目录
一、基本并查集实现两个操作
1. 合并两个集合
2. 查询某个元素的祖宗节点
二、两个优化
1. 路径压缩 O(logn)
2. 按秩合并O(logn) ------ 不常用
三、并查集扩展
1. 记录每个集合的大小( 绑定到根节点上 )
2. 记录每个点到根节点的距离( 绑定到每个元素上 ) ------ 可以处理这个点与根节点的关系的问题
四、Acwing --- 1250 - 格子游戏
原题链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1252/
代码如下:
//技巧:一维 (x,y) --> x*n+y ( x,y从0开始 )
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=40010;
int n,m;
int p[N];
int get(int x,int y){
return x*n+y;
}
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x])p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<n*n;i++)p[i]=i;
int ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int x,y;
char d;
cin>>x>>y>>d;
x--,y--;
int a=get(x,y);//坐标对应的编号
int b;
if(d=='D')b=get(x+1,y);
else b=get(x,y+1);
int pa=find(a),pb=find(b);
if(pa==pb){
ans=i;
break;
}
p[pa]=pb;
}
if(!ans)puts("draw");
else cout<<ans<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}五、Acwing --- 1252 - 搭配购买
原题链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/1254/

思路:搭配在一起的花相当于一个连通块(并查集做),可以看成一个物品,然后做01背包。
代码如下:
//并查集 + 01背包
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=10010;
int n,m,k;
int p[N];
int v[N],w[N];
int f[N];
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x])p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m>>k;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)p[i]=i;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>v[i]>>w[i];
while(m--){
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
int pa=find(a),pb=find(b);
if(pa!=pb){
v[pb]+=v[pa];
w[pb]+=w[pa];
p[pa]=p[pb];
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(p[i]==i){
for(int j=k;j>=v[i];j--){
f[j]=max(f[j],f[j-v[i]]+w[i]);
}
}
}
cout<<f[k]<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}六、Acwing --- 237 - 程序自动分析
原题链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/239/

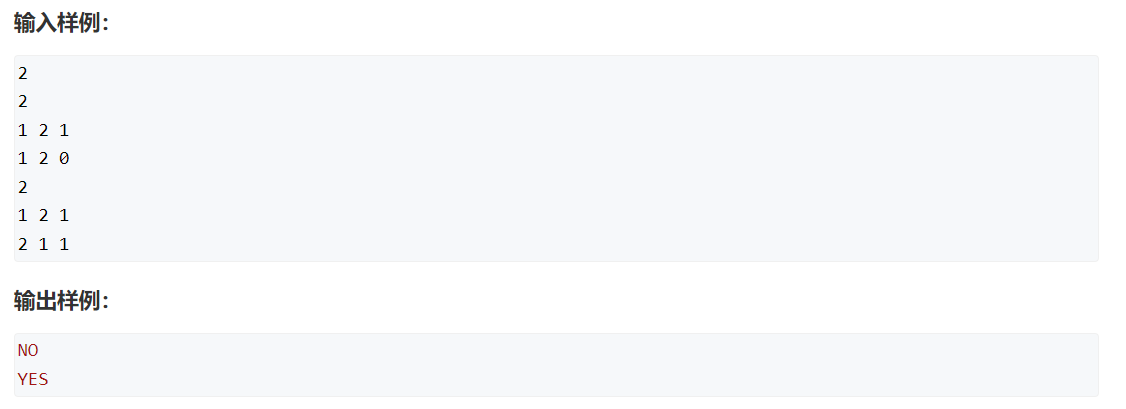
步骤:
1. 离散化 ---- 1e9 --> 2e6
离散化的要求:1. 保序 --- 排序+判重+二分
2. 不要求保序 :1)map 2)hash
2. 约束条件的顺序“无所谓”
1)先考虑所有相等约束,将所有相等约束合并---不可能有矛盾
2)再考虑不等条件,依次判断每个不等条件 i , j 是否在同一个集合中----可能有矛盾
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=200010;
int n,m;
int p[N];
unordered_map<int,int> S;
struct Node{
int x,y,e;
}no[N];
int get(int x){
if(S.count(x)==0)S[x]=++n;
return S[x];
}
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x])p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
n=0;
S.clear();
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
int x,y,e;
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&e);
no[i]={get(x),get(y),e};
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)p[i]=i;
//合并所有相等的约束条件
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(no[i].e==1){
int pa=find(no[i].x),pb=find(no[i].y);
p[pa]=pb;
}
}
//检查所有的不等条件
bool flag=false;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(no[i].e==0){
int pa=find(no[i].x),pb=find(no[i].y);
if(pa==pb){
flag=true;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag)cout<<"NO"<<endl;
else cout<<"YES"<<endl;
}
int main(){
int t;
//t=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}七、Acwing --- 238 - 银河英雄传说
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/240/

