题目
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
For example:
A = [2,3,1,1,4],
return true.
A = [3,2,1,0,4],
return false.
思路一:递归
可以通到小数据,但不可以通过大数据。大数据超时。
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(int A[], int n) {
// Start typing your C/C++ solution below
// DO NOT write int main() function
return myjump(A,n,0);
}
bool myjump(int A[], int n, int i)
{
if(i==n-1)
return true;
if(i>n-1)
return false;
int step = A[i];
while(step)
{
bool result = false;
result = myjump(A, n, i+step);
if(result)
return true;
step--;
}
return false;
}
};
思路二:迭代
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(int A[], int n) {
// Start typing your C/C++ solution below
// DO NOT write int main() function
vector<bool> isreach(n,false);
isreach[n-1] = true;
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
{
int step = A[i];
while(step){
if(i+step<n)
{
isreach[i]=isreach[i]||isreach[i+step];
if(isreach[i])
break ;
}
step--;
};
}
return isreach[0];
}
};
思路三
每次都跳到最大步,如果过了 target ,返回 true。
虽然能通过大小数据集,但是该代码是有问题的。
例如: 3 2 2 0 1 4 是返回true的,但是本代码返回false。
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(int A[], int n) {
// Start typing your C/C++ solution below
// DO NOT write int main() function
if(n==1)
return true;
int i=0;
while(i<n)
{
i+=A[i];
if(i>=n-1)
return true;
else
{
if(A[i]==0)
return false;
}
}
}
};
思路四
根正思路三的代码之后,得到正确的代码,扫描一遍,每次记录可以到达的最远距离。
思路三跳到最远距离,中间会遗漏部分可能解。
而本方法还是每一步都判断了,所以遍历了所有可能的解。
class Solution
{
public:
bool canJump(int A[], int n)
{
// Start typing your C/C++ solution below
// DO NOT write int main() function
if(n<=1)
return true;
int curmax = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(A[i]==0)
{
if(curmax<=i)
return false;
}
if(A[i]>0)
{
if(A[i]+i>curmax)
curmax = A[i]+i;
if(curmax>=n-1)
return true;
}
}
}
};
最新 java
We can track the maximum index that can be reached. The key to solve this problem is to find: 1) when the current position can not reach next position (return false) , and 2) when the maximum index can reach the end (return true).
The largest index that can be reached is: i + A[i].
Here is an example:
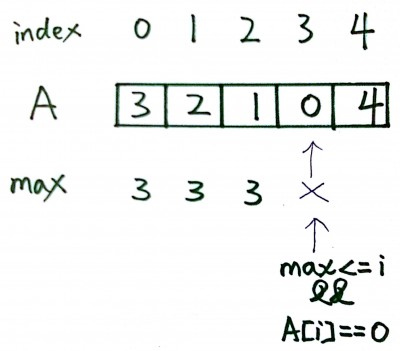
Java Solution
public boolean canJump(int[] A) {
if(A.length <= 1)
return true;
int max = A[0]; //max stands for the largest index that can be reached.
for(int i=0; i<A.length; i++){
//if not enough to go to next
if(max <= i && A[i] == 0)
return false;
//update max
if(i + A[i] > max){
max = i + A[i];
}
//max is enough to reach the end
if(max >= A.length-1)
return true;
}
return false;
}





















 344
344

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








