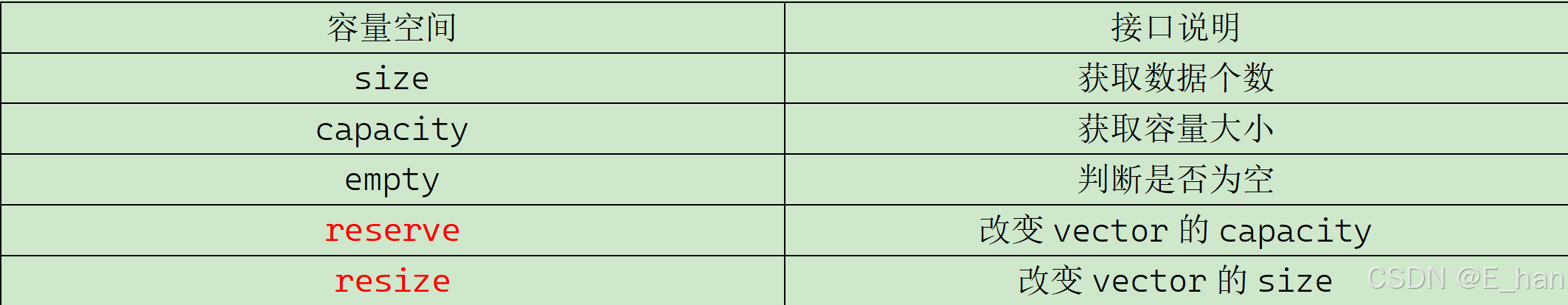
(1)reserve函数:改变capacity,空间不够时,VS下按照1.5倍扩容,g++下按照2倍扩容
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 1);
v.reserve(20);
cout << v.size() << endl;
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(15);
cout << v.size() << endl;
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.reserve(5);
cout << v.size() << endl;
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}

在VS2022环境下(与Linux下一致):当n<=size时,不会对vector进行缩容,当n>size时,会扩容到n甚至更大(扩容改变的是capacity)
(2)resize函数:改变size
- n<size时:会删除数据,直到size==n
- n==size时:不动
- n>size时:插入数据,空间不够就扩容
int main()
{
vector<int> v(10, 1);
v.reserve(20);
cout << v.size() << endl;
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(15, 2);//在10个1后面补上了5个2
cout << v.size() << endl;
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(25, 3);
cout << v.size() << endl;//在15个数据后面补上了10个3
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
v.resize(5);
cout << v.size() << endl;//删到只剩下5个1
cout << v.capacity() << endl;
return 0;
}
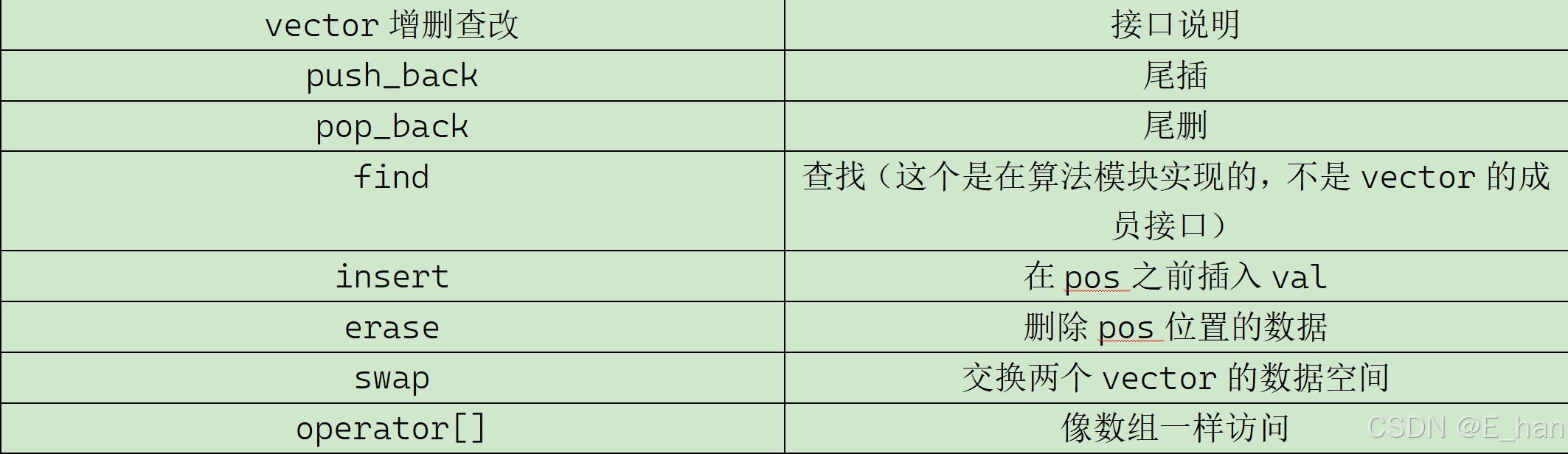
4.增删查改
二、用vector模拟二维数组
int main()
{
vector<int> v(5, 1);
vector<vector<int>> vv(10, v);
vv[2][1] = 2;
