0. Eigen/四元数/欧拉角/旋转矩阵 相关系列文章
- SLAM——之Eigen入门(矩阵运算及几何模块)
- SLAM——之Eigen函数库,一个相对复杂的EIgen使用实例
- SLAM——Eigen函数库:矩阵块运算,block操作
- 欧拉角和旋转矩阵相互转换
- 四元数与三维向量相乘运算
- 四元数求导
本节介绍如何求解线性系统,计算几种分解,比如LU,QR,SVD等。
1. 线性求解类型及其精度与速度的对比
问题:假设有一个系统方程写成如下矩阵的形式
A
x
=
b
Ax =b
Ax=b
其中A,b是矩阵,b也可以是向量,当想要求解x时,可以选择多种分解方式,取决于矩阵A的形式以及考虑的速度和精度,下面是一个简单的例子
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix3f A;
Vector3f b;
A << 1,2,3, 4,5,6, 7,8,10;
b << 3, 3, 4;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
cout << "Here is the vector b:\n" << b << endl;
Vector3f x = A.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(b);
cout << "The solution is:\n" << x << endl;
}
解为
Here is the matrix A:
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 10
Here is the vector b:
3
3
4
The solution is:
-2
1
1
例子中colPivHouseholderQr()方法返回一个类ColPivHouseholderQR的对象,因此那句话也可以写成
ColPivHouseholderQR<Matrix3f> dec(A);
Vector3f x = dec.solve(b);
这里ColPivHouseholderQR是QR分解的意思,适用于各种矩阵并且速度够快,下面是几种分解的对比
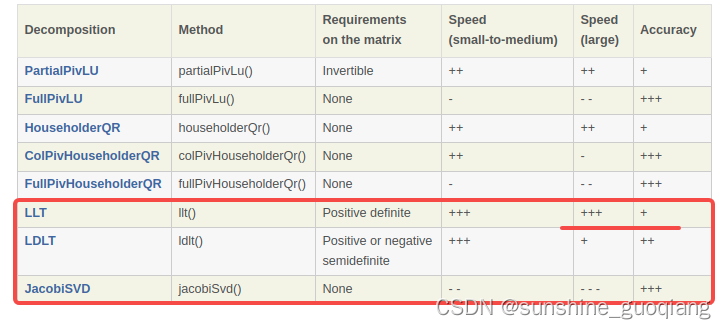
以上分解都提供了solve()方法。比如当矩阵是正定的时候,表中说明LLT和LDLT是不错的选择:
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix2f A, b;
A << 2, -1, -1, 3;
b << 1, 2, 3, 1;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
cout << "Here is the right hand side b:\n" << b << endl;
Matrix2f x = A.ldlt().solve(b);
cout << "The solution is:\n" << x << endl;
}
Here is the matrix A:
2 -1
-1 3
Here is the right hand side b:
1 2
3 1
The solution is:
1.2 1.4
1.4 0.8
2. 计算特征值和特征向量
这里需要特征分解,确保矩阵是自伴矩阵。下面是一个使用SelfAdjointEigenSolver的例子,使用EigenSolver或者ComplexEigenSolver,可以容易的适用到普通矩阵上。计算特征值和特征向量时不要求一定收敛,当然这种情况很少见。
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix2f A;
A << 1, 2, 2, 3;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Matrix2f> eigensolver(A);
if (eigensolver.info() != Success) abort();
cout << "The eigenvalues of A are:\n" << eigensolver.eigenvalues() << endl;
cout << "Here's a matrix whose columns are eigenvectors of A \n"
<< "corresponding to these eigenvalues:\n"
<< eigensolver.eigenvectors() << endl;
cout<<"A*vec(1) = \n"<<A*(eigenSolver.eigenvectors().col(0))<<endl;
cout<<"e(1)*vec(1) = \n"<<eigenSolver.eigenvalues()(0)*eigenSolver.eigenvectors().col(0);
}
Here is the matrix A:
1 2
2 3
The eigenvalues of A are:
-0.236
4.24
Here's a matrix whose columns are eigenvectors of A
corresponding to these eigenvalues:
-0.851 -0.526
0.526 -0.851
A*vec(1) =
0.200811
-0.124108
e(1)*vec(1) =
0.200811
-0.124108
3. 计算特征值和特征向量
这里需要特征分解,确保矩阵是自伴矩阵。下面是一个使用SelfAdjointEigenSolver的例子,使用EigenSolver或者ComplexEigenSolver,可以容易的适用到普通矩阵上。计算特征值和特征向量时不要求一定收敛,当然这种情况很少见。
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix2f A;
A << 1, 2, 2, 3;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Matrix2f> eigensolver(A);
if (eigensolver.info() != Success) abort();
cout << "The eigenvalues of A are:\n" << eigensolver.eigenvalues() << endl;
cout << "Here's a matrix whose columns are eigenvectors of A \n"
<< "corresponding to these eigenvalues:\n"
<< eigensolver.eigenvectors() << endl;
