作者 | wenbo9 编辑 | 自动驾驶之心
原文链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1982760169126510973
点击下方卡片,关注“自动驾驶之心”公众号
>>自动驾驶前沿信息获取→自动驾驶之心知识星球
本文只做学术分享,如有侵权,联系删文
DiffusionDrive: Truncated Diffusion Model for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
https://github.com/hustvl/DiffusionDrive
https://github.com/hustvl/DiffusionDriveV2
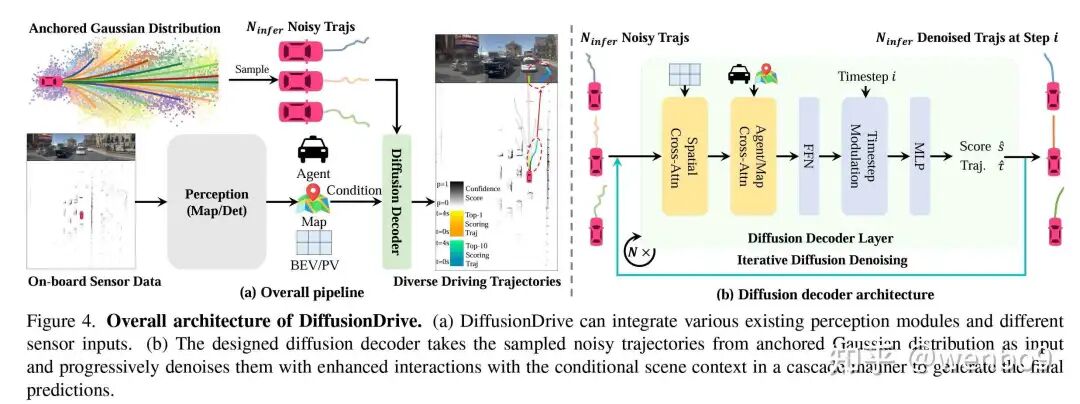
DiffusionDriveV2: Reinforcement Learning-Constrained Truncated DiffusionModeling in E2E AD
环境编码(bev和自车状态)
★参考文献:TransFuser代码
TransFuser: Imitation with Transformer-Based Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
★参考文献:GoalFlow代码
GoalFlow: Goal-Driven Flow Matching for Multimodal Trajectories Generation in End-to-End Autonomous Driving
# bev_feature_upscale(bz,64,64,64), bev_feature(bz,512,8,8)
bev_feature_upscale, bev_feature, _ = self._backbone(camera_feature, lidar_feature)
bev_feature = self._bev_downscale(bev_feature).flatten(-2, -1).permute(0, 2, 1) # (bz,64,256)
#自车当前状态编码
status_encoding = self._status_encoding(status_feature) # (1,256)
keyval = torch.concatenate([bev_feature, status_encoding[:, None]], dim=1) # (bz,64 + 1,256)
keyval += self._keyval_embedding.weight[None, ...]
