有关静态链表的介绍(来自网络):
静态链表( static linked list )
分配一整片连续的内存空间,各个结点集中安置,逻辑结构上相邻的数据元素,存储在指定的一块内存空间中,数据元素只允许在这块内存空间中随机存放,这样的存储结构生成的链表称为静态链表。也就是说静态链表是用数组来实现链式存储结构,静态链表实际上就是一个结构体数组
首先,代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define DEFAULT_SIZE 5
typedef struct StaticLinkedNode
{
char data;
int next;
} *NodePtr;
typedef struct StaticLinkedList
{
NodePtr nodes;
int* used;
} *ListPtr;
ListPtr initLinkedList()
{
//The pointer to the whole list space.
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
//Allocate total space.
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
//The first node is the header.
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
//Only the first node is used.
tempPtr->used[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++)
{
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}// Of for i
return tempPtr;
}// Of initLinkedList
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr)
{
int p = 0;
while (p != -1)
{
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
printf("\r\n");
}// Of printList
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition)
{
int p, q, i;
//Step 1:Search to the position
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++)
{
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1)
{
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
//step 2:Construct anew node
for (i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++)
{
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0)
{
//This is identical to malloc.
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
if (i == DEFAULT_SIZE)
{
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}//Of if
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
//Step 3: Now link.
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}// Of insertElement
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar)
{
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar))
{
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1)
{
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}// Of if
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
//This statement is identical to free(q)
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}// Of deleteElement
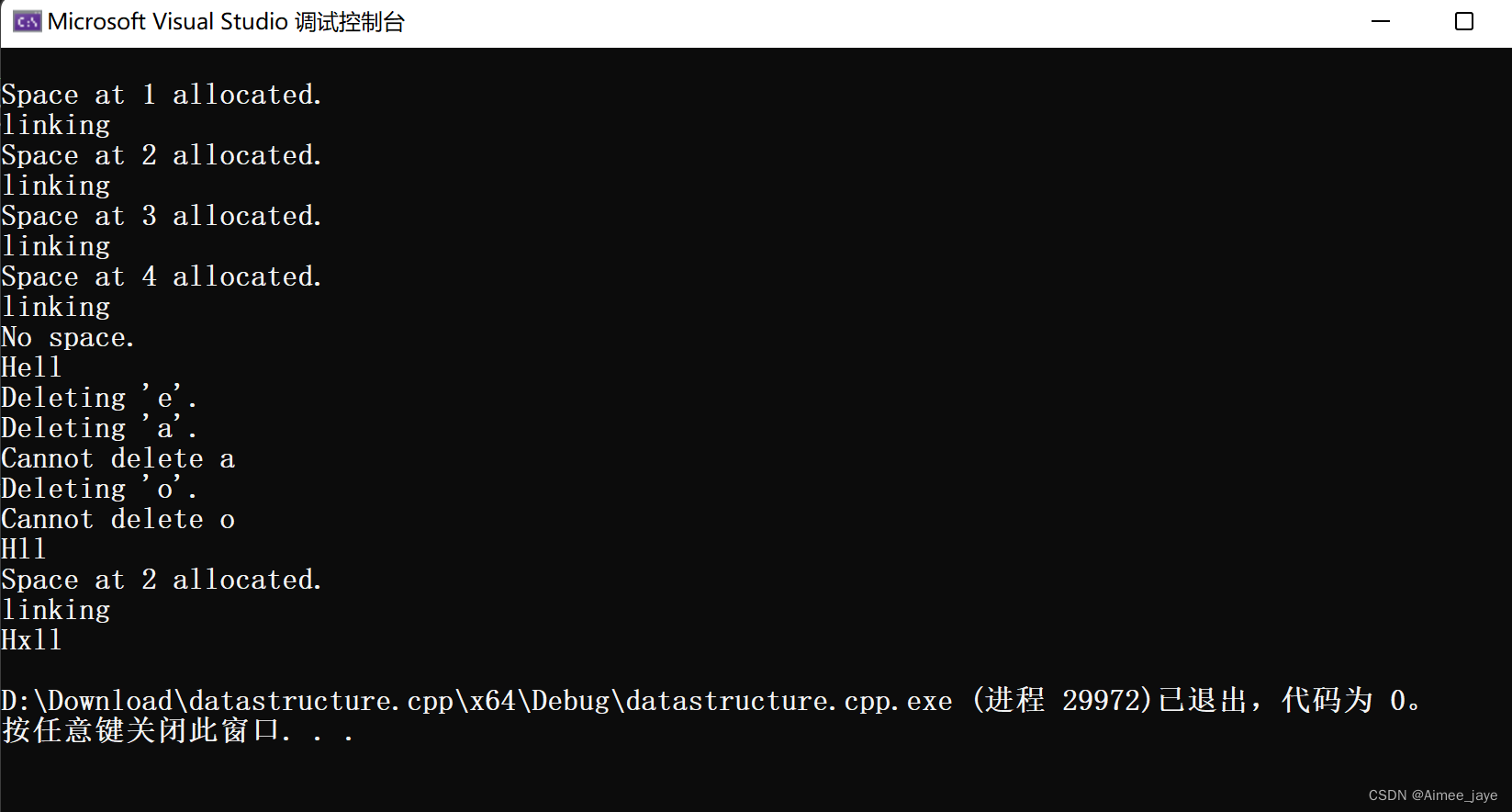
void appendInsertDeleteTest()
{
// Step 1:Initialize an empty list
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
//Step 2:Add some characters
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
