05 – 06. Java学习 – 类与对象、封装、ArrayList集合
一、类与对象
一个类里面我们可以定义:
- 成员属性(变量): 描述的是当前事物的公共的属性
- 成员方法: 描述的是当前事物的公共行为
1. 在类里面定义方法
我们在类中定义的都是非静态方法,即不带static关键字
// 例子
public class Employee {
public String name; // 姓名
public int age; // 年龄
public double salary; // 薪水
// 描述员工的基本信息
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println("员工姓名:" + name + " 员工年龄:" + age + " 员工薪水:" + salary);
}
}
2. 方法的调用
需要调用类中的成员函数时,需要创建类对象,通过对象名来调用
// 例子:
public class TestEmployee {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee employee = new Employee();
//给对象的属性赋值
employee.name = "eric";
employee.age = 18;
employee.salary = 2000.0;
//调用方法:如果被调用的方法是一个非静态(static)的方法,通过对象名称调用 对象名.方法名
employee.showInfo();
}
}
方法调用总结:
- 在同一个类的方法内部,在静态方法中是可以直接调用静态方法的
- 在同一个类的方法内部,静态方法中是不能调用非静态方法的,会直接编译报错
- 在同一个类的方法内部,在非静态方法中,可以直接调用静态方法,也可以直接调用非静态的方法
3. static关键字
static关键字是java修饰符中的一种,被其修饰的资源为静态资源。
静态资源和非静态资源的区别是:静态资源的加载时机是早于非静态资源的,JVM在加载类的字节码文件时,首先会将字节码文件进行解析,将静态资源找出来随着字节码文件的加载而加载。且静态资源被所有对象所共享,内存中只有一个副本,当且仅当在类初次加载时会被初始化。
而非静态资源,在对象创建后才会加载。存在多个副本,各个对象拥有的副本互不影响。
二、封装
1. 什么是封装
隐藏事物的实现细节,对外提供公开的访问方式
2. 封装的使用
- 使用priavte关键字修饰成员变量
- 提供操作成员变量的方法:getXX()、setXX()
2.1. private关键字
与public关键字一样,private关键字也是一个访问修饰符,既可以用来修饰方法,也可以用来修饰变量。
但是,被private关键字修饰的资源,只能在自己的类内部使用,外部无法使用被private关键字修饰的资源。(目前这句话是对的,在了解完反射后,这句话就会产生些问题)
// 定义一个类
public class Person {
private String name; // private关键字修饰成员变量
public String address;
public void showInfo(){
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
method1();
}
// private关键字修饰方法
private void method1(){
System.out.println("这是一个私有的方法");
}
}
// 测试类
public class TestPerson {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
// person.name = "AA"; // 编译报错,因为name是private关键字修饰的
person.address = "CHN";
// person.method1(); // 编译报错 因为method1方法是private关键字修饰的
}
}
2.2. this关键字
在类中使用变量的时候,如果一个类中出现了同名的变量(例如一个成员变量、一个局部变量)。此时若在方法内使用变量,java编译器会根据就近原则,使用局部变量,若我们想要指定使用成员变量,就可以使用this关键字
this关键字使用格式:
- this.变量名
- this.方法名
// 例子:this.变量名,this.方法名我们下面在构造函数中举例
public class Person {
private String name;
//提供公有的get、set方法,供外部操作私有成员
public void setName(String name){
// = 号左边的name并不是成员变量的name。因为现在一个类的内部出现了两个同名的name。
// 在使用的时候,就会按照就近原则的方式去使用name
// name = name;
// this.name 指的就是成员变量name
this.name = name;
}
}
3. 构造方法
**构造函数的格式:**
public 类名(参数列表){
//构造方法体
}
注意:构造函数没有返回值,所以我们不需要添加返回值类型,更不需要添加void
3.1. 构造方法的使用
注意:
- 构造函数是可以重载的,在一个类里面可以定义多个构造函数的。
- 如果一个类里面存在多个构造函数,是可以使用this关键字来进行构造函数的调用。注意:只能多参数的构造函数去调用少的参数的构造函数
// 例子:
public class Animal {
private String name;
private String color;
private int age;
public Animal(){
System.out.println("Animal无参数的构造函数执行了.....");
}
public Animal(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public Animal(String name,String color){
//this.name = name;
this(name); // 调用带一个参数的构造函数
this.color = color;
}
public Animal(String name,String color,int age){
//this.name = name;
//this.color = color;
this(name,color); // 调用带两个参数的构造函数
this.age = age;
System.out.println("带3个参数的构造函数执行了.....");
}
}
三、集合 – ArrayList
简单来讲,Java中集合就是替换掉定长数组的一种引用数据类型
集合和数组的区别:
- 长度区别
- 数组:长度固定
- 集合:长度可变
- 内容区别
- 数组:可以存储基本数据类型和引用数据类型
- 集合:存储引用数据类型,基本数据类型会自动装箱拆箱变为引用数据类型(存储的是对象的地址)
- 元素区别
- 数组:只能存储同一种类型成员
- 集合:可以存储不同类型成员(不过一般也只存储同一种类型的数据)
虽然集合分很多种,像单列集合Collection和双列结合Map,单列集合下还分为元素有序且可以重复的List和元素无序且不可重复的Set。
不过在这里我们只会以ArrayList举例,来简单的了解一下集合。
1. ArrayList