query = self._query_embedding.weight[None, ...].repeat(batch_size, 1, 1)
# 参考detr目标检测,直接预测自车和多个障碍物
query_out = self._tf_decoder(query, keyval)
trajectory_query, agents_query = query_out.split(self._query_splits, dim=1)Trajectory Planning Module
多尺度bev特征
concat_cross_bev = keyval[:,:-1].permute(0,2,1).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, concat_cross_bev_shape[0], concat_cross_bev_shape[1])
# upsample to the same shape as bev_feature_upscale
concat_cross_bev = F.interpolate(concat_cross_bev, size=bev_spatial_shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
cross_bev_feature = bev_feature_upscale
cross_bev_feature = torch.cat([concat_cross_bev, cross_bev_feature], dim=1)
cross_bev_feature = self.bev_proj(cross_bev_feature.flatten(-2,-1).permute(0,2,1))
cross_bev_feature = cross_bev_feature.permute(0,2,1).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, bev_spatial_shape[0], bev_spatial_shape[1])planner anchor归一化+加噪+反归一化
获取anchors: 首先在训练数据集上对自车未来轨迹的真值进行K-Means聚类,得到一系列anchors ,每一个anchor 是一条轨迹线: 。
在anchors上加入高斯噪声: 传统的扩散步骤是不断地在每一个都加入一些噪声,而在本文中是基于anchors的位置加入高斯噪声的。
其中 表示第 个step。
plan_anchor = np.load(plan_anchor_path) # [bs, 20,8,2]
self.plan_anchor = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(plan_anchor, dtype=torch.float32), requires_grad=False,)
plan_anchor = self.plan_anchor.unsqueeze(0).repeat(bs,1,1,1)
odo_info_fut = self.norm_odo(plan_anchor)
timesteps = torch.randint(0, 50, (bs,), device=device )
noise = torch.randn(odo_info_fut.shape, device=device)
noisy_traj_points = self.diffusion_scheduler.add_noise(original_samples=odo_info_fut, noise=noise, timesteps=timesteps,).float()
noisy_traj_points = torch.clamp(noisy_traj_points, min=-1, max=1)
noisy_traj_points = self.denorm_odo(noisy_traj_points)投射带噪声的planner anchor轨迹点的pos embed为query
traj_pos_embed = gen_sineembed_for_position(noisy_traj_points,hidden_dim=64) # [bs, 20, 8, 64]
traj_pos_embed = traj_pos_embed.flatten(-2) # [bs, 20, 512]
traj_feature = self.plan_anchor_encoder(traj_pos_embed)
traj_feature = traj_feature.view(bs,noisy_traj_points.shape[1],-1)对时间进行编码
time_embed = self.time_mlp(timesteps)
time_embed = time_embed.view(bs,1,-1)轨迹预测(前向加噪)
