1、面向对象编程(oop)思想

![]()
面向过程,就是按照我们分析好的步骤,按照步骤解决问题。
面向对象是以功能来划分问题,而不是步骤。


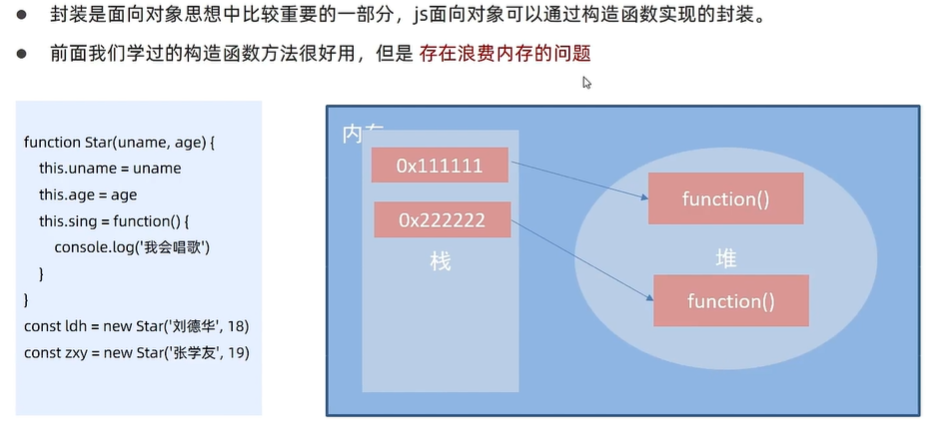
2、构造函数
3、原型
1)原型

<script>
// function Star(uname, age) {
// this.uname = uname
// this.age = age
// this.sing = function () {
// console.log('唱歌')
// }
// }
// const peo1 = new Star('张三', 18)
// const peo2 = new Star('李四', 18)
// console.log(peo1.sing === peo2.sing); // false
function Star(uname, age) {
this.uname = uname
this.age = age
// this.sing = function () {
// console.log('唱歌')
// }
}
Star.prototype.sing = function () {
console.log('唱歌')
}
const peo1 = new Star('张三', 18)
const peo2 = new Star('李四', 18)
peo1.sing()
peo2.sing()
console.log(peo1.sing === peo2.sing); // true
</script>

<script>
let that
function Star(uname, age) {
// that = this
// console.log(that)
this.uname = uname
this.age = age
}
// 原型对象里面的函数 this 指向的还是实例对象 peo
Star.prototype.sing = function () {
that = this
console.log('唱歌')
}
// 构造函数里面的 this 就是实例对象 peo
const peo = new Star('张三', 18)
peo.sing()
console.log(that === peo); // true
</script>
例子:给数组扩展方法
<script>
// 给数组扩展求最大值方法和求和方法
// 最大值
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
Array.prototype.max = function () {
// 展开运算符
return Math.max(...this)
// this 指向实例对象
}
console.log(arr.max()) // 3
// 求和方法
Array.prototype.sum = function () {
return this.reduce((prev, item) => prev + item, 0)
}
console.log(arr.sum()) //6
console.log([11, 22, 33].sum()) // 66
</script>
2)constructor属性
每个原型对象里面都有个constructor属性(constructor构造函数)
作用:该属性指向该原型对象的构造函数

<script>
function hs() { }
const res = new hs()
console.log(hs.prototype)
console.log(hs.prototype.constructor === hs) // true
</script>

<script>
function hs() { }
// hs.prototype.name = function () {
// console.log('张三')
// }
// hs.prototype.age = function () {
// console.log(18)
// }
console.log(hs.prototype) // 有constructor
hs.prototype = {
// 重新指回这个原型对象的构造函数
constructor: hs,
name: function () {
console.log('张三')
},
age: function () {
console.log(18)
}
}
console.log(hs.prototype) // 如果不加 constructor: hs 无constructor,不清楚原型对象了
</script>
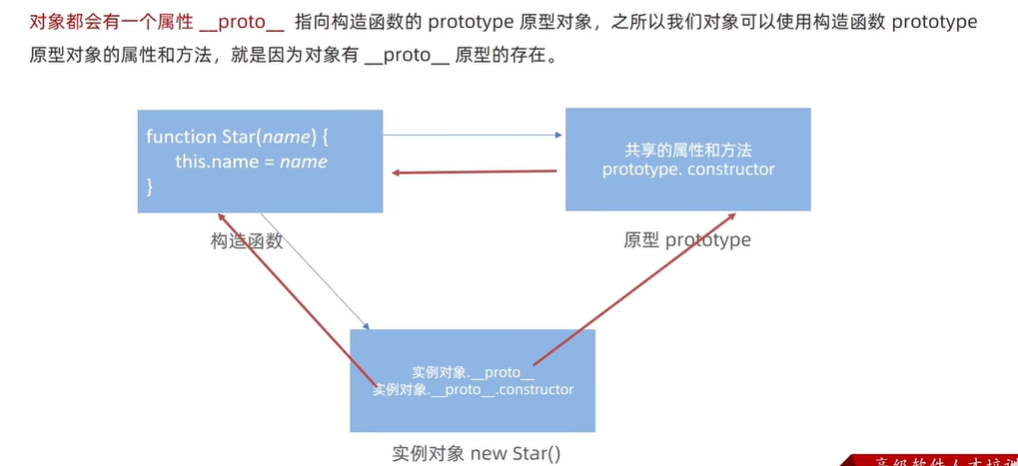
3)对象原型 __proto__