ArrayList顾名思义,继承自List接口,其存储的数据是有序的,即元素进去的顺序和元素出来的顺序一样,且在ArrayList中存储的元素是可重复的。
ArrayList可以存储批量的元素,其底层就是一个可变长的Object类型数组。
ArrayList的基本使用:
// 例子:
public class TestArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//构建一个长度为10的Object类型的空数组。存储数据类型是任意的
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
list.add(3.14); //向集合中添加元素
list.add("hello");
list.add(100);
list.add(true);
//如果我们要指定集合存储元素的数据类型 <String> 指定集合存储的数据类型是String
ArrayList<String> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
list1.add("hadoop");
list1.add("java");
list1.add("spring");
/**
* 在集合中存储整型的数据
* 注意:<int> 是不对的,因为泛型里面只能指定引用数据类型
*/
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
}
}
2. 泛型
在上面ArrayList的例子中,我们能看到在ArrayList类型后会有一个被“<>”括起来的引用类型,这种形式其实就是对泛型的实现。
那么什么是泛型?
泛型,即“参数化类型”,其本质是为了将类型参数化。
其实我们可以将泛型与方法的参数列表类比去理解,在ArrayList类内部,可以看到其类名的写法是ArrayList< E >

这个< E >其实就相当于方法的形参,而我们创建ArrayList对象时所传入的引用参数类型< Integer >,就相当于方法的实参。

泛型的目的也和参数列表类似,约束传入数据的数据类型,如果数据类型不匹配,编译器就直接报错。
例如,我们设定了一个泛型为< String >的ArrayList,当我们向其中添加类型为Integer的数据时,编译器就会报错。
// 例子:
@Test
public void test02(){
ArrayList<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("aaa");
list.add("bbb");
list.add("ccc");
// list.add(111); 编译直接报错
}
2.1. 泛型的继承
在Java多态中,我们可以使用父类引用装载子类对象,也叫向上转型。
那么我们能不能再泛型中也实现多态呢?
- ArrayList< T > 泛型集合中,传入 < T > 中的数据类型相同时
// 例子:
@Test
public void test03(){
// 可以向上转型,但泛型传入的类型必须相同
List<String> list01=new ArrayList<String>(); // 可以
// List<String> list02=new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 编译器报错
}
那么,如果我们在<>之间使用向上转型可行吗?也就是说将ArrayList< Integer >对象赋给List< Number >变量可行吗?
@Test
public void test04(){
// List<Number> list01 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 编译报错
// ArrayList<Number> list02 = new ArrayList<Integer>(); // 编译报错
}
实际并不可行,编译器会报错,说明在一般泛型中,不能向上转型。
原例子的原因是说:
- 当一个 ArrayList< Integer > 向上转型为 ArrayList< Number > 类型后,这个 ArrayList< Number > 集合就可以接收其他继承自Number的子类对象。
- 但是,ArrayList< Number > 实际上和 ArrayList< Integer > 是同一个集合,而在泛型的定义中, ArrayList< Integer > 集合是不可以接收其他类型对象的。这是因为,在使用 get() 方法获取集合元素的时候,编译器会自动将其他类型对象强转成 Integer 对象,而这会产生 ClassCastException 异常。
但是由于在IDEA泛型向上转型会直接报错,这个例子我就没办法复现了。总而言之就是, ArrayList< Integer > 和 ArrayList< Number > 两者之间没有继承关系。
不过,如果你需要泛型能够处理某一类型范围内的类型参数,比如某个泛型类和它的子类。你可以使用泛型通配符,但是这里就不做赘述了。
3. 基本数据类型的包装类
由于集合中只能存储引用数据类型。所以我们需要了解基本数据类型对应的引用数据类型,即基本数据类型的包装类。
八大基本数据类型的包装类概览:
| 基本数据类型 | 包装数据类型 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
4. 装箱拆箱
装箱:将基本数据类型转换成包装类型。比如将int数据类型转换成Integer数据类型。
拆箱:将包装数据类型转换成基本数据类型。比如Integer转换成int。
4.1. 装箱
以Integer为例,演示手动装箱和自动装箱的方法:
// 例子:
@Test
public void test06() {
// 手动装箱
int num = 100;
// 手动装箱
Integer integer01 = new Integer(num);
// 手动装箱:valueOf将int型转换成Integer型
Integer integer02 = Integer.valueOf(num);
System.out.println(integer01);
System.out.println(integer02);
// 自动装箱:jdk5之后,提供了自动装箱的方法(在底层依旧调用了valueOf)
Integer integer03 = 100;
System.out.println(integer03);
}
了解完装箱,下面来看一个Integer的例子:
@Test
public void test07() {
Integer i1 = 127;
Integer i2 = 127;
System.out.println(i1 == i2); // true
Integer i3 = 128;
Integer i4 = 128;
System.out.println(i3 == i4); // false
Integer k1 = new Integer(100);
Integer k2 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(k1 == k2); // false
}
这个结果好像有点奇怪,按道理说Integer作为一个引用类型,两个Integer类型变量比较的应该是其值在内存中的地址,为什么会出现127地址为true,而128地址为false的情况呢?
