Fibonacci
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 20957 | Accepted: 14366 |
Description
In the Fibonacci integer sequence, F0 = 0, F1 = 1, and Fn = Fn − 1 + Fn − 2 for n ≥ 2. For example, the first ten terms of the Fibonacci sequence are:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, …
An alternative formula for the Fibonacci sequence is
 .
.
Given an integer n, your goal is to compute the last 4 digits of Fn.
Input
The input test file will contain multiple test cases. Each test case consists of a single line containing n (where 0 ≤ n ≤ 1,000,000,000). The end-of-file is denoted by a single line containing the number −1.
Output
For each test case, print the last four digits of Fn. If the last four digits of Fn are all zeros, print ‘0’; otherwise, omit any leading zeros (i.e., print Fn mod 10000).
Sample Input
0
9
999999999
1000000000
-1
Sample Output
0
34
626
6875
Hint
As a reminder, matrix multiplication is associative, and the product of two 2 × 2 matrices is given by
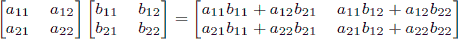 .
.
Also, note that raising any 2 × 2 matrix to the 0th power gives the identity matrix:
 .
.
其实矩阵快速幂和数的快速幂很像 其实都用到二分的思想
//矩阵快速幂
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define LL __int64
#define MOD 1000
typedef struct MATRIX
{
int mat[50][50];
}MATRIX;
MATRIX mat_multiply (MATRIX a,MATRIX b,int n)
{
MATRIX c; //c[i][j]= Σ a[i][k]*b[k][j]
memset(c.mat,0,sizeof(c.mat));
/*
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //a矩阵一行一行往下
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) //b矩阵一列一列往右
for(int k=0;k<n;k++) //使a矩阵 第i行第k个元素 乘以 b矩阵 第j列第k个元素
if(a[i][k] && b[k][j]) //剪枝(添条件,设门槛),提高效率,有一个是0,相乘肯定是0
c.mat[i][j]+=a.mat[i][k]*b.mat[k][j];
*/
//上面也是可以的,但是下面的剪枝更好一些,效率更高一些,但是运算顺序有点难想通,,,
//上面就是C[i][j]一次就求出来,下面就是每次c[i][j]求出一项【就是上面红体字,每次各求一列】
for(int k=0;k<n;k++) //这个可以写到前面来,
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
if(a.mat[i][k]) //剪枝:如果a.mat[i][k]是0,就不执行了
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
if(b.mat[k][j]) //剪枝:如果b.mat[i][k]是0,就不执行了
{
c.mat[i][j]+=a.mat[i][k]*b.mat[k][j];
if(c.mat[i][j]>=MOD) //这个看实际需求,要不要取模
c.mat[i][j]%=MOD; //取模的复杂度比较高,所以尽量减少去模运算,添加条件,只有当大于等于MOD的时候才取余
}
return c;
}
MATRIX mat_quick_index(MATRIX a,int N,int n)
{
MATRIX E; //单位矩阵,就像数值快速幂里,把代表乘积的变量初始化为1
// memset(E.mat,0,sizeof(E.mat)); //置零,单位矩阵除了主对角线都是1,其他都是0
// for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //初始化单位矩阵【就是主对角线全是1】
// E.mat[i][i]=1;
//把E初始化 单位矩阵(主对角线) 乘与任何矩阵都是它本身
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
E.mat[i][j]=(i==j); //酷炫*炸天的初始化!!!
while(N>0)
{
if(N & 1)
E=mat_multiply(E,a,n);
N>>=1;
a=mat_multiply(a,a,n);
}
return E;
}
int main()
{
int n,N; //n为矩阵(方阵)规模,几行,N为指数
MATRIX A,C;
memset(A.mat,0,sizeof(A.mat));
memset(C.mat,0,sizeof(C.mat));
scanf("%d",&n); //矩阵规模,这里是方阵,行数等于列数
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //初始化A矩阵
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
scanf("%d",&A.mat[i][j]);
scanf("%d",&N);
C=mat_quick_index(A,N,n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) //打印C矩阵
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
printf("%3d",C.mat[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
此题题解
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int mod=10000;
struct node
{
int a[2][2];
node(){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));//记得初始化
}
};
node mul(node p,node q)
{
node t;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
for(int k=0;k<2;k++){
t.a[i][j]=(t.a[i][j]+p.a[i][k]*q.a[k][j])%mod;
}
}
}
return t;
}
node binary(node e,int n)
{
node t;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++){
for(int j=0;j<2;j++){
t.a[i][j]=(i==j);
}
}
while(n>0){
if(n&1){
t=mul(t,e);
}
n>>=1;
e=mul(e,e);
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)==1,n!=-1){
node e;
//初始化
e.a[0][0]=1;
e.a[0][1]=1;
e.a[1][0]=1;
e.a[1][1]=0;
node tt=binary(e,n);
printf("%d\n",tt.a[0][1]);
}
return 0;
}
























 7243
7243

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