<script>
function hs() { }
const res = new hs()
console.log(res)
// 对象原型 __proto__ 指向该构造函数的原型对象
console.log(res.__proto__ === hs.prototype) // true
// 对象原型里面有 constructor 指向 构造函数 hs
console.log(res.__proto__.constructor === hs.prototype.constructor) // true
console.log(res.__proto__.constructor === hs) // true
</script>
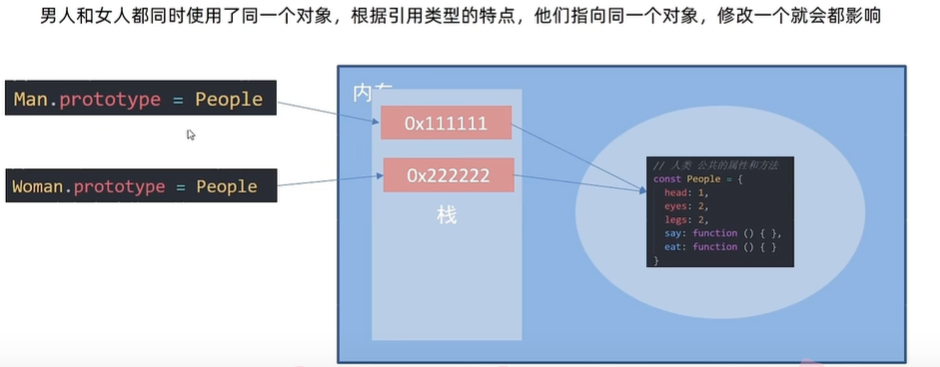
4)原型继承
<script>
// 公共部分放到原型上
// const hs = {
// eyes: 2,
// head: 1
// }
// 构造函数 new 出来的对象 结构一样,但是对象不一样
function hs() {
this.eyes = 2
this.head = 1
}
// hx构造函数 想继承hs
function hx() {
}
// hx通过原型来继承hs
// 子类的原型 = new 父类
hx.prototype = new hs()
// 指回原来的构造函数
hx.prototype.constructor = hs
hx.prototype.name = function () {
console.log('abc')
}
const res = new hx()
console.log(res)
// hy构造函数 想继承hs
function hy() {
}
// 通过原型来继承hs
hy.prototype = new hs()
// 指回原来的构造函数
hy.prototype.constructor = hy
const cnt = new hy()
console.log(cnt)
</script>
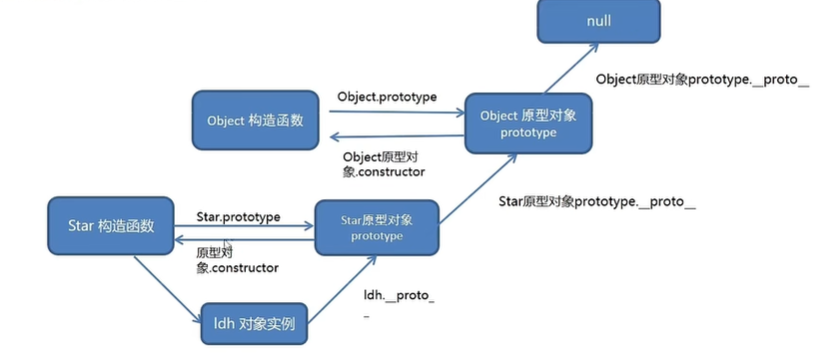
5)原型链
__proto__串起来的链
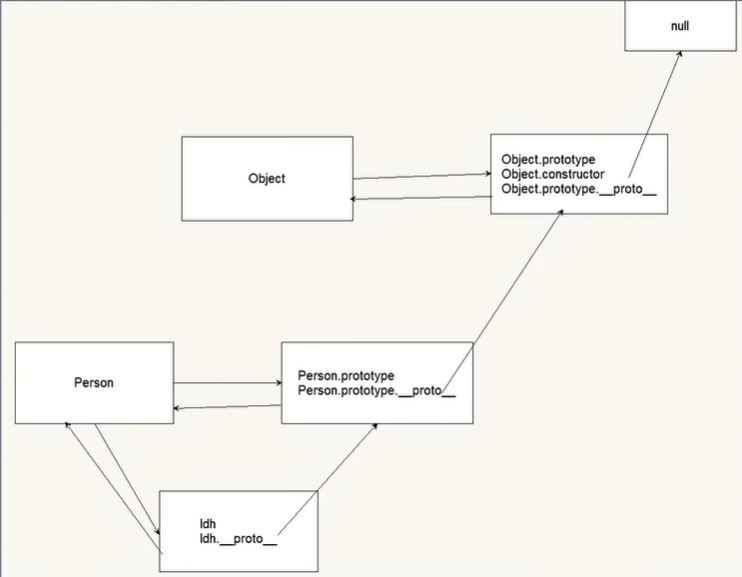
<script>
console.log(Object)
console.log(Object.prototype)
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__) // 指向 null
function peo() {
}
const res = new peo()
// console.log(res.__proto__ === peo.prototype) // true
console.log(peo.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true
</script>