要了解这个问题,我们可以来分析一下“Integer = 值”,这种这种赋值方式的原理。
这种赋值方式底层其实还是调用的valueOf方法,进入Integer类内部可以看到valueOf方法的源码:
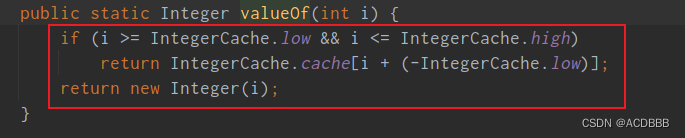
而low和high的值为:
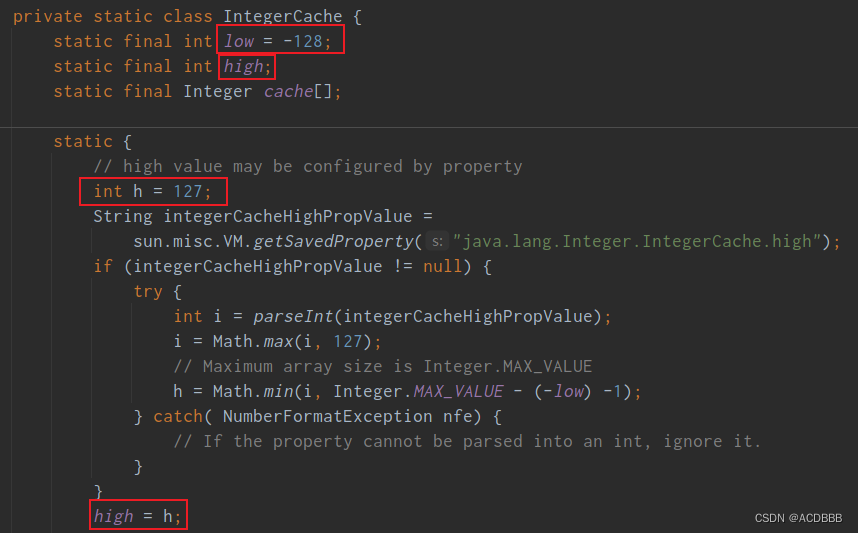
通过源码观察可知,如果数据的范围是-128~127之间,创建对象之后,之间将其丢在缓存中,下一次创建的时候,查看缓存中是否存在,如果存在就直接引用即可。如果超过了这个范围。对象直接在堆内存中创建。
于是,上面例子的内存表现应该是:
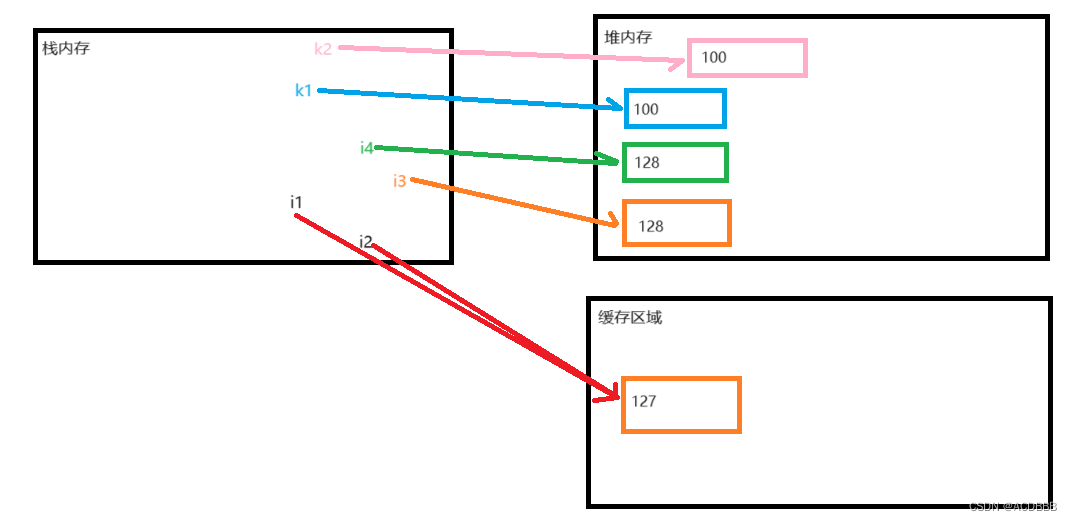
由于用new关键字创建的对象会直接在堆内存中开辟一块空间存储,因此即便100在范围内,地址也不会相等。
扩展:字符串的创建方式(与Integer相似)
@Test
public void test08() {
String str1 = "hello";
String str2 = "hello";
String str3 = new String("hello");
String str4 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(str1 == str2); // true
System.out.println(str2 == str3); // false
System.out.println(str3 == str4); // false
System.out.println(str3.equals(str4)); // true
}
字符串创建的方式也有两种,一种是直接赋值,一种是使用new关键字进行创建。
直接赋值创建的原理: 首先会在字符串常量池中检查是否存在一个内容为hello的字符串对象,如果没有就直接创建。如果存在就不再创建,而是直接取引用已经存在的字符串对象。
使用new关键字创建原理:在堆内存中开辟一块内存空间存放字符串对象。不管字符串的内容是否一样,都要重新创建。
4.2. 拆箱
以Integer为例,演示自动拆箱和手动拆箱
@Test
public void test09(){
// 手动拆箱示例
Integer integerValue01 = 10;
int intValue01 = integerValue01.intValue(); // 使用intValue()方法进行拆箱
// 自动拆箱示例
Integer integerValue02 = 10;
int intValue02 = integerValue02; // 自动拆箱
}
4.3. 字符串转换成基本数据类型
// 例子:
@Test
public void test10(){
String str = "100";
// "100" --> 100
int i = Integer.parseInt(str); //将字符串类型的数字转换成int类型的数字
System.out.println(i);
byte b = Byte.parseByte("20"); // 将字符串转换成byte字节
System.out.println(b);
short s = Short.parseShort("60");
System.out.println(s);
long l = Long.parseLong("11211");
System.out.println(l);
float f = Float.parseFloat("66.66F");
System.out.println(f);
double d = Double.parseDouble("666.666");
System.out.println(d);
boolean flag = Boolean.parseBoolean("true");
System.out.println(flag);
}
字符串转换成char比较特殊,转换的方式有两种:
- 转换功能的方法 —— char[] toCharArray() : 将字符串转换成字符数组
- 获取功能的方法 —— char charAt(int index) : 获取指定索引位置的字符
@Test
public void test11(){
// 字符串转换成字符
String message = "hello,world";
char[] chars = message.toCharArray(); // 将字符串转换成字符数组
for(char c : chars){
System.out.print(c + "\t");
}
char first_char = message.charAt(0); // 获取指定位置上的字符
System.out.println(first_char);
}
4.4. 包装类型转换成字符串
以Integer转换成String为例:
@Test
public void test12(){
// 包装类型转换成String
Integer num3 = 200;
String str1 = num3 + ""; // 任何数字和字符串进行运算都会变成一个字符串。
System.out.println(str1);
String str2 = String.valueOf(num3);// Integer转换成String
System.out.println(str2);