//Step 3: Delete some characters(the first occurence).
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
printList(tempList);
}// Of appendInsertDeletTest
int main()
{
appendInsertDeleteTest();
return 0;
}
初始化
ListPtr initLinkedList()
{
//The pointer to the whole list space.
ListPtr tempPtr = (ListPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList));
//Allocate total space.
tempPtr->nodes = (NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
tempPtr->used = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * DEFAULT_SIZE);
//The first node is the header.
tempPtr->nodes[0].data = '\0';
tempPtr->nodes[0].next = -1;
//Only the first node is used.
tempPtr->used[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++)
{
tempPtr->used[i] = 0;
}// Of for i
return tempPtr;
}// Of initLinkedList
-
首先定义一个指向静态链表的指针
tempPtr,然后动态地分配了一个sizeof(struct StaticLinkedList)大小的内存空间给tempPtr,并用malloc()函数来实现。 -
然后为静态链表中的节点分配内存,一共
DEFAULT_SIZE个,每个节点的大小是sizeof(struct StaticLinkedNode),然后用一个名为tempPtr->nodes的指针数组来保存每个节点的地址,这样tempPtr->nodes[i]就指向了第i个节点的地址。 -
为静态链表中的
used数组分配内存,大小为DEFAULT_SIZE * sizeof(int),它用于记录每个节点是否被使用。used[i] = -1表示某个节点是被使用的,而used[i] = 0表示某个节点是空闲的。 -
初始化链表中的第一个节点(也就是头结点),
头结点的data成员为空字符、next成员为-1。 -
最后
for循环初始化used数组,将其初始值设为0,表示所有的节点都是空闲的。
打印静态链表
void printList(ListPtr paraListPtr)
{
int p = 0;
while (p != -1)
{
printf("%c", paraListPtr->nodes[p].data);
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
printf("\r\n");
}// Of printList
printList是一个函数,参数为指向静态链表的指针paraListPtr。- 然后定义了一个整型变量p,并将其赋值为0,这里的
p表示当前要打印的节点的下标。 - 在while循环中,
只要p不等于-1,就打印指向p节点的数据即paraListPtr->nodes[p].data然后将p的值更新为下一个节点的下标,即paraListPtr>nodes[p].next
插入元素
void insertElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar, int paraPosition)
{
int p, q, i;
//Step 1:Search to the position
p = 0;
for (i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++)
{
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
if (p == -1)
{
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.\r\n", paraPosition);
return;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
//step 2:Construct anew node
for (i = 1; i < DEFAULT_SIZE; i++)
{
if (paraListPtr->used[i] == 0)
{
//This is identical to malloc.
printf("Space at %d allocated.\r\n", i);
paraListPtr->used[i] = 1;
q = i;
break;
}//Of if
}//Of for i
if (i == DEFAULT_SIZE)
{
printf("No space.\r\n");
return;
}//Of if
paraListPtr->nodes[q].data = paraChar;
//Step 3: Now link.
