1、日期对象

1)实例化
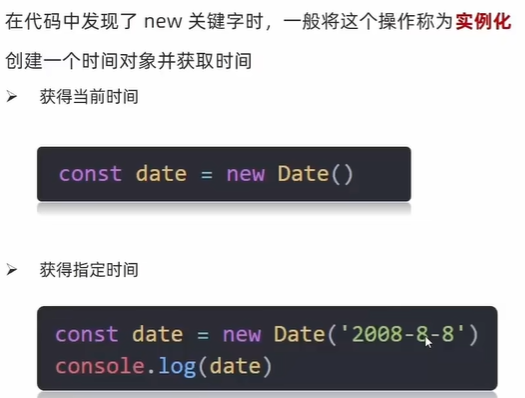
2)日期对象方法
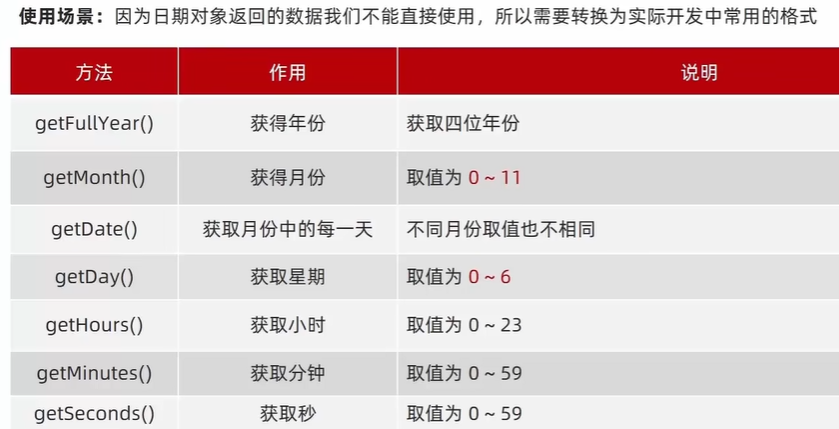
<script>
//获得日期对象
const date = new Date()
//使用方法
console.log(date.getFullYear());
console.log(date.getMonth() + 1); // getMonth() : 0~11
console.log(date.getDate());
console.log(date.getDay()); // getDay() : 0~6
console.log(date.getHours());
console.log(date.getMinutes());
console.log(date.getSeconds());
</script>
格式化日期:xxxx年x月x日 xx:xx:xx
<script>
//获得日期对象
const div = document.querySelector('div')
// function getMyDate() {
// const date = new Date()
// let h = date.getHours()
// let m = date.getMinutes()
// let s = date.getSeconds()
// h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h
// m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m
// s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s
// return `今天是: ${date.getFullYear()}年${date.getMonth() + 1}月${date.getDate()}号 ${h}:${m}:${s}`
// }
// div.innerHTML = getMyDate()
// setInterval(function () {
// div.innerHTML = getMyDate()
// }, 1000)
// 第二种写法
// 得到日期对象
const date = new Date()
div.innerHTML = date.toLocaleString() // 显示年月日 时分秒
// div.innerHTML = date.toLocaleDateString() // 显示年月日
// div.innerHTML = date.toLocaleTimeString() //显示时分秒
setInterval(function () {
const date = new Date()
div.innerHTML = date.toLocaleString()
}, 1000)
</script>
3)时间戳

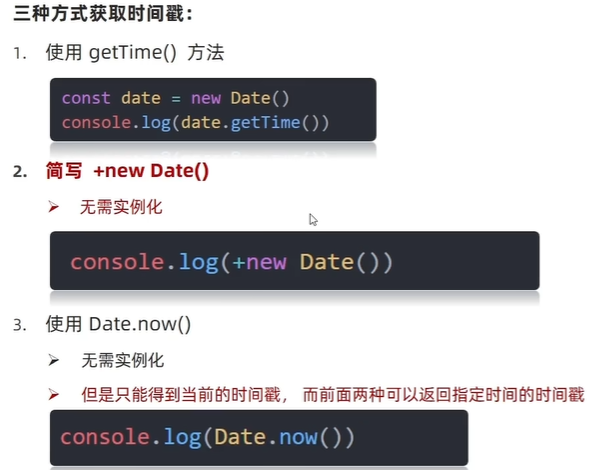
<script>
// 1. getTime()
// 实例化 new Date()返回对象 字符串
const date = new Date()
console.log(date.getTime());
//2. +new Date() 数字型
console.log(+new Date());
//3. Date.now()
console.log(Date.now());
</script>
4)案例:倒计时