String str3 = num3.toString();// toString方法在使用的时候,一定要注意不要出现空对象去调用toString方法
System.out.println(str3);
}
5. 八大包装类型常用方法
5.1. Byte类型
@Test
public void byteTest(){
//演示 : Byte类常用方法
//1. byte byteValue(): 返回当前Byte类对象对应的值,以byte类型作接收。
Byte b = 127; //自动装箱
byte bB = b.byteValue();
System.out.println("byte类型变量bB = " + bB);
//2. static int compare(byte x, byte y): 比较两个byte变量的值, 返回值为前面byte变量的值减去后面byte变量的值。
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
byte temp_b_0 = 5;
byte temp_b_1 = 1;
int i = Byte.compare(temp_b_0, temp_b_1);
System.out.println("temp_b_0 - temp_b_1 = " + i);
//3. int compareTo(Byte anotherByte): 比较两个Byte类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Byte temp_B_0 = 55;
Byte temp_B_1 = 11;
int i1 = temp_B_0.compareTo(temp_B_1);
System.out.println("temp_B_0 - temp_B_1 = " + i1);
//4. double doubleValue(): 与方法1同理
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
double bb1 = b.doubleValue();
System.out.println("double类型变量bb1 = " + bb1);
//5. int intValue(): 与方法1同理
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
int bb2 = b.intValue();
System.out.println("int类型变量bb2 = " + bb2);
//6. static int parseByte(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> byte类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
byte temp_b_2 = Byte.parseByte("1");
System.out.println("byte类型变量temp_b_2 = " + temp_b_2);
//7. String toString(): 将当前Byte对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Byte temp_B_2 = 127;
String string_0 = temp_B_2.toString();
System.out.println("Byte类型对象temp_B_2的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//8. static String toString(byte b): 将指定的byte值转换为String对象
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
byte temp_b_3 = 2;
String string_1 = Byte.toString(temp_b_3);
System.out.println("byte类型变量temp_b_3的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//9. static Byte valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> Byte类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Byte temp_B_3 = Byte.valueOf("11");
System.out.println("Byte类型对象temp_B_3的值 = " + temp_B_3);
}
5.2. Short类
@Test
public void shortTest(){
// 演示:Short类常用方法
//1. short shortValue(): 返回当前Short对象的值,以short基本类型作接收。
Short temp_S_0 = 128; //自动装箱
short temp_s_0 = temp_S_0.shortValue();
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_0 = " + temp_s_0);
// int intValue()
// double doubleValue()
//......等等同方法1格式一样的方法,用法原理与方法1相同.
