计数排序
统计给定一个集合中,每个数字出现的次数,然后根据次数,依次将对应数组按顺序放回
但是计数排序有局限性,只能一次统计已知一定范围内的元素。
如下列示例代码中,找到数组元素最大值,然后创建以最大值为大小的数组,作为桶进行技术,会造成空间浪费,也有一定局限性。
代码实现
// only for 0~200 value
public static void countSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int[] bucket = new int[max + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
bucket[arr[i]]++;
}
int i = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < bucket.length; j++) {
while (bucket[j]-- > 0) {
arr[i++] = j;
}
}
}
基数排序
通过基数排序对数组{53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214, 154, 63, 616}
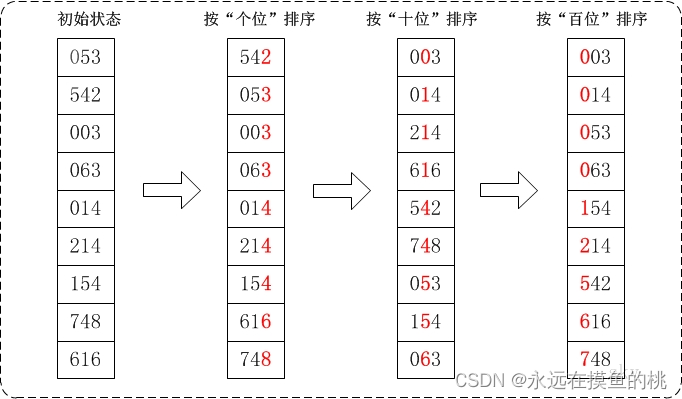
大概流程就是从个位开始,入桶进行排序;然后找更高位接着,入桶进行排序,依次类推,最终使得数组有序。
局限性:受限于元素种类,一般来讲元素要是10进制的正整数
代码实现

public class RadixSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[] {53, 3, 542, 748, 14, 214, 154, 63, 616};
radixSort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
public static void radixSort(int[] arr) {
if (arr == null || arr.length < 2) {
return;
}
radixSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1, maxbits(arr));
}
// 找最大值的十进制位数digit
private static int maxbits(int[] arr) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
max = Math.max(max, arr[i]);
}
int res = 0;
while (max != 0) {
res++;
max /= 10;
}
return res;
}
// arr[L..R]排序 , 最大值的十进制位数digit
public static void radixSort(int[] arr, int L, int R, int digit) {
int radix = 10; // 桶个数
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
// 有多少个数就准备多大的辅助空间
int[] help = new int[R - L + 1];
for (int d = 1; d <= digit; d++) { // 有多少位就进出几次
// 10个空间
// count[0] 当前位(d位)是0的数字有多少个
// count[1] 当前位(d位)是(0和1)的数字有多少个
// count[2] 当前位(d位)是(0、1和2)的数字有多少个
// count[i] 当前位(d位)是(0~i)的数字有多少个
// 相当于10和桶
int[] count = new int[radix]; // count[0..9]
for (i = L; i <= R; i++) {
// 获取d位上的数,在count桶中对应位置+1
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
count[j]++;
}
// 求前缀和,遍历所有桶,进行前缀累加
for (i = 1; i < radix; i++) {
count[i] = count[i - 1] + count[i];
}
// 根据前缀和,将对应的数字放到辅助数组的正确位置上
for (i = R; i >= L; i--) {
j = getDigit(arr[i], d);
// 设count[j]代表位置值为c;则存储的下标范围为 0~c-1,从后往前存储
help[count[j] - 1] = arr[i];
// 存入一个值,则count[j]--
count[j]--;
}
// 最终将这次排序的结果复制到原数组中,进行下一位数的排序
for (i = L, j = 0; i <= R; i++, j++) {
arr[i] = help[j];
}
}
}
// 获取x的第d位数字
public static int getDigit(int x, int d) {
return ((x / ((int) Math.pow(10, d - 1))) % 10);
}
}







 本文介绍了两种非比较型排序算法——计数排序和基数排序。计数排序适用于已知范围内的元素,通过创建桶存储每个数字出现的次数,然后依次放回。基数排序则利用数字的每一位进行桶排序,适合处理10进制正整数。文章提供了详细的代码实现,并分析了两种排序算法的局限性。
本文介绍了两种非比较型排序算法——计数排序和基数排序。计数排序适用于已知范围内的元素,通过创建桶存储每个数字出现的次数,然后依次放回。基数排序则利用数字的每一位进行桶排序,适合处理10进制正整数。文章提供了详细的代码实现,并分析了两种排序算法的局限性。
















 3386
3386

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