instanceof 作用
<script>
console.log(Object)
console.log(Object.prototype)
console.log(Object.prototype.__proto__) // 指向 null
function peo() {
}
const res = new peo()
// console.log(res.__proto__ === peo.prototype) // true
console.log(peo.prototype.__proto__ === Object.prototype) // true
console.log(res instanceof peo) // true
console.log(res instanceof Object) // true
console.log(res instanceof Array) // false
console.log([1, 2, 3] instanceof Array) // true
console.log(Array instanceof Object) // true
</script>
4、案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>面向对象封装消息提示</title>
<style>
.modal {
width: 300px;
min-height: 100px;
box-shadow: 0 0 10px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
border-radius: 4px;
position: fixed;
z-index: 999;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate3d(-50%, -50%, 0);
background-color: #fff;
}
.modal .header {
line-height: 40px;
padding: 0 10px;
position: relative;
font-size: 20px;
}
.modal .header i {
font-style: normal;
color: #999;
position: absolute;
right: 15px;
top: -2px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.modal .body {
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
}
.modal .footer {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
padding: 10px;
}
.modal .footer a {
padding: 3px 8px;
background: #ccc;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 2px;
margin-right: 10px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.modal .footer a.submit {
background-color: #369;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="delete">删除</button>
<button id="login">登录</button>
<!-- <div class="modal">
<div class="header">温馨提示 <i>x</i></div>
<div class="body">您没有删除权限操作</div>
</div> -->
<script>
// 模态框
function Modal(title = '', message = '') {
// 创建modal 模态框盒子
// 创建div标签
this.modalBox = document.createElement('div')
// 给div标签添加类名为modal
this.modalBox.className = 'modal'
// modal盒子内部填充2个div标签并且修改文字内容
this.modalBox.innerHTML = `
<div class="header">${title} <i>x</i></div>
<div class="body">${message}</div>
`
console.log(this.modalBox)
}
// new Modal('温馨提示', '你没有权限删除')
// new Modal('友情提示', '你还没有注册账号')
Modal.prototype.open = function () {
// 先判断页面中是否有modal盒子
const box = document.querySelector('.modal')
box && box.remove()
// 注意这个方法不要用箭头函数 因为我们需要用到 this
// 把刚才创建的modalBox 显示到页面body中
document.body.append(this.modalBox)
// 盒子显示后,可以绑定点击事件
this.modalBox.querySelector('i').addEventListener('click', () => {
// 这个this指向实例对象
this.close()
})
}
Modal.prototype.close = function () {
this.modalBox.remove()
}
document.querySelector('#delete').addEventListener('click', () => {
// 先调用Modal构造函数
const del = new Modal('温馨提示', '你没有权限删除')
// 实例对象调用open方法
del.open()
})
document.querySelector('#login').addEventListener('click', () => {
// 先调用Modal构造函数
const login = new Modal('友情提示', '你还没有注册账号')
// 实例对象调用open方法
login.open()
})
</script>
</body>
</html>





















 966
966

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