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.countdown {
width: 240px;
height: 305px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 1;
color: #fff;
background-color: brown;
/* background-size: 240px; */
/* float: left; */
overflow: hidden;
}
.countdown .next {
font-size: 16px;
margin: 25px 0 14px;
}
.countdown .title {
font-size: 33px;
}
.countdown .tips {
margin-top: 80px;
font-size: 23px;
}
.countdown small {
font-size: 17px;
}
.countdown .clock {
width: 200px;
margin: 18px auto 0;
padding-top: 18px;
overflow: hidden;
}
.countdown .clock span,
.countdown .clock i {
display: block;
text-align: center;
line-height: 34px;
font-size: 23px;
float: left;
}
.countdown .clock span {
width: 34px;
height: 34px;
border-radius: 2px;
background-color: #303430;
}
.countdown .clock i {
width: 20px;
font-style: normal;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="countdown">
<p class="next">今天是2225年9月28日</p>
<p class="title">十一倒计时</p>
<p class="clock">
<span id="day">00</span>
<i>:</i>
<span id="hour">00</span>
<i>:</i>
<span id="minutes">25</span>
<i>:</i>
<span id="second">20</span>
</p>
<p class="tips">25/10/1 00:00:00</p>
</div>
<script>
// 函数封装
function getResTime() {
const now = +new Date()
const last = +new Date('2025-10-1 00:00:00')
const res = (last - now) / 1000 //秒
let s = parseInt(res % 60)
s = s < 10 ? '0' + s : s
let m = parseInt(res / 60 % 60)
m = m < 10 ? '0' + m : m
let h = parseInt(res / 60 / 60 % 24)
h = h < 10 ? '0' + h : h
let d = parseInt(res / 60 / 60 / 24)
d = d < 10 ? '0' + d : d
document.querySelector('#day').innerHTML = d
document.querySelector('#hour').innerHTML = h
document.querySelector('#minutes').innerHTML = m
document.querySelector('#second').innerHTML = s
}
function getToday() {
const today = new Date()
return `今天是${today.getFullYear()}年${today.getMonth() + 1}月${today.getDate()}日`
}
const next = document.querySelector('.next')
next.innerHTML = getToday()
setInterval(function () {
next.innerHTML = getToday()
}, 1000)
getResTime()
setInterval(getResTime, 1000)
</script>
</body>
</html>
2、节点操作
1)DOM节点
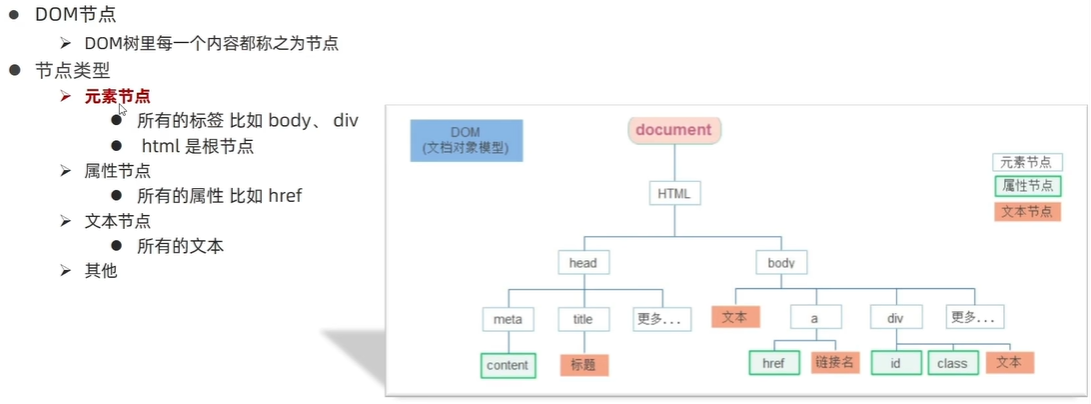
主要操作标签(元素节点)
2)查找结点
(1)父节点查找


子元素.parentNode
<body>
<div class="grandpa">
<div class="dad">
<div class="bady"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const baby = document.querySelector('.baby')
console.log(baby) // 返回dom对象
console.log(baby.parentNode) // 返回 bady 父节点 是对象
console.log(baby.parentNode.parentNode) // 返回 bady 父节点 的父节点 是对象
</script>
</body>
(2) 案例:关闭广告
多个相同类名的盒子关闭思路:使用document.querySelectorAll获得伪数组
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.box {
position: relative;
width: 300px;
height: 100px;
background-color: skyblue;
margin: 50px auto;
}
.boxx {
position: absolute;
top: 0;
right: 5px;
font-size: 20px;
color: #fff
}
.boxx:hover {
cursor: pointer
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="boxx">x</div>
</div>
<div class="box">
<div class="boxx">x</div>
</div>
<div class="box">
<div class="boxx">x</div>
</div>
<script>
const boxx = document.querySelectorAll('.boxx') //伪数组
console.log(boxx);
for (let i = 0; i < boxx.length; i++) {
boxx[i].addEventListener('click', function () {
this.parentNode.style.display = 'none'
})
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
(3)查找子节点