cout<<"A*vec(1) = \n"<<A*(eigenSolver.eigenvectors().col(0))<<endl;
cout<<"e(1)*vec(1) = \n"<<eigenSolver.eigenvalues()(0)*eigenSolver.eigenvectors().col(0);
}
Here is the matrix A:
1 2
2 3
The eigenvalues of A are:
-0.236
4.24
Here's a matrix whose columns are eigenvectors of A
corresponding to these eigenvalues:
-0.851 -0.526
0.526 -0.851
A*vec(1) =
0.200811
-0.124108
e(1)*vec(1) =
0.200811
-0.124108
4. 计算逆和行列式
尽管逆和行列式是基本的数学概念,但是在数值/线性代数中却不像纯数学中那么受欢迎。求逆运算通常由solve()代替,行列式一般并不是检测矩阵是否可逆的好方法。当然对于比较小的矩阵时行列式和逆还是比较有用的。
尽管存在以上矩阵分解的方法,你仍然可以直接调用inverse()方法和determinant()方法。如果你的矩阵尺寸比较小(4x4)那么Eigen可以避免使用LU分解,而是使用数学公式,这样更高效。
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix3f A;
A << 1, 2, 1,
2, 1, 0,
-1, 1, 2;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
cout << "The determinant of A is " << A.determinant() << endl;
cout << "The inverse of A is:\n" << A.inverse() << endl;
}
Here is the matrix A:
1 2 1
2 1 0
-1 1 2
The determinant of A is -3
The inverse of A is:
-0.667 1 0.333
1.33 -1 -0.667
-1 1 1
5. 最小二乘解
求最小二乘解最精确的方式是使用SVD分解。Eigen提供了JacobiSVD类,他的solve()方法计算了最小二乘解。
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
MatrixXf A = MatrixXf::Random(3, 2);
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
VectorXf b = VectorXf::Random(3);
cout << "Here is the right hand side b:\n" << b << endl;
cout << "The least-squares solution is:\n"
<< A.jacobiSvd(ComputeThinU | ComputeThinV).solve(b) << endl;
}
Here is the matrix A:
0.68 0.597
-0.211 0.823
0.566 -0.605
Here is the right hand side b:
-0.33
0.536
-0.444
The least-squares solution is:
-0.67
0.314
其他方法,比如Cholesky分解或QR分解,会更快一些但是解稍微不那么可靠。
6. 将求解和构造分开
上面的例子中,当分解对象创建时分解就开始计算了(写在同一句中),当然可以有方法将他们独立开来:
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using namespace std;
using namespace Eigen;
int main()
{
Matrix2f A, b;
LLT<Matrix2f> llt;
A << 2, -1, -1, 3;
b << 1, 2, 3, 1;
cout << "Here is the matrix A:\n" << A << endl;
cout << "Here is the right hand side b:\n" << b << endl;
cout << "Computing LLT decomposition..." << endl;
llt.compute(A);
cout << "The solution is:\n" << llt.solve(b) << endl;
A(1,1)++;
cout << "The matrix A is now:\n" << A << endl;
cout << "Computing LLT decomposition..." << endl;
llt.compute(A);
cout << "The solution is now:\n" << llt.solve(b) << endl;
}
Here is the matrix A:
2 -1
-1 3
Here is the right hand side b:
1 2
3 1
Computing LLT decomposition...
The solution is:
1.2 1.4
1.4 0.8
The matrix A is now:
2 -1
-1 4
Computing LLT decomposition...
The solution is now:
1 1.29
1 0.571
最终,你可以告诉分解的构造函数去预先分配一个给定尺寸矩阵的内存,这样之后分解矩阵时就不会执行动态内存分配了(当矩阵是固定尺寸时,根本不会有动态内存分配这回事),可以通过传递给分解的构造函数尺寸作为参数来实现,比如
HouseholderQR<MatrixXf> qr(50,50);
MatrixXf A = MatrixXf::Random(50,50);
qr.compute(A); // no dynamic memory allocation





 本文介绍了Eigen库在矩阵运算、线性方程求解、特征值与特征向量计算、逆矩阵与行列式、最小二乘解、分解与构造分离等方面的应用,涵盖了LU、QR、SVD等多种分解方法的对比与实践示例。
本文介绍了Eigen库在矩阵运算、线性方程求解、特征值与特征向量计算、逆矩阵与行列式、最小二乘解、分解与构造分离等方面的应用,涵盖了LU、QR、SVD等多种分解方法的对比与实践示例。


















 3514
3514

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