轨迹和bev特征的cross attention
traj_feature = self.cross_bev_attention(traj_feature,noisy_traj_points,bev_feature,bev_spatial_shape)
attention_weights = self.attention_weights(queries)
attention_weights = attention_weights.view(bs, num_queries, num_points).softmax(-1)
attention_weights = attention_weights.unsqueeze(1)
value = self.value_proj(bev_feature)
grid = normalized_trajectory.view(bs, num_queries, num_points, 2)
# Sample features
sampled_features = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(value, grid, mode='bilinear',
padding_mode='zeros', align_corners=False) # bs, C, num_queries, num_points
out = (attention_weights * sampled_features).sum(dim=-1)
out = out.permute(0, 2, 1).contiguous() # bs, num_queries, C
out = self.output_proj(out)轨迹和agents_query特征的cross attention
self.cross_agent_attention(traj_feature, agents_query,agents_query)[0]轨迹和ego_query特征的cross attention
ego_query=trajectory_query
self.cross_ego_attention(traj_feature, ego_query,ego_query)[0]轨迹和时间t特征的尺度和偏移融合
# feedforward network
traj_feature = self.norm3(self.ffn(traj_feature))
traj_feature = self.time_modulation(traj_feature, time_embed,global_cond=None,global_img=global_img)
self.scale_shift_mlp = nn.Sequential(nn.Mish(), nn.Linear(condition_dims, embed_dims*2),)
scale_shift = self.scale_shift_mlp(global_feature)
scale,shift = scale_shift.chunk(2,dim=-1)
traj_feature = traj_feature * (1 + scale) + shift轨迹分类分数和去噪轨迹预测
将扩散(加噪声)后得到的 个带噪声的轨迹 输入到diffusion decoder 中,预测分类分数 和去噪后的轨迹 ,整个过程可以用公式表述为:
其中 是conditional information,本文中用的是感知特征来进行控制。
poses_reg, poses_cls = self.task_decoder(traj_feature) #bs,20,8,3; bs,20
traj_feature = traj_feature.view(bs, ego_fut_mode,-1)
plan_cls = self.plan_cls_branch(traj_feature).squeeze(-1)
traj_delta = self.plan_reg_branch(traj_feature)
plan_reg = traj_delta.reshape(bs,ego_fut_mode, self.ego_fut_ts, 3)
# 最终轨迹 = 轨迹偏移 + 原始轨迹
poses_reg[...,:2] = poses_reg[...,:2] + noisy_traj_points
poses_reg[..., StateSE2Index.HEADING] = poses_reg[..., StateSE2Index.HEADING].tanh() * np.piMode Selector
轨迹生成(反向去燥):根据plan_anchor,记录网络输出的所有中间去燥的结果,以及最终的去燥结果。
plan_anchor = self.plan_anchor.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).repeat(bs,num_groups, 1, 1, 1)