//2. static int compare(short x, short y): 比较两个short变量的值, 返回值为前面short变量的值减去后面short变量的值。
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
short temp_s_1 = 6;
short temp_s_2 = 3;
int i = Short.compare(temp_s_1, temp_s_2);
System.out.println("temp_s_1 - temp_s_2 = " + i);
//3. int compareTo(Short anotherShort): 比较两个Short类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Short temp_S_1 = 66;
Short temp_S_2 = 33;
int i1 = temp_S_1.compareTo(temp_S_2);
System.out.println("temp_S_1 - temp_S_2 = " + i1);
//4. static int parseShort(String xxx) : 字符串类型 ——> short基本类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
short temp_s_3 = Short.parseShort("128");
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_3 = " + temp_s_3);
//5. String toString(): 将当前Short对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Short temp_S_3 = 1277;
String string_0 = temp_S_3.toString();
System.out.println("Short类型对象temp_S_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//6. static String toString(short s): 将指定的short值转换为String对象
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
short temp_s_4 = 2;
String string_1 = Short.toString(temp_s_4);
System.out.println("short类型变量temp_s_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//7. static Short valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> Short类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Short temp_S_4 = Short.valueOf("1111");
System.out.println("Short类型对象temp_S_4的值 = " + temp_S_4);
}
5.3. Integer类
@Test
public void IntegerTest() {
// 演示: Integer类常用方法
//1. int intValue(): 返回当前Integer对象的值,以int基本类型作接收。
Integer temp_I_0 = 1280; //自动装箱
int temp_i_0 = temp_I_0.intValue();
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_0 = " + temp_i_0);
//2. static int compare(int x, int y): 比较两个int变量的值。如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
int temp_i_1 = 7;
int temp_i_2 = 11;
int i = Integer.compare(temp_i_1, temp_i_2);
System.out.println("temp_i_1和temp_i_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
//3. int compareTo(Integer anotherInteger): 比较两个Integer类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Integer temp_I_1 = 77;
Integer temp_I_2 = 11;
int i1 = temp_I_1.compareTo(temp_I_2);
System.out.println("temp_I_1和temp_I_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
//4. static int parseInt(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> int基本类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
int temp_i_3 = Integer.parseInt("4444");
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_3 = " + temp_i_3);
//5. String toString(): 将当前Integer对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Integer temp_I_3 = 11217;
String string_0 = temp_I_3.toString();
System.out.println("Integer类型对象temp_I_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//6. static String toString(int s): 将指定的int值转换为String对象
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
int temp_i_4 = 111111;
String string_1 = Integer.toString(temp_i_4);
System.out.println("int类型变量temp_i_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//7. static Integer valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> Integer类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Integer temp_I_4 = Integer.valueOf("1111");
System.out.println("Integer类型对象temp_I_4的值 = " + temp_I_4);
//8. static int max(int x, int y) 和 min(int x, int y): 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("100和101哪个数更大?" + Integer.max(100, 101));
System.out.println("200和201哪个数更小?" + Integer.min(200, 201));
//9. static int sum(int x, int y): 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("100 + 201 = " + Integer.sum(100, 201));
}
5.4. Long类
@Test
public void LongTest() {
// 演示: Long类常用方法
//1. long longValue(): 返回当前Long对象的值,以long基本类型作接收。
Long temp_L_0 = 2224L; //自动装箱
long temp_l_0 = temp_L_0.longValue();
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_0 = " + temp_l_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//2. static int compare(long x, long y): 比较两个long变量的值. 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
long temp_l_1 = 222L;
long temp_l_2 = 111L;
int i = Long.compare(temp_l_1, temp_l_2);
System.out.println("temp_l_1和temp_l_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//3. int compareTo(Long anotherLong): 比较两个Long类对象的值,返回值同方法2
Long temp_L_1 = 773L;
Long temp_L_2 = 113L;
int i1 = temp_L_1.compareTo(temp_L_2);
System.out.println("temp_L_1和temp_L_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//4. static long parseLong(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> long基本类型
long temp_l_3 = Long.parseLong("35252");
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_3 = " + temp_l_3);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//5. String toString(): 将当前Long对象的值转换为String类型
Long temp_L_3 = 11217L;
String string_0 = temp_L_3.toString();
System.out.println("Long类型对象temp_L_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//6. static String toString(long l): 将指定的long值转换为String对象
long temp_l_4 = 222222;
String string_1 = Long.toString(temp_l_4);