// vv.operator[](2).operator[](1) = 2;
for (size_t i = 0; i < vv.size(); i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < vv[i].size(); ++j)
{
cout << vv[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
三、vector的迭代器失效问题
1.用迭代器遍历vector的规范
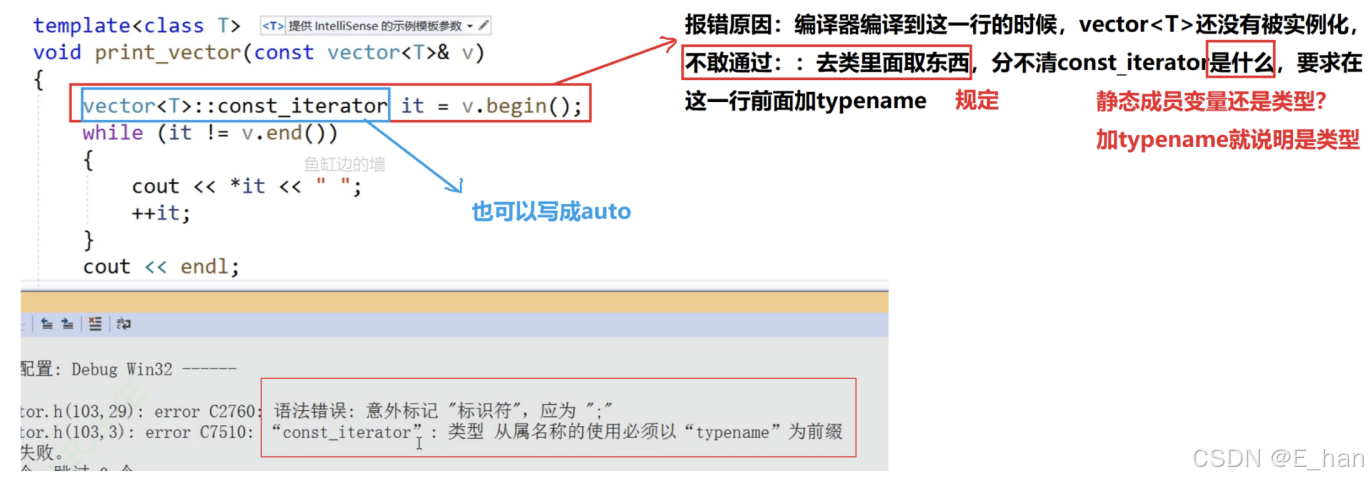
注意:类模板还没有实例化的时候,如果直接用::从类模板里面取类型,编译器会报错,因为此时编译器无法识别这个::后面的东西是类型还是静态成员变量,在行首加上typename即可解决这个问题(typename告诉了编译器这个东西是类型)
2.迭代器失效问题
迭代器的主要作用:让算法不用关心底层数据结构,底层就是指针或者对指针的封装。如vector的迭代器就是原生指针T*,使用时要小心失效
(1)扩容导致的野指针现象:扩容之后,迭代器还指向旧空间,但旧空间已被释放,产生野指针
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
auto it = v.begin();
v.resize(100, 8);
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
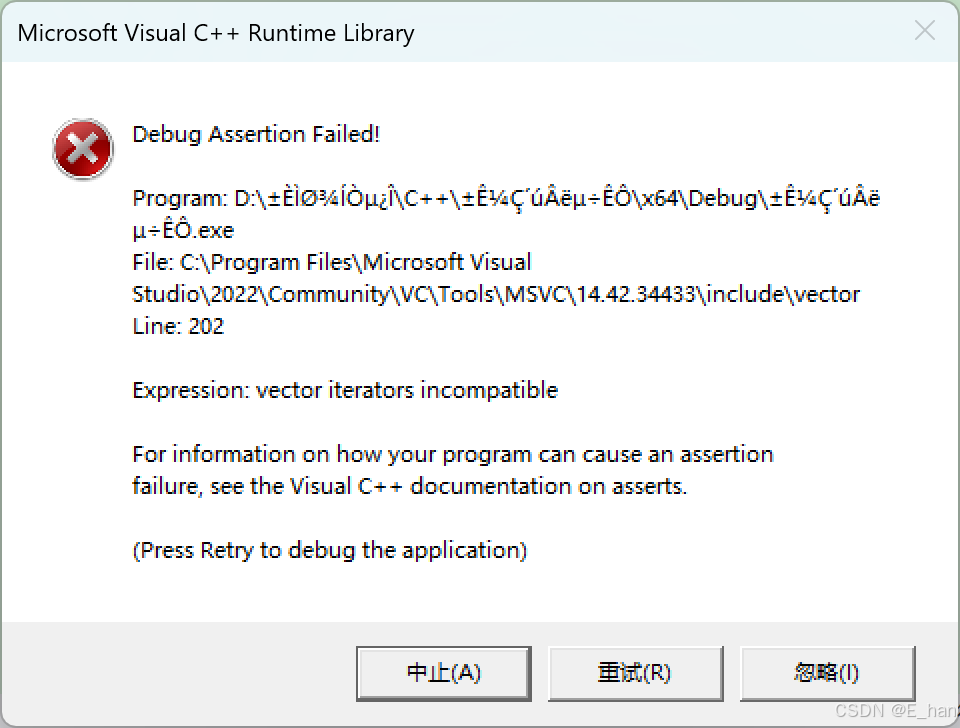
结论是:resize以后vs就认为迭代器已经失效了(会报错),就别再访问了
(2)位置的意义变了
如:erase操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
v.erase(it);
++it; //此处迭代器已经失效,不能再访问
}
return 0;
}
//解决方案如下
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 1, 2, 3, 4 };
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
it = v.erase(it); //更新迭代器的位置
else
++it;
}
return 0;
}
第一段程序运行依旧会报错,原因是编译器认为it已经失效了,不允许再访问,要访问只能如第二段程序一样,更新it之后再访问

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