printf("linking\r\n");
paraListPtr->nodes[q].next = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = q;
}// Of insertElement
insertElement是一个函数,其参数为指向静态链表的指针paraListPtr,要插入的字符paraChar,以及要插入的位置paraPosition。- 首先,定义了两个
整型变量p和q,用于记录当前节点和新节点的下标,以及一个整型变量i用于循环计数。 - 在Step 1中,从静态链表头节点开始遍历找到要插入的位置。每次将p更新为当前节点的下一个节点。如果遍历到链表末尾仍未找到要插入的位置,就输出错误信息并返回。
- 在Step 2中,先用循环找到一个未使用的节点,也就是
used数组值为0的节点。找到未使用节点后,将其标记为已使用即used为1,并将q的值更新为其下标。如果没有找到未使用节点,就输出错误信息并返回。 - 然后将新节点的数据设置为paraChar。 在Step 3中,将新节点与链表中的节点连接起来。
首先将新节点的下一个节点设置为原位置节点的下一个节点,然后将原位置节点的下一个节点设置为新节点。
删除元素
void deleteElement(ListPtr paraListPtr, char paraChar)
{
int p, q;
p = 0;
while ((paraListPtr->nodes[p].next != -1) && (paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].data != paraChar))
{
p = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
}// Of while
if (paraListPtr->nodes[p].next == -1)
{
printf("Cannot delete %c\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}// Of if
q = paraListPtr->nodes[p].next;
paraListPtr->nodes[p].next = paraListPtr->nodes[paraListPtr->nodes[p].next].next;
//This statement is identical to free(q)
paraListPtr->used[q] = 0;
}// Of deleteElement
deleteElement是一个函数,参数为指向静态链表的指针paraListPtr以及要删除的字符paraChar。- 首先定义了两个
整型变量p和q,用于记录当前节点和删除节点的下标。 - 在while循环中,从静态链表头节点开始遍历,找到要删除的节点位置。如果当前节点的下一个节点不是要删除的节点,就继续向下遍历。如果遍历到链表末尾未找到要删除的节点,就输出错误信息并返回。
- 在找到要删除的节点后,记录其下标为q,将其从链表中删除。思路是将
当前节点p的下一个节点设置为删除节点q的下一个节点,使删除节点q从链表中脱离注意,此时该节点空间仍未被释放。 - 最后,将删除节点所占用的数组位置的
used值设置为0,表示该位置已经释放,具有了类似于free的作用。
测试
void appendInsertDeleteTest()
{
// Step 1:Initialize an empty list
ListPtr tempList = initLinkedList();
printList(tempList);
//Step 2:Add some characters
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
printList(tempList);
//Step 3: Delete some characters(the first occurence).
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'x', 1);
printList(tempList);
}// Of appendInsertDeletTest
appendInsertDeleteTest是一个函数,没有参数和返回值。- 在函数中首先创建了一个
空链表tempList,并调用了printList函数打印出该链表。 - 调用
insertElement函数向tempList链表中添加了5个元素('H','e','l','l','o'),然后再次调用printList函数打印出该链表。 - 接着通过调用
deleteElement函数,删除了3个元素('e','a','o'),并输出删除结果。注意,因为该链表中并没有字符’a’,所以无法删除。然后再次调用printList函数打印出该链表。 - 调用
insertElement函数,在链表的第二个位置插入一个元素’x’,并再次调用printList函数打印出该链表。





 文章介绍了静态链表的概念,通过C语言代码展示了如何初始化、插入元素和删除元素。静态链表使用数组实现链式存储结构,通过分配连续内存空间存储节点,并用额外的used数组记录节点使用情况。示例代码包括初始化链表、打印链表、插入元素和删除元素的函数实现。
文章介绍了静态链表的概念,通过C语言代码展示了如何初始化、插入元素和删除元素。静态链表使用数组实现链式存储结构,通过分配连续内存空间存储节点,并用额外的used数组记录节点使用情况。示例代码包括初始化链表、打印链表、插入元素和删除元素的函数实现。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