plan_anchor = plan_anchor.view(bs, num_groups * self.ego_fut_mode, *plan_anchor.shape[3:]) # bs num_groups * 20, 8, 2
diffusion_output = self.norm_odo(plan_anchor)
trunc_timesteps = torch.ones((bs,), device=device, dtype=torch.long) * 8
diffusion_output = self.diffusionrl_scheduler.add_noise(original_samples=diffusion_output, noise=noise, timesteps=trunc_timesteps)
# roll_timesteps [18, 16, 14, 12, 10, 8, 6, 4, 2, 0]
roll_timesteps = (np.arange(0, step_num) * step_ratio).round()[::-1].copy().astype(np.int64)
roll_timesteps = torch.from_numpy(roll_timesteps).to(device)
for i, k in enumerate(roll_timesteps[:]):
poses_reg_list, poses_cls_list = self.diff_decoder(
traj_feature, noisy_traj_points, bev_feature, bev_spatial_shape,
agents_query, ego_query, time_embed, status_encoding, global_img)
prev_sample, log_prob, _ = self.diffusionrl_scheduler.step(
model_output=x_start, timestep=k, sample=diffusion_output, eta=eta,)
diffusion_output = prev_sample
all_diffusion_output.append(prev_sample) # BG N 8 2使用PDM评分器计算网络输出的所有模态的轨迹以及真值轨迹的cost:
scores_np - 主评分矩阵:基于PDM评分器对轨迹的多个维度进行评估后的综合分数
metric_cache - 指标缓存:每个场景计算过程中用到的中间结果和参考数据(避免重复计算)
sub_scores - 子项评分:轨迹在不同维度上的细分评分
# 安全性检查(碰撞检测、驶出道路等)
safety_score = check_safety(traj, scenario_data['agents'], scenario_data['map'])
# 舒适性评估(加速度、加加速度、曲率连续性)
comfort_score = check_comfort(traj)
# 规则遵守(交通灯、车道保持、速度限制)
rule_score = check_rules(traj, scenario_data['traffic_rules'])
# 进度评估(是否到达目标)
progress_score = check_progress(traj, scenario_data['goal'])
# 物理可行性(动力学约束)
feasibility_score = check_feasibility(traj, vehicle_dynamics)
# 综合评分(加权平均)
total_score = (
safety_weight * safety_score +
comfort_weight * comfort_score +
rule_weight * rule_score +
progress_weight * progress_score +
feasibility_weight * feasibility_score
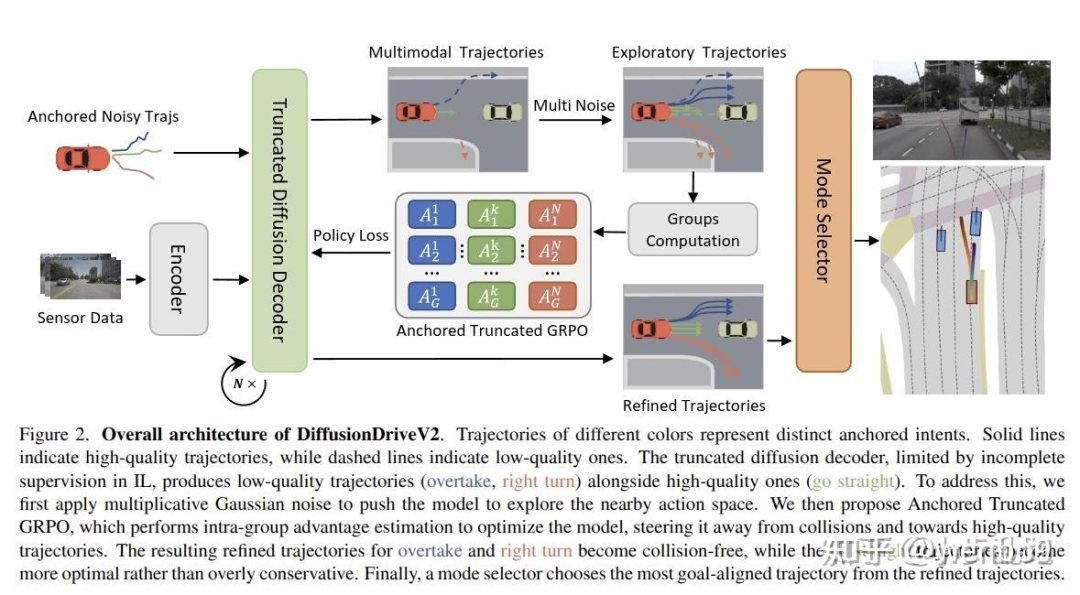
)我们提出锚点内GRPO(Intra-Anchor GRPO)。对于每个锚点,首先通过随机高斯噪声和探索噪声对其进行扩散,生成 个轨迹变体组成的组;随后在该组内执行GRPO更新,而非跨不同锚点的组进行更新。该方法将策略优化约束在每个特定行为意图的状态空间内,引导模型生成更安全、更面向目标的轨迹,同时不损害其多模态能力。强化学习损失函数可表示为:
其中 为折扣系数,用于缓解早期去噪步骤中的不稳定性; 为优势函数,GRPO通过计算组相对优势进行估计,无需价值模型:
为基于最终去噪轨迹 计算的单一奖励估计值,该奖励被应用于扩散链中的所有去噪步骤,且每个步骤的影响通过去噪折扣 进行缩放。