(4)查找兄弟节点
好处:之前是无脑的想要谁就获取谁,现在可以省一次获取

3)增加节点(重点)
eg:发布评论
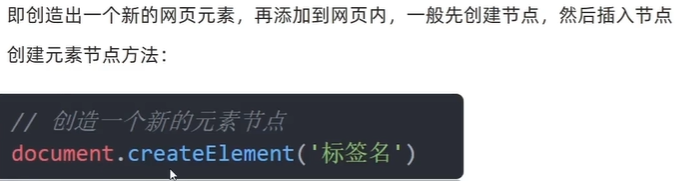
(1)创建节点
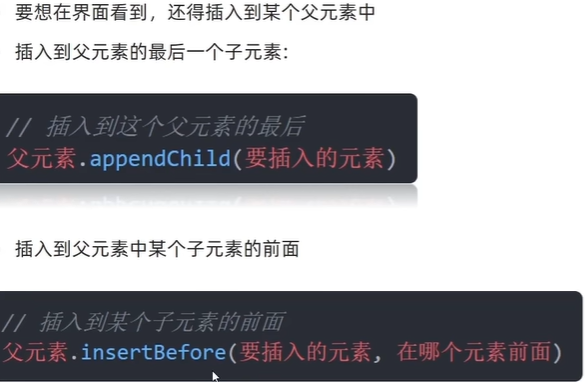
(2)追加节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<ul>
<li>我在你前面</li>
<li>我在你后面</li>
</ul>
<script>
// // 创建节点
// const div = document.createElement('div')
// // 追加节点 作为父元素的最后一个子元素
// document.body.appendChild(div)
const ul = document.querySelector('ul')
const li = document.createElement('li')
li.innerHTML = 'Hello World!'
// ul.children 是ul里面所有li的伪数组
ul.insertBefore(li, ul.children[0])
</script>
</body>
</html>
(3)案例:学成在线
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.w {
width: 1200px;
margin: auto;
}
body {
background-color: #f3f5f7;
}
li {
list-style: none;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
}
.clearfix:before,
.clearfix:after {
content: "";
display: table;
}
.clearfix:after {
clear: both;
}
.box {
margin-top: 30px;
}
.box-hd {
height: 45px;
}
.box-hd h3 {
float: left;
font-size: 20px;
color: #494949;
}
.box-hd a {
float: right;
font-size: 12px;
color: #a5a5a5;
margin-top: 10px;
margin-right: 30px;
}
/* 把li 的父亲ul 修改的足够宽一行能装开5个盒子就不会换行了 */
.box-bd ul {
width: 1225px;
}
.box-bd ul li {
position: relative;
top: 0;
float: left;
width: 228px;
height: 270px;
background-color: #fff;
margin-right: 15px;
margin-bottom: 15px;
transition: all .3s;
}
.box-bd ul li a {
display: block;
}
.box-bd ul li:hover {
top: -8px;
box-shadow: 0 15px 30px rgb(0 0 0 / 10%);
}
.box-bd ul li img {
width: 100%;
}
.box-bd ul li h4 {
margin: 20px 20px 20px 25px;
font-size: 14px;
color: #050505;
font-weight: 400;
}
.box-bd .info {
margin: 0 20px 0 25px;
font-size: 12px;
color: #999;
}
.box-bd .info span {
color: #ff7c2d;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box w">
<div class="box-hd">
<h3>精品推荐</h3>
<a href="#">查看全部</a>
</div>
<div class="box-bd">
<ul class="clearfix">
</ul>
</div>
</div>
<script>
let data = [
{
src: '/images/course01.png',
title: 'Think PHP 5.0 博客系统实战项目演练',
num: 1125
},
{
src: '/images/course02.png',
title: 'Android 网络动态图片加载实战',
num: 357
},
{
src: '/images/course03.png',
title: 'Angular2 大前端商城实战项目演练',
num: 22250
},
{
src: '/images/course04.png',
title: 'Android APP 实战项目演练',
num: 389
},
{
src: '/images/course05.png',
title: 'UGUI 源码深度分析案例',
num: 124
},
{
src: '/images/course06.png',
title: 'Kami2首页界面切换效果实战演练',
num: 432
},
{
src: '/images/course07.png',
title: 'UNITY 从入门到精通实战案例',
num: 888
},
{
src: '/images/course08.png',
title: 'Cocos 深度学习你不会错过的实战',
num: 590
},
]
const ul = document.querySelector('.box-bd ul')
// 根据数据个数,创建对应的 li
for (let i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
const li = document.createElement('li')
// 追加
li.innerHTML = `
<a href="#">
<img src=${data[i].src} alt="">
<h4>
${data[i].title}
</h4>
<div class="info">
<span>高级</span> • <span>${data[i].num}</span>人在学习
</div>
</a>
`
ul.appendChild(li)
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
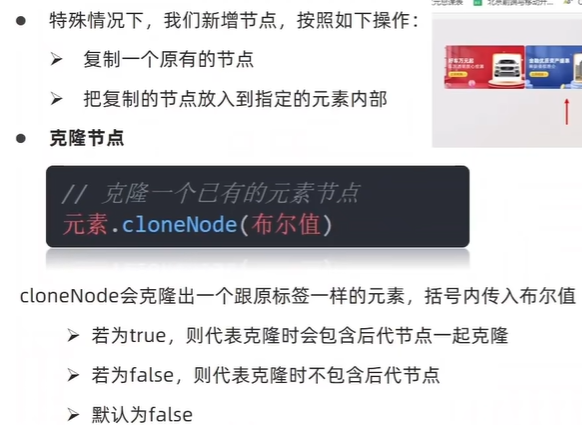
(4)克隆节点
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector('ul')
//克隆节点 元素.cloneNode()
// const li1 = ul.children[0].cloneNode(true)
// 追加
// ul.appendChild(li1) cloneNode(false) 只克隆标签 默认false
ul.appendChild(ul.children[0].cloneNode(true))
</script>
</body>
</html>
4)删除节点

