Machine Learining —— hw02:Logistic
1、hw02作业理解

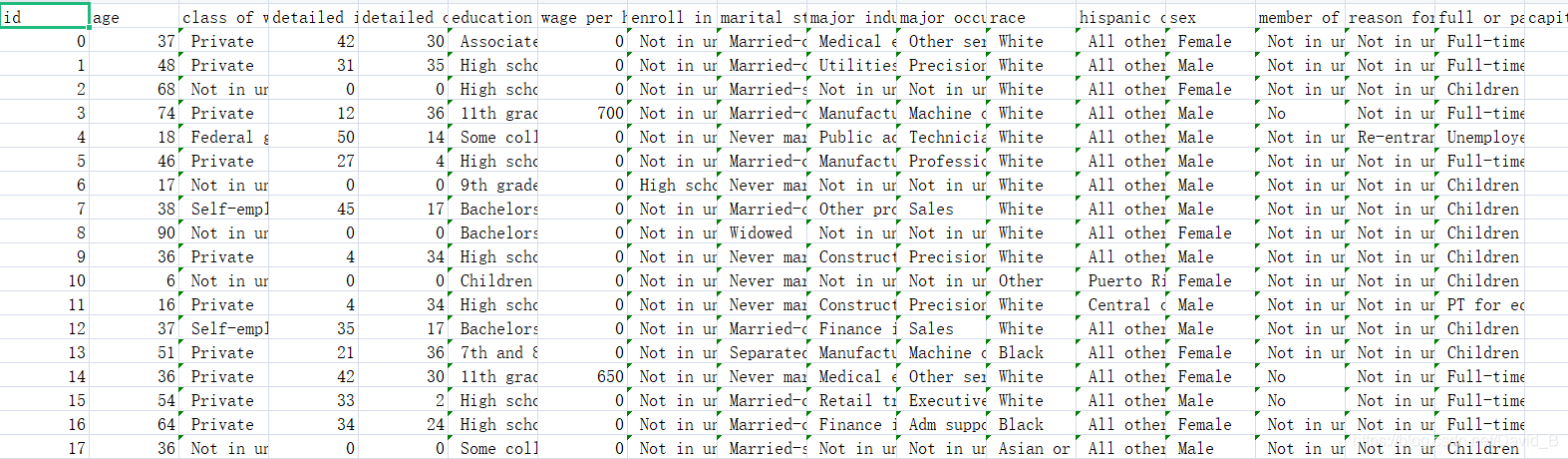
作业中共给了6份资料:输出结果格式、测试集(不带标签)、训练集、X_train、Y_train、X_test。观察可知后三个文件是已事先把数据整理成csv格式的数据,于是训练数据共54256个,测试大约20000个、参数510个
- 二分类问题(Binary Classification)
- 模型输入510维,输出一个布尔值表示“是”或“否”
——使用Logistic Regression model
2、数据预处理
读取数据
##读取文件
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(0)
#随机种子(暂未弄懂)
X_train_fpath = './hw2/data/X_train'
Y_train_fpath = './hw2/data/Y_train'
X_test_fpath = './hw2/data/X_test'
output_fpath = './output_{}.csv'
X_train、Y_train、X_test三个文件夹已经将数据进行了初步处理,可用Notepad++打开
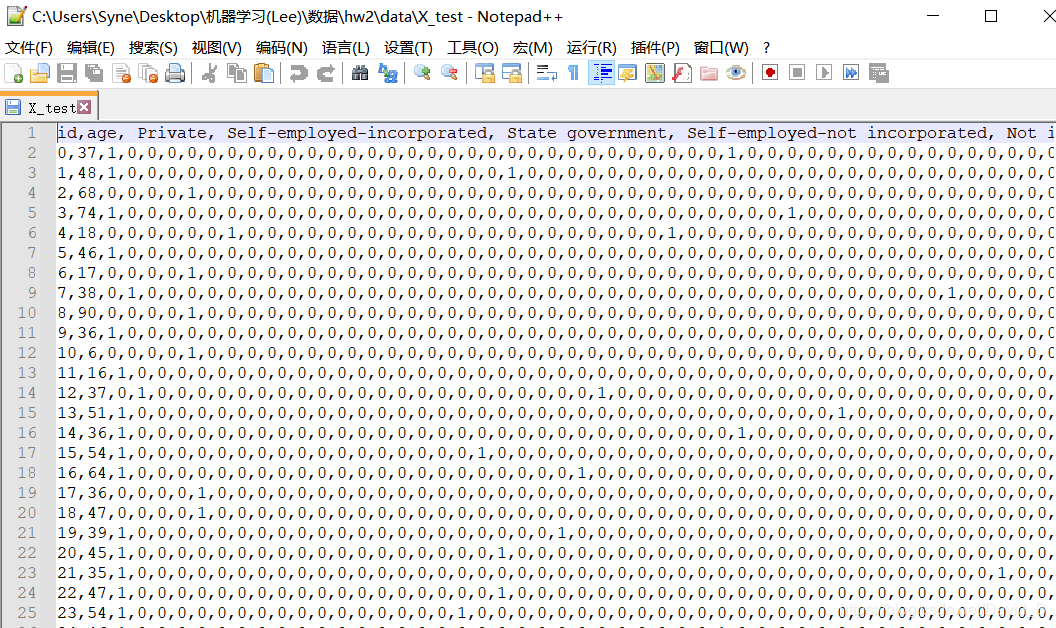
打开后通过观察可以得到,第一行是表头信息,数据之间用逗号隔开,读取数据但是第一行和第一列不需要
#Parse csv files to numpy array
with open(X_train_fpath) as f:
next(f)
#f文件是可迭代对象,此处调用一次跳过文件的第一行
X_train = np.array([line.strip('\n').split(',')[1:] for line in f], dtype = float)
#按行读取数据line.strip('\n').split(',')删除数据中的换行符,遇到','就隔开
with open(Y_train_fpath) as f:
next(f)
Y_train = np.array([line.strip('\n').split(',')[1] for line in f], dtype = float)
#此处Y_train文件的处理不一样(因为第一次复制粘贴前一句的代码导致Y_train数据格式不一致找了半天bug)
with open(X_test_fpath) as f:
next(f)
X_test = np.array([line.strip('\n').split(',')[1:] for line in f], dtype = float)
Normalize处理
对X_train和X_test分别调用函数完成标准化
符号解释:
- X:将被处理的数据
- train:当处理训练集数据是为"True",处理测试集数据时为"Flase"
- specific_column:被标准化处理的列的索引值,如果是"None",则所有的列都将被处理
- X_mean:训练集数据的均值
- X_std:训练集数据的方差
#Normalize处理
def _normalize(X, train = True, specified_column = None, X_mean = None, X_std = None):
#利用此函数对x进行标准化处理,均值(mean)和方差(std)将在数据处理过程中计算
if specified_column == None:
specified_column = np.arange(X.shape[1])
#X.shape[1]:X的列数
#np.arange()函数输出列的ID:[0 1 2 3 4 5......]
if train:
X_mean = np.mean(X[:, specified_column], 0).reshape(1, -1)
X_std = np.std(X[:, specified_column], 0).reshape(1, -1)
#np.mean(X, 0)对列求平均
#reshape(1, -1)转化为1行