# 计算生成轨迹的基础优势函数
reward_group = reward_group.view(bs, num_groups, self.ego_fut_mode) # (B,G,N)
mean_grouped_rewards = reward_group.mean(dim=1)
std_grouped_rewards = reward_group.std(dim=1)
advantages = (reward_group - mean_grouped_rewards.unsqueeze(1)) / (std_grouped_rewards.unsqueeze(1) + 1e-4)
# 只保留 “好于 GT” 的正向样本,对比学习:通过与ground truth对比来定义"好"轨迹
mask_positive = (reward_group > (reward_gt-1e-6)) # (B,G) bool
advantages = advantages.clamp(min=0) * mask_positive.float() # 负 adv 归 0锚点内GRPO虽能防止模式崩溃,但完全隔离不同模式会引发新问题:优势估计丧失全局可比性。例如,某一模式中次优但安全的轨迹可能获得负优势,而另一模式中危险且存在碰撞的轨迹若为其组内“最优”样本,则可能获得正优势。这种依赖局部组内比较的方式会向模型传递误导性学习信号。
具体实现方式为修改锚点内GRPO的优势估计 :将所有负优势截断为0,并对存在碰撞的轨迹分配-1的强惩罚:
这一设计为模型提供了清晰且一致的学习信号。随后,该截断优势 将替代公式(7)中的 用于强化学习损失计算。
# 根据子奖励调节优势
if k == 'no_collision' or k == 'drivable_area':
# 对于安全性指标: 如果不满足条件(值不为1),优势设为-1
zero_mask = (v != 1)
advantages = torch.where(zero_mask, torch.full_like(advantages, -1.0), advantages)
# 创建时间折扣因子
# discount: [0.8^3, 0.8^2, 0.8^1, 0.8^0] = [0.512, 0.64, 0.8, 1.0]
discount = torch.tensor(
[
0.8 ** (step_num - i - 1) # 指数衰减: 越远的未来折扣越大
for i in range(step_num)
]
).to(advantages.device) # 形状: (T,)
# 未来时间步的奖励权重降低
advantages = advantages * discount # (B, M, T)Loss
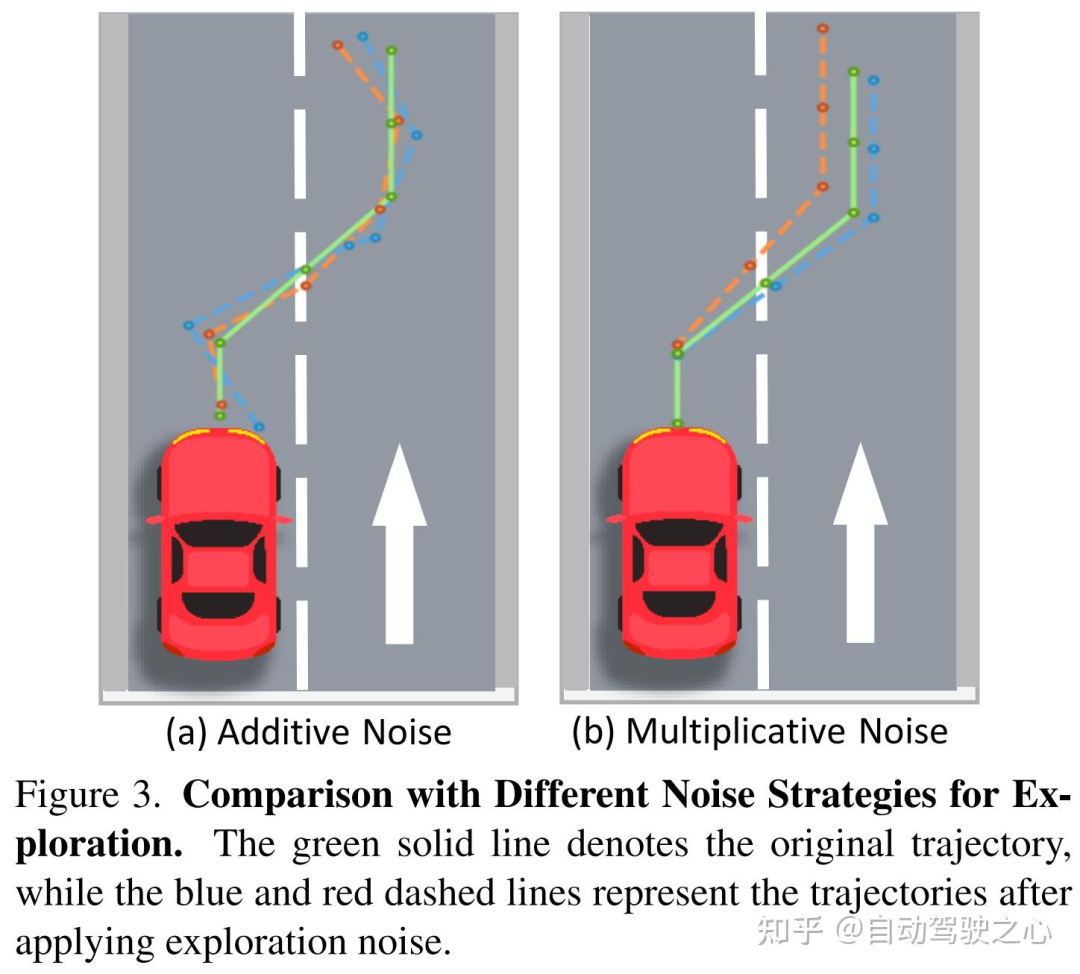
DiffusionDrive采用DDIM更新规则,将去噪步数大幅减少。该更新规则通常通过设置 作为确定性采样器使用。为实现更广泛的探索并避免狄拉克分布下的似然计算问题,我们在训练阶段设置 以引入探索噪声(等价于采用DDPM),而在验证阶段保持 以实现确定性推理。然而,由于轨迹的近端段与远端段存在固有尺度不一致性,直接在每个点施加加法高斯噪声会破坏轨迹的结构完整性,降低探索质量。
如图3(a)所示,对标准化轨迹 施加加法高斯噪声 后,生成的探索路径通常呈锯齿状(类似折线),丧失了原始轨迹的平滑性。为保留轨迹连贯性,我们提出仅添加两个乘法高斯噪声(一个纵向噪声、一个横向噪声),其表达式为 ,其中 。这种尺度自适应乘法噪声确保生成的探索路径保持平滑,如图3(b)所示。
在强化学习中,引入探索噪声是推动模型探索新行为的重要手段,
加性噪声:轨迹的近端(proximal segments)和远端(distal segments)存在固有的尺度不一致性。简单地在每个点上添加相同的加性高斯噪声,会导致轨迹的结构完整性被破坏,使其变得不连贯且“锯齿状”(jagged),如图 3(a) 所示。这会降低探索的质量
乘性噪声:它不是直接添加噪声,而是通过一个乘法因子来调整轨迹的每个点。具体来说,它只添加两个乘法高斯噪声:一个沿纵向(longitudinal),一个沿横向(lateral)。这种乘法形式使得噪声的大小能够根据轨迹自身的尺度自动调整。对于轨迹上距离较远、坐标值较大的点,相同的乘法噪声会产生更大的绝对扰动,反之亦然,从而自然地保持轨迹的连贯性和平滑性,如图 3(b) 所示。
if prev_sample is None:
# 乘性噪声
variance_noise_horizon = randn_tensor(
[model_output.shape[0],model_output.shape[1],1,1], generator=generator, device=model_output.device, dtype=model_output.dtype
) * std_dev_t_mul + 1.0
variance_noise_vert = randn_tensor(