System.out.println("long类型变量temp_l_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//7. static Long valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> Long类型
Long temp_L_4 = Long.valueOf("111241");
System.out.println("Long类型对象temp_L_4的值 = " + temp_L_4);
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//8. static long max(long x, long y) 和 min(long x, long y): 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("10000和10100哪个数更大?" + Long.max(10000, 10100));
System.out.println("20000和20100哪个数更小?" + Long.min(20000, 20100));
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
//9. static long sum(long x, long y): 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("11111111 + 8888889 = " + Long.sum(11111111, 8888889));
}
5.5. Character类
@Test
public void charTest() {
//演示: Character类常用方法
//1. 装箱拆箱: valueOf() 和 charValue()
Character character_0 = Character.valueOf('S');
char char_0 = character_0.charValue();
System.out.println("Character类对象character_0的字符是:" + character_0);
System.out.println("char基本类型变量char_0 = " + char_0);
//2. static int compare(char x, char y): 返回前面字符ASCII码值 - 后面字符ASCII值的int类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
int i1 = Character.compare('A', 'F');
System.out.println("ASCII码值'A' - 'F' = " + i1);
//3. int compareTo(Character anotherCharacter): 比较两个Character类对象的字符,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Character character_1 = 'a'; //自动装箱
Character character_2 = 'd';
int i2 = character_1.compareTo(character_2);
System.out.println("character_1 - character_2 = " + i2);
//4. static boolean isDigit(char c1): 判断该字符是不是数字
//5. static boolean isLetter(char c2): 判断该字符是不是字母
//6. static boolean isUpperCase(char c3): 判断该字符是不是大写形式
//7. static boolean isLowerCase(char c4): 判断该字符是不是小写形式
//8. static boolean isWhitespace(char c5): 判断该字符是不是空格
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是数字 : " + Character.isDigit('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是字母 : " + Character.isLetter('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是大写形式 : " + Character.isUpperCase('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是小写形式 : " + Character.isLowerCase('A'));
System.out.println("\'A\'是不是空格 : " + Character.isWhitespace('A'));
//9. static char toUpperCase(char c): 将该字符转换为大写形式,以char类型作接收
//10. static char toLowerCase(char c): 将该字符转换为小写形式,以char类型作接收
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
char c1 = Character.toUpperCase('n');
char c2 = Character.toLowerCase('B');
System.out.println("\'n\'字符的大写形式为:" + c1);
System.out.println("\'B\'字符的小写形式为:" + c2);
}
5.6. Float类
@Test
public void floatTest() {
//演示: Float类常用方法
//1. float floatValue(): 返回当前Float对象的值,以float基本类型作接收。
Float temp_F_0 = 1024.11F; //自动装箱
float temp_f_0 = temp_F_0.floatValue();
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_0 = " + temp_f_0);
//2. static int compare(float x, float y): 比较两个float变量的值, 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
float temp_f_1 = 222.11F;
float temp_f_2 = 222.11F;
int i = Float.compare(temp_f_1, temp_f_2);
System.out.println("temp_f_1和temp_f_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
//3. int compareTo(Float anotherFloat): 比较两个Float类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Float temp_F_1 = 222.11F;
Float temp_F_2 = 123.11F;
int i1 = temp_F_1.compareTo(temp_F_2);
System.out.println("temp_F_1和temp_F_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
//4. static float parseFloat(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> float基本类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
float temp_f_3 = Float.parseFloat("35252.11125");
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_3 = " + temp_f_3);
//5. String toString(): 将当前Float对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Float temp_F_3 = 12144217.12F;
String string_0 = temp_F_3.toString();
System.out.println("Float类型对象temp_F_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//6. static String toString(float f): 将指定的float值转换为String对象
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
float temp_f_4 = 222222.11F;
String string_1 = Float.toString(temp_f_4);
System.out.println("float类型变量temp_f_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//7. static float valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> float类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Float temp_F_4 = Float.valueOf("111241.1235");
System.out.println("Float类型对象temp_F_4的值 = " + temp_F_4);
//8. static float max(float x, float y) 和 min(float x, float y): 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("10000.00 和 10100.11谁更大?" + Float.max(10000.00F, 10100.11F));
System.out.println("200.00 和 201.88谁更小?" + Float.min(200.00F, 201.88F));
//9. static float sum(float x, float y): 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("11111.11 + 8889.022 = " + Float.sum(11111.11F, 8889.022F));
}
5.7. Double类
@Test
public void doubleTest() {
//演示: Double类常用方法
//1. double doubleValue(): 返回当前Double对象的值,以double基本类型作接收。
Double temp_D_0 = 1024.5; //自动装箱
double temp_d_0 = temp_D_0.doubleValue();
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_0 = " + temp_d_0);