X[:, specified_column] = (X[:, specified_column] - X_mean) / (X_std + 1e-8)
#1e-8防止除零
return X, X_mean, X_std
#调用函数标准化训练数据和测试数据
X_train, X_mean, X_std = _normalize(X_train, train = True)
X_test, _, _ = _normalize(X_test, train = False, specified_column = None, X_mean = X_mean, X_std = X_std)
#用 _ 存储无用值
#用X_train的均值和方差来标准化X_test???(未懂)
分割X_train为测试集和验证集
对原来的X_train进行分割,分割比例为train:dec = 9:1
#分割测试集和验证集
def _train_dev_split(X, Y, dev_ratio = 0.25):
train_size = int(len(X) * (1 - dev_ratio))
return X[: train_size], Y[: train_size], X[train_size:], Y[train_size:]
#返回分割好的四组数据
#调用分割函数
dev_ratio = 0.1
X_train, Y_train, X_dev, Y_dev = _train_dev_split(X_train, Y_train, dev_ratio = dev_ratio)
train_size = X_train.shape[0] #求得行数
dev_size = X_dev.shape[0]
test_size = X_test.shape[0]
data_dim = X_train.shape[1] #求得列数
print('Size of training set: {}'.format(train_size))
print('Size of development set: {}'.format(dev_size))
print('Size of testing set: {}'.format(test_size))
print('Dimension of data: {}'.format(data_dim))
output:
Size of training set: 48830
Size of development set: 5426
Size of testing set: 27622
Dimension of data: 510
3、Logistic Regression
定义一些数据处理函数
- _shuffle(X,Y):X和Y是两个数组,如果分别随机打乱X和Y,那么X和Y的对应关系就会被破坏,在此生成行编号,对行的编号进行打乱,就可以获得一一对应的打乱后的X和Y
- _sigmoid(z): σ ( z ) \sigma(z) σ(z)函数
- _np.clip(a, x1, x2):其中a是数组,x1和x2分别表示最大值和最小值,将最小值前的数字都改成最小值,最大值后的数字都改成最大值
- _f(X, w, b):Logistic Regression函数 f w , b ( X ) = σ ( w x + b ) f_{w,b}(X)=\sigma(wx+b) fw,b(X)=σ(wx+b),参数是w和b
- _predict(X, w, b):根据X,w,b的值,计算预测值y
- np.round():返回四舍五入值,
- _accuracy(Y_pred, Y_label):预测精度,如:
Y_label = 0, Y_pred = 0, 1 - | Y p r e d − Y l a b e l Y_{pred}-Y_{label} Ypred−Ylabel| = 1, 预测正确
Y_label = 0, Y_pred = 1, 1 - | Y p r e d − Y l a b e l Y_{pred}-Y_{label} Ypred−Ylabel| = 0, 预测错误
def _shuffle(X, Y):
#“洗牌”函数,打乱元素
randomize = np.arange(len(X))
#获取x的行数组成一组数列:[0 1 2 ......]
