list的介绍
1.底层是双向链表,节点主要由三部分构成,节点数据,上一个节点的指针和下一个节点的指针
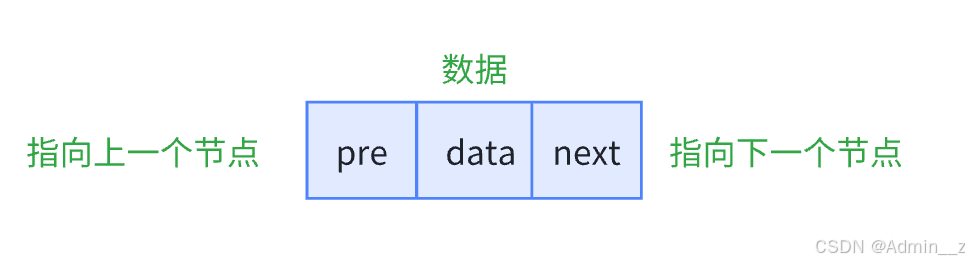
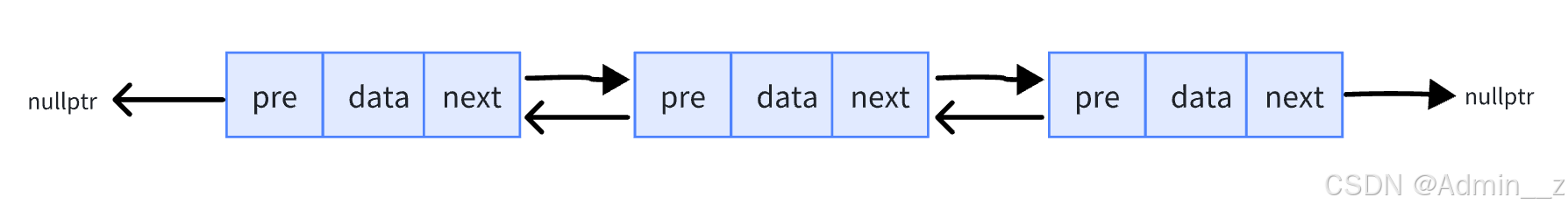
list结构设计
list结构分为三部分:list类,节点类(ListNode),迭代器类(ListIterator)
- list类:成员变量一般只有链表的头结点,成员函数负责初始化,插入删除等功能。
- ListNode类:定义节点的结构
- ListIterator类:封装节点的指针,用来模仿指针的功能,实现*,++等功能
节点类的实现(ListNode)
template <class T>
struct ListNode
{
T _data;
ListNode<T>* _pre;
ListNode<T>* _next;
ListNode(const T& data = T())
{
_data = data;
_pre = _next = nullptr;
}
};
迭代器类的讲解与实现(ListIterator)
讲解
为什么要实现迭代器类
由于链表的数据存储位置是分散的,节点内部需要节点的指针来把数据连接在一起,不能像数组一样直接通过指针解引用来获取数据,所以需要迭代器类对节点的封装,模仿指针的行为
类成员函数的讲解
- *的模拟实现
对指针解引用是为了获取该地址的数据,节点的数据存在节点的_data成员变量中,所以解引用可以通过返回节点的_data值来实现 - ->的模拟实现
->运算符是为了通过指针访问节点的成员变量,所以就需要获取当前节点数据的指针,需要注意的是在使用时,编译器简化成一个->,所以list的->的使用和其他容器无异 - 迭代器++模拟实现
节点中有下一个结点的结点指针,可以通过next指针对当前结点指针的覆盖,完成迭代器的++
注意
类模板参数添加了T的引用和T的指针,这里是为了list类可以根据传不同的参数实例化出iterator类和const_iterator类
实现
template <class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Node* _pnode;
ListIterator(Node* pnode = nullptr)
{
_pnode = pnode;
}
ListIterator(const Self& l )
{
_pnode = l._pnode;
}
T& operator*()
{
return _pnode->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &(operator*());
}
Self operator++()
{
return Self(_pnode->_next);
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp = *this;
_pnode = _pnode->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self operator--()
{
return Self(_pnode->_pre);
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp = this;
this = this->_pnode->_pre;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return _pnode !=l._pnode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return _pnode == l._pnode;
}
};
list类的实现
template <class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
list()
{
_phead = new Node();
_phead->_pre = _phead;
_phead->_next = _phead;
}
void emptyInit()
{
_phead = new Node();
_phead->_pre = _phead;
_phead->_next = _phead;
}
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
emptyInit();
while (n--)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
emptyInit();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
emptyInit();
for (const_iterator it=l.begin();it!=l.end();it++)
{
push_back(*it);
}
}
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l)
{
//clear();
swap(l);
return *this;
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
// List Capacity
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
// List Access
T& front()
{
return *begin();
}
const T& front()const
{
return *begin();
}
T back()
{
return *(--end());
}
const T back()const
{
return *(--end());
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_phead->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_phead);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_phead->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(_phead);
}
void push_back(const T& val)
{
insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& val)
{
insert(begin(), val);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
//// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* pre = pos._pnode->_pre;
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
pre->_next = newnode;
newnode->_pre = pre;
newnode->_next = pos._pnode;
pos._pnode->_pre = newnode;
_size++;
return pos;
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* pre = pos._pnode->_pre;
Node* next = pos._pnode->_next;
if (pre == next)
{
delete pre->_next;
pre->_next = nullptr;
return _phead;
}
pre->_next = next;
next->_pre = pre;
delete pos._pnode;
pos._pnode = nullptr;
_size--;
return next;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it!=end())
{
it=erase(it);
}
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _phead;
_phead = nullptr;
}
void swap(list<T> l)
{
std::swap(_phead, l._phead);
std::swap(_size, l._size);
}
private:
Node* _phead;
size_t _size;
};





















 334
334

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