//2. static int compare(double x, double y): 比较两个double变量的值, 如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0。
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
double temp_d_1 = 888.88;
double temp_d_2 = 888.88;
int i = Double.compare(temp_d_1, temp_d_2);
System.out.println("temp_d_1和temp_d_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i);
//3. int compareTo(Double anotherDouble): 比较两个Double类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Double temp_D_1 = 123.1234;
Double temp_D_2 = 1234.123;
int i1 = temp_D_1.compareTo(temp_D_2);
System.out.println("temp_D_1和temp_D_2,如果前一个数大,返回1;如果前一个数小,返回-1;相等则返回0 : " + i1);
//4. static double parseDouble(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> double基本类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
double temp_d_3 = Double.parseDouble("35252.11125");
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_3 = " + temp_d_3);
//5. String toString(): 将当前Float对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Double temp_D_3 = 3333144217.12;
String string_0 = temp_D_3.toString();
System.out.println("Double类型对象temp_D_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//6. static String toString(double f): 将指定的double值转换为String对象
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
double temp_d_4 = 233.333333333;
String string_1 = Double.toString(temp_d_4);
System.out.println("double类型变量temp_d_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//7. static double valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> double类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Double temp_D_4 = Double.valueOf("66666.1235");
System.out.println("Double类型对象temp_D_4的值 = " + temp_D_4);
//8. static double max(double x, double y) 和 min(double x, double y): 获取两个数中的最大值和最小值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("134.23 和 111.11, 哪个数更大?" + Double.max(134.23, 111.11));
System.out.println("222.111 和 111.222, 哪个数更小?" + Double.min(222.111, 111.222));
//9. static double sum(double x, double y): 返回(x + y)的值
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
System.out.println("11111.11 + 8889.022 = " + Double.sum(11111.11, 8889.022));
}
5.8. Boolean类
@Test
public void booleanTest() {
//演示: Boolean类常用方法
//1. boolean booleanValue(): 返回当前Boolean对象的值,以boolean基本类型作接收。
Boolean temp_B_0 = true; //自动装箱
boolean temp_b_0 = temp_B_0.booleanValue();
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_0 = " + temp_b_0);
//2. static int compare(boolean x, boolean y): 比较两个boolean变量的值,两个变量真值相同返回0。否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1.
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
boolean temp_b_1 = false;
boolean temp_b_2 = true;
int i = Boolean.compare(temp_b_1, temp_b_2);
int ii = Boolean.compare(temp_b_2, temp_b_1);
int iii = Boolean.compare(temp_b_2, temp_b_2);
System.out.println("temp_b_1和temp_b_2, 两个真值相同返回1;否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + i);
System.out.println("temp_b_2和temp_b_1, 两个真值相同返回1;否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + ii);
System.out.println("temp_b_2和temp_b_2, 两个真值相同返回1;否则返回值取决于传入第一个boolean变量的真值,true返回1,false返回-1 : " + iii);
//3. int compareTo(Boolean anotherBoolean): 比较两个Boolean类对象的值,返回值同方法2
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Boolean temp_B_1 = false;
Boolean temp_B_2 = false;
int i1 = temp_B_1.compareTo(temp_B_2);
System.out.println("temp_B_1和temp_B_2的真值情况是 : " + i1);
//4. static int parseBoolean(String xxx): 字符串类型 ——> boolean基本类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
boolean temp_b_3 = Boolean.parseBoolean("666");
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_3 = " + temp_b_3);
//5. String toString(): 将当前Boolean对象的值转换为String类型
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
Boolean temp_B_3 = false;
String string_0 = temp_B_3.toString();
System.out.println("Boolean类型对象temp_B_3的字符串形式为:" + string_0);
//6. static String toString(boolean s): 将指定的boolean值转换为String对象
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
boolean temp_b_4 = true;
String string_1 = Boolean.toString(temp_b_4);
System.out.println("boolean类型变量temp_b_4的字符串形式为:" + string_1);
//7. static Short valueOf(...): 字符串类型 ——> Boolean类型
System.out.println("----------------------------------");
Boolean temp_B_4 = Boolean.valueOf("false");
System.out.println("Boolean类型对象temp_B_4的值 = " + temp_B_4);
}
6. 集合的常用方法
- add(E e): 将指定的元素添加到集合中的末尾处
@Test
public void test01(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(111);
list.add(222);
list.add(333);
list.add(444);
list.add(555);
}
- get(int index): 根据指定的下标获取集合中的元素
@Test
public void test02(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(111);
list.add(222);
list.add(333);
list.add(444);
list.add(555);
System.out.println(list.get(3)); // 444
}
- size(): 描述集合中元素的个数
@Test
public void test03(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(111);
list.add(222);
list.add(333);
list.add(444);
list.add(555);
System.out.println(list.get(3)); // 444
System.out.println(list.size()); // 5
}
- remove(int index): 根据指定的下标删除集合中的元素,并返回
@Test
public void test04(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(111);