<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
</ul>
<script>
const ul = document.querySelector('ul')
// 删除节点 父元素.removeChild(子元素)
ul.removeChild(ul.children[0])
</script>
</body>
3、M端事件
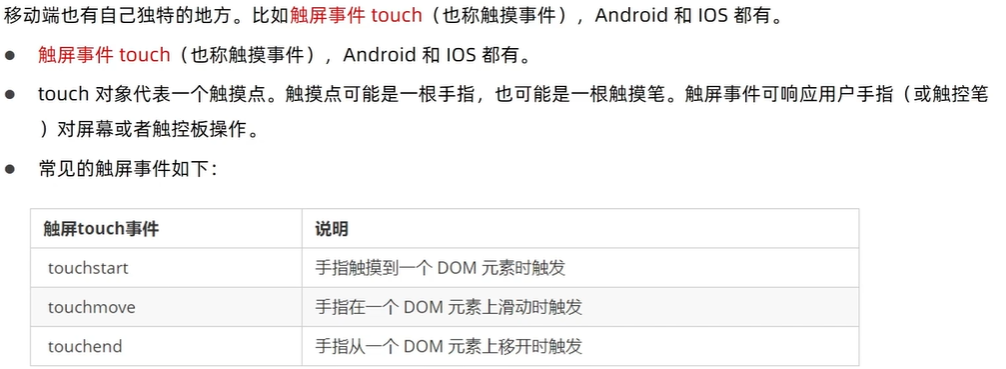
<script>
const div = document.querySelector('div')
// 触摸
div.addEventListener('touchstart', function () {
console.log(1);
})
// 离开
div.addEventListener('touchend', function () {
console.log(2);
})
//移动
div.addEventListener('touchmove', function () {
console.log(3);
})
</script>
4、js 插件推荐

