目录
以下文章参考文档
<set> - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
map - C++ Reference (cplusplus.com)
一、底层结构
C++中的set和map的底层结构是红黑树,红黑树是⼀颗平衡⼆叉搜索树。
(若不知道什么是红黑树的可以看看这篇文章->C++:红黑树的实现-优快云博客)
二、set
1、set的介绍
- set底层是用红黑树实现,增删查效率是(O(logN)) ,迭代器遍历是走的搜索树的中序,所以是有序的。
- set的声明如下,T就是set底层关键字的类型。
- set默认要求T支持小于比较,如果不支持或者想按自己的需求走可以自行实现仿函数传给第⼆个模版参数(⼀般情况下,我们都不需要传后两个模版参数)
- set中只能存在一个相同的值,若插入相同的值给set,将会插入失败。
std::set template < class T, // set::key_type/value_type class Compare = less<T>, // set::key_compare/value_compare class Alloc = allocator<T> // set::allocator_type > class set;
set的支持正向和反向迭代遍历,遍历默认按升序顺序,因为底层是⼆叉搜索树,迭代器遍历走的中序;支持迭代器就意味着支持范围for,set的iterator和const_iterator都不支持迭代器修改数据,修改关键字数据,破坏了底层搜索树的结构。
2、set的使用
(1)set的插入(insert)
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(5);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(5);
auto it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
打印结果↓
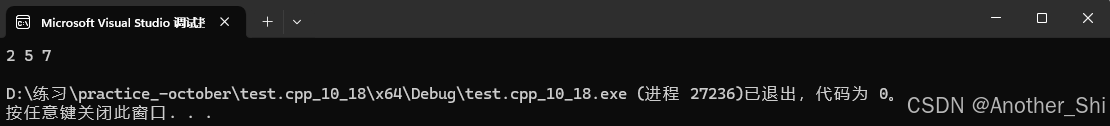
如set介绍里第四条所述,set中只能存在一个相同的值,插入重复的5将会插入失败。而且set的底层是红黑树,(平衡二叉搜索树) 用迭代器遍历是用中序遍历,所以打印结果会是升序排列。
注:不能使用迭代器来改变set里的值,会报错的,因为改变set里的值可能会导致set的结构失效。
还可以这样插入
s.insert({ 2,8,3,9 });
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;当然也可以插入string类型
set<string> strset = { "sort", "insert", "add" };
// 遍历string⽐较ascll码⼤⼩顺序遍历的
for (auto& e : strset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;(2)find和erase使用
(a)删除最小值
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> s = { 4,2,7,2,8,5,9 };
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 删除最⼩值
s.erase(s.begin());
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}如set介绍里第一条所述,迭代器遍历是走的搜索树的中序,所以set的begin的位置就是最小值的位置,我们可以很轻松的删除set里的最小值,但set里的最大值不是end,--end的位置才是最大值。
(b)直接删除x
// 直接删除x
int x;
cin >> x;
int num = s.erase(x);
if (num == 0)
{
cout << x << "不存在!" << endl;
}
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;当我们删除失败的时候会返回0,所以我们可以利用返回值来判断set里是否有要删除的那个值。
(3)直接查找在利用迭代器删除x
// 直接查找在利⽤迭代器删除x
cin >> x;
auto pos = s.find(x);
if (pos != s.end())
{
s.erase(pos);
}
else
{
cout << x << "不存在!" << endl;
}
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;利用find接口,若找到了要查找的值,返回那个值的迭代器的位置,反之,返回end迭代器的位置。
(3)lower_bound和upper_bound的使用
lower_bound和upper_bound也算是个查找函数。
如:lower_bound(10)会返回set里大于等于10的值,它迭代器的位置。upper_bound(40)会返回set里大于40的值,它的迭代器的位置。
#include<iostream>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> myset;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
myset.insert(i * 10); // 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 实现查找到的[itlow,itup)包含[30, 60]区间
// 返回 >= 30
auto itlow = myset.lower_bound(30);
// 返回 > 60
auto itup = myset.upper_bound(60);
// 删除这段区间的值
myset.erase(itlow, itup);
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}打印结果↓
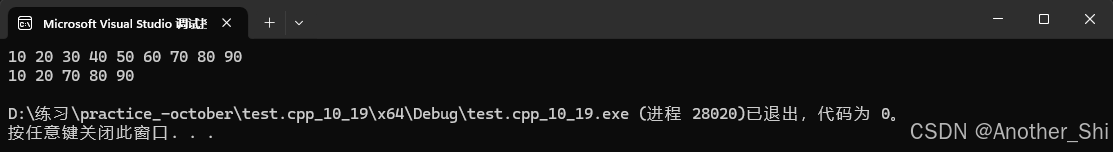
三、map
1、map的介绍
- map的声明如下,Key就是map底层关键字的类型,T是map底层value的类型,set默认要求Key支持小于比较。
- 如果不支持或者需要的话可以自行实现仿函数传给第⼆个模版参数。⼀般情况下,我们都不需要传后两个模版参数。
- map底层是用红黑树实现,增删查改效率是O(logN) ,迭代器遍历是⾛的中序,所以是按key有序顺序遍历的。
- map中只能存在一个相同的Key,若插入相同的值给map,将会插入失败。
std::map
template < class Key, // map::key_type
class T, // map::mapped_type
class Compare = less<Key>, // map::key_compare
class Alloc = allocator<pair<const Key,T> > // map::allocator_type
> class map;打个比方:map里的Key就是动物园里的各个园区的钥匙,钥匙只能开指定园区的锁,不能改变,但可以被销毁也就是删除。而T就是园区里的动物,可以改变它的数量和种类……
总而言之,map里的Key不能改变,可以删除;T可以改变。
2、map的使用
(1)构造遍历及增删查使用
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, string> dict = { {"left", "左边"}, {"right", "右边"},
{"insert", "插⼊"},{ "string", "字符串" } };
dict.insert({"left", "左边,剩余"});
auto it = dict.begin();
while (it != dict.end())
{
cout << it->first << ":" << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}打印结果如下:

map会按Key来排序。
若要访问map里的数据要指定是访问Key还是T,如上里的first就是Key而second是T。
若插入的Key与map里已有的Key相同,则会插入失败。
(2)map的迭代器和[]的使用
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西⽠", "苹果", "西⽠", "苹果", "苹果", "西⽠",
"苹果", "⾹蕉", "苹果", "⾹蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
// 先查找⽔果在不在map中
// 1、不在,说明⽔果第⼀次出现,则插⼊{⽔果, 1}
// 2、在,则查找到的节点中⽔果对应的次数++
auto ret = countMap.find(str);
if (ret == countMap.end())
{
countMap.insert({ str, 1 });
}
else
{
ret->second++;
}
}
for (const auto& e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}这是利用迭代器来计数Key,map里面没有要插入的Key,插入map,若有,就++这个Key的T。
但map里的[]是比较特殊的存在。上面的代码可以改成↓
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string arr[] = { "苹果", "西⽠", "苹果", "西⽠", "苹果", "苹果", "西⽠",
"苹果", "⾹蕉", "苹果", "⾹蕉" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& str : arr)
{
countMap[str]++;
}
for (const auto& e : countMap)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}一般的 stl 里的重载 [] 运算符的作用是查找和修改,但map里的重载 [] 运算符多了一个插入操作,当对象里没有 [] 要使用的值,map里会先插入一个值,然后再使用它。




















 2453
2453

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