list.add(222);
list.add(333);
list.add(444);
list.add(555);
System.out.println(list.get(3)); // 444
System.out.println(list.size()); // 5
System.out.println(list.remove(4)); // 555
System.out.println(list.size()); // 4
}
- clear(): 清空集合中的所有元素
@Test
public void test05(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(111);
list.add(222);
list.add(333);
list.add(444);
list.add(555);
System.out.println(list.get(3)); // 444
System.out.println(list.size()); // 5
System.out.println(list.remove(4)); // 555
System.out.println(list.size()); // 4
list.clear();
System.out.println(list.size()); // 0
}
- addAll(Collection<? extends E> c): 将一个集合中的所有元素追加到另外一个集合的尾部
@Test
public void test06(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list02.add(1111);
list02.add(2222);
list02.add(3333);
list02.add(4444);
list02.add(5555);
System.out.println(list01.addAll(list02)); // true
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 333, 444, 555, 1111, 2222, 3333, 4444, 5555]
}
- Object[] toArray():将集合转换成数组
@Test
public void test07(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
Object[] objects = list01.toArray(); //将集合转换成数组
for(Object o : objects){
System.out.println(o);
}
}
- set(int index, E element):将指定下标的元素修改成新的元素
@Test
public void test08(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
Integer set = list01.set(5, 111);
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 111]
}
- int indexOf(Object o):获取指定元素在集合中第一次出现的下标
@Test
public void test09(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
Integer set = list01.set(5, 111);
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 111]
System.out.println(list01.indexOf(333)); // 2
}
- lastIndexOf(Object o):获取指定元素在集合中最后一次出现的下标
@Test
public void test10(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
Integer set = list01.set(5, 111);
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 111]
System.out.println(list01.indexOf(333)); // 2
System.out.println(list01.lastIndexOf(111)); // 5
}
- isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
@Test
public void test11(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
System.out.println(list01.isEmpty()); // false
System.out.println(list02.isEmpty()); // true
}
- boolean contains(Object o):判断集合是否包含指定的元素,包含返回true,不包含返回false
@Test
public void test12(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
System.out.println(list01.isEmpty()); // false
System.out.println(list02.isEmpty()); // true
System.out.println(list01.contains(666)); // false
System.out.println(list01.contains(111)); // true
}
- retainAll(Collection<?> c):取两个集合的交集
@Test
public void test13(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list02.add(1111);
list02.add(111);
list02.add(2222);
System.out.println(list01.retainAll(list02)); // true
System.out.println(list01); // [111]
}
- iterator(): 迭代器,遍历集合中的元素
- listIterator(集合的长度):逆序迭代器
@Test
public void test14(){
ArrayList<String> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add("111");
list01.add("222");
list01.add("333");
Iterator<String> iterator = list01.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
String value = iterator.next();
System.out.println(value);
}
// 逆序迭代器
ListIterator<String> listIterator = list01.listIterator(list01.size());
while (listIterator.hasPrevious()){
String previous = listIterator.previous();
System.out.println(previous);
}
}
- sort(Comparator<? super E> c): 集合排序
@Test
public void test15(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(111);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(555);
System.out.println(list01); // [333, 444, 222, 111, 333, 555]
list01.sort(new MyComparator());
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 555]
}
// 定义比较器的实现类
class MyComparator implements Comparator<Integer> {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o1 - o2; //升序
// return o2 - o1; //降序
}
}
- clone(): 克隆拷贝
@Test
public void test16(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list02.add(333);
list02.add(444);
ArrayList<Integer> clone = (ArrayList<Integer>)list01.clone();
System.out.println(clone); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 555]
}
- removeAll(Collection<?> c): 批量删除元素
@Test
public void test17(){
ArrayList<Integer> list01 = new ArrayList<>();
list01.add(111);
list01.add(222);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(333);
list01.add(444);
list01.add(555);
ArrayList<Integer> list02 = new ArrayList<>();
list02.add(333);
list02.add(444);
ArrayList<Integer> clone = (ArrayList<Integer>)list01.clone();
System.out.println(clone); // [111, 222, 333, 333, 444, 555]
System.out.println(list01.removeAll(list02)); // true
System.out.println(list01); // [111, 222, 555]
}
- subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex):截取集合
@Test
public void test18(){
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(111,222,333,444));
list.add(555);
System.out.println(list);
// 根据指定区间截取一个子集合
List<Integer> subList = list.subList(0, 3); // 区间范围遵循前闭后开的原则[0,3)
System.out.println(subList); // [111, 222, 333]
}






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