np.random.shuffle(randomize)
#随机打乱行数,但是各行X和Y仍是对应的
return (X[randomize], Y[randomize])
def _sigmoid(z):
return np.clip(1 / (1.0 + np.exp(-z)), 1e-8, 1 - (1e-8))
#计算z的sigmoid,将数组中元素限制在(1e-8, 1 - (1e-8))之间,防溢出
def _f(X, w, b):
return _sigmoid(np.matmul(X, w) + b)
#np.matmul(X,w)矩阵乘法
def _predict(X, w, b):
return np.round(_f(X, w, b)).astype(np.int)
#round()四舍五入后,astype(np.int)转换为整型
def _accuracy(Y_pred, Y_label):
acc = 1 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_pred - Y_label))
#abs()取绝对值
return acc
Loss Function
第n个训练数据为 ( x n , y ^ n ) , x n = [ x 1 n , x 2 n , . . . , x i n , . . . ] (x^n,\hat{y}^n),x^n=[x^n_1,x^n_2,...,x^n_i,...] (xn,y^n),xn=[x1n,x2n,...,xin,...]( x n x^n xn表示第n个训练数据)
预测值 y n = f w , b ( x n ) = σ ( w x n + b ) = 1 1 + e − ( w x n + b ) = 1 1 + e − ( ∑ w i x i n + b ) = σ ( z ) y^n=f_{w,b}(x^n)=\sigma(wx^n+b)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-(wx^n+b)}}=\frac{1}{1+e^{-(\sum w_ix^n_i+b)}}=\sigma(z) yn=fw,b(xn)=σ(wxn+b)=1+e−(wxn+b)1=1+e−(∑wixin+b)1=σ(z)
w ∗ , b ∗ = a r g m a x w , b L ( w , b ) = a r g m i n w , b ( − l n L ( w , b ) ) w^*,b^*=arg\mathop{max}\limits_{w,b}L(w,b)=arg\mathop{min}\limits_{w,b}(-lnL(w,b)) w∗,b∗=argw,bmaxL(w,b)=argw,bmin(−lnL(w,b))
对Logistic Regression的损失函数 L ( f ) L(f) L(f)取对数ln并乘以-1。
最优参数





 本文档详细介绍了Logistic Regression和概率生成模型的实现过程。首先,对数据进行预处理,包括读取、标准化、分割训练集和验证集。接着,使用Logistic Regression模型,通过梯度下降法训练模型,并计算训练和验证集的损失及准确率。然后,探讨了概率生成模型,计算类别均值、协方差和权重,评估训练集的准确率。最后,对代码进行了改进,如引入Adagrad优化和特征二次项,并给出了测试集的预测结果。
本文档详细介绍了Logistic Regression和概率生成模型的实现过程。首先,对数据进行预处理,包括读取、标准化、分割训练集和验证集。接着,使用Logistic Regression模型,通过梯度下降法训练模型,并计算训练和验证集的损失及准确率。然后,探讨了概率生成模型,计算类别均值、协方差和权重,评估训练集的准确率。最后,对代码进行了改进,如引入Adagrad优化和特征二次项,并给出了测试集的预测结果。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1369
1369

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