[model_output.shape[0],model_output.shape[1],1,1], generator=generator, device=model_output.device, dtype=model_output.dtype
) * std_dev_t_mul + 1.0
variance_noise_mul = torch.cat((variance_noise_horizon,variance_noise_vert),dim=-1)
variance_noise_mul = variance_noise_mul.repeat(1,1,model_output.shape[2],1)
# 加性噪声
variance_noise_x = randn_tensor(
[model_output.shape[0],model_output.shape[1],1,1], generator=generator, device=model_output.device, dtype=model_output.dtype
)
variance_noise_y = randn_tensor(
[model_output.shape[0],model_output.shape[1],1,1], generator=generator, device=model_output.device, dtype=model_output.dtype
)
variance_noise_add = torch.cat((variance_noise_x,variance_noise_y),dim=-1)
variance_noise_add = variance_noise_add.repeat(1,1,model_output.shape[2],1)
prev_sample = prev_sample_mean * variance_noise_mul + std_dev_t_add * variance_noise_add根据计算的每一步加噪输出,计算log_prob?
std_dev_t_mul = torch.clip(std_dev_t, min=0.1)
log_prob = (
-((prev_sample.detach() - prev_sample_mean) ** 2) / (2 * (std_dev_t_mul**2))
- torch.log(std_dev_t_mul)
- torch.log(torch.sqrt(2 * torch.as_tensor(math.pi)))
)
log_prob = log_prob.sum(dim=(-2, -1))此外,与原始GRPO通过添加策略模型与参考模型之间的KL散度实现正则化类似,我们引入额外的模仿学习损失,以防止模型过拟合并保障其通用驾驶能力。组合损失函数为
其中 为权重系数。
真值监督:先用anchors和真值 匹配,得到和真值最接近的anchor,然后这个anchor周围的“噪声轨迹”作为正样本( ),其他的则看作是负样本( )
target_traj = targets["trajectory"]
dist = torch.linalg.norm(target_traj.unsqueeze(1)[...,:2] - plan_anchor, dim=-1)
dist = dist.mean(dim=-1)
mode_idx = torch.argmin(dist, dim=-1)
mode_idx = mode_idx[...,None,None,None].repeat(1,1,ts,d)
best_reg = torch.gather(poses_reg, 1, mode_idx).squeeze(1)
target_classes_onehot = torch.zeros([bs, num_mode],
dtype=poses_cls.dtype, layout=poses_cls.layout, device=poses_cls.device)
target_classes_onehot.scatter_(1, cls_target.unsqueeze(1), 1)
loss_cls = self.cls_loss_weight * py_sigmoid_focal_loss(
poses_cls, target_classes_onehot, weight=None,
gamma=2.0, alpha=0.25, reduction='mean', avg_factor=None)loss由“轨迹恢复”和“分类置信度”两部分组成: 是loss权重
reg_loss = self.reg_loss_weight * F.l1_loss(best_reg, target_traj)自动驾驶之心
自动驾驶知识星球交流社区





















 612
612

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