5、案例:学生信息表
分析:业务模块:点击录入,录入数据、点击删除,删除数据
本次案例尽量减少dom操作,采取操作数据的形式;增加和删除都是针对于数组的操作,然后再将数组数据渲染到页面中。
思路:拆两个模块:新增和删除;我们先声明一个空的数组;点击录入,根据数据,生成对象,追加到数组中;再将数组数据渲染到页面表格的行;点击删除,删除的是对应数组里的数据;再将数组数据渲染到页面。
什么都不输时,点击录入,我们会发现表单会跳转,我们要阻止这种行为。
info.addEventListener('submit',function(e){
// 什么都不输,点录入,表单会跳转,阻止这种行为
// 阻止默认行为 表单不跳转
e.preventDefault()
})
同时,什么都不输时,点击录入,我们也会发现,表单中会出现空白数据,此时,我们发现这些存储数据的表单都有name属性,那么,我们可以获取带有name属性的表单,然后我们遍历他们,只要有一个为空,就中断程序return。注意:书写的位置要放在新增数据的前面(不满足条件,就不需要录入),阻止默认行为的后面。
const items = document.querySelectorAll('[name]')
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
if (items[i].value === '') {
alert('输入内容不能为空')
}
}
总代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>学生信息</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: #721c24;
}
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #333;
margin: 20px 0;
}
table {
margin: 0 auto;
width: 800px;
border-collapse: collapse;
color: #004085;
}
th {
padding: 10px;
background: #cfe5ff;
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: 400;
}
td,
th {
border: 1px solid #b8daff;
}
td {
padding: 10px;
color: #666;
text-align: center;
font-size: 16px;
}
tbody tr {
background: #fff;
}
tbody tr:hover {
background: #e1ecf8;
}
.info {
width: 900px;
margin: 50px auto;
text-align: center;
}
.info input,
.info select {
width: 80px;
height: 27px;
outline: none;
border-radius: 5px;
border: 1px solid #b8daff;
padding-left: 5px;
box-sizing: border-box;
margin-right: 15px;
}
.info button {
width: 60px;
height: 27px;
background-color: #004085;
outline: none;
border: 0;
color: #fff;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.info .age {
width: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>新增学员</h1>
<form class="info" autocomplete="off">
姓名:<input type="text" class="uname" name="uname" />
年龄:<input type="text" class="age" name="age" />
性别:
<select name="gender" class="gender">
<option value="男">男</option>
<option value="女">女</option>
</select>
薪资:<input type="text" class="salary" name="salary" />
就业城市:<select name="city" class="city">
<option value="北京">北京</option>
<option value="上海">上海</option>
<option value="广州">广州</option>
<option value="深圳">深圳</option>
<option value="杭州">杭州</option>
</select>
<button class="add">录入</button>
</form>
<h1>就业榜</h1>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>学号</th>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
<th>性别</th>
<th>薪资</th>
<th>就业城市</th>
<th>操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!--
<tr>
<td>1001</td>
<td>欧阳霸天</td>
<td>19</td>
<td>男</td>
<td>15000</td>
<td>上海</td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
-->
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
// 获取表单中的元素
const uname = document.querySelector('.uname')
const age = document.querySelector('.age')
const gender = document.querySelector('.gender')
const salary = document.querySelector('.salary')
const city = document.querySelector('.city')
const tbody = document.querySelector('tbody')
const items = document.querySelectorAll('[name]')
// 声明空数组,增删对这个数组操作
const arr = []
// 录入数据
// 表单提交
const info = document.querySelector('.info')
info.addEventListener('submit', function (e) {
// 什么都不输,点录入,表单会跳转,阻止这种行为
// 阻止默认行为 表单不跳转
e.preventDefault()
// 表单验证
// 遍历
for (let i = 0; i < items.length; i++) {
if (items[i].value === '') {
alert('输入内容不能为空')
}
}
// 创建新的对象,存储录入的数据
const obj = {
stuId: arr.length + 1,
uname: uname.value,
age: age.value,
gender: gender.value,
salary: salary.value,
city: city.value
}
// 将对象放在数组中
arr.push(obj)
// 录入数据后,重置表单,恢复默认表单
this.reset()
// 调用渲染函数
render()
})
// 由于录入,删除数据都需要渲染函数,因此封装函数
function render() {
// 为了解决录入数据时,会把录入之前数组中的数据打印一次,录入之后,再次打印数组中的所有数据
// 因此,渲染数据时,先清空 tbody
tbody.innerHTML = ''
// 遍历数组
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
const tr = document.createElement('tr')
tr.innerHTML = `
<td>${arr[i].stuId}</td>
<td>${arr[i].uname}</td>
<td>${arr[i].age}</td>
<td>${arr[i].gender}</td>
<td>${arr[i].salary}</td>
<td>${arr[i].city}</td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:" data-id=${i}>删除</a>
</td>
`
// 追加元素 父元素.appendChild(子元素)
tbody.appendChild(tr)
}
}
// 删除操作
//事件委托
tbody.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
// 点击删除
if (e.target.tagName === 'A') {
// 删除数组中对应的数据
arr.splice(e.target.dataset.id, 1)
}
// 重新渲染
render()
})
</script>
</body>
</html>






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