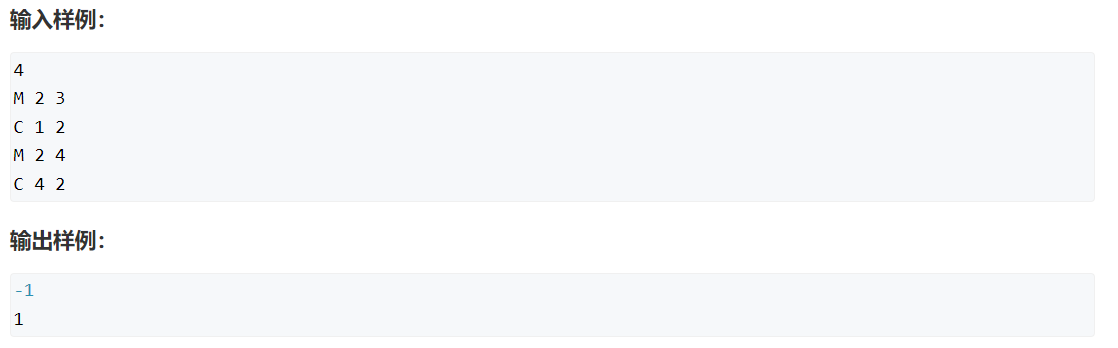
怎么做 :1. 不问间隔多少战舰 ----简单的并查集
2. 同时维护间隔多少战舰 --- 统一维护当前战舰到排头的距离 ( 前缀和思想 )
思路:1. 让排头当根节点
2. 假设把a放在b后面,则d[pa]=s[pb] , s[pb] += s[pa]
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=30010;
int m;
int p[N],s[N],d[N];//d[x]表示x到p[x]的距离
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x]){
int root=find(p[x]);
d[x]+=d[p[x]];
p[x]=root;
}
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1;i<N;i++){
p[i]=i;
s[i]=1;
}
while(m--){
char op[2];
int a,b;
scanf("%s%d%d",op,&a,&b);
int pa=find(a),pb=find(b);
if(op[0]=='M'){
if(pa!=pb){
d[pa]=s[pb];
s[pb]+=s[pa];
p[pa]=pb;
}
}else{
if(pa!=pb)puts("-1");
else printf("%d\n",max(abs(d[a]-d[b])-1,0));
}
}
}
int main(){
int t;
t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--)solve();
return 0;
}八、Acwing --- 239 - 奇偶游戏
原题链接:https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/241/

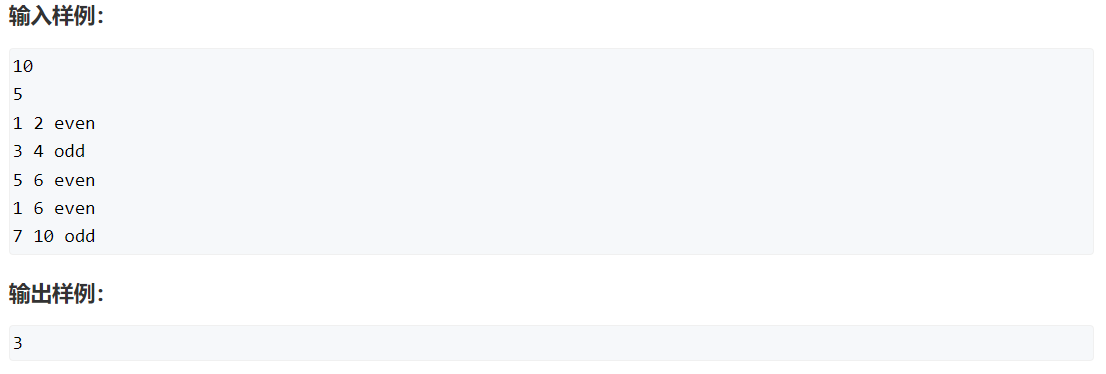
代码如下:
1. 带边权的并查集
//并查集 + 离散化
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=10010;
int n,m;
int p[N],d[N];
unordered_map<int,int> S;
int get(int x){
if(S.count(x)==0)S[x]=++n;
return S[x];
}
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x]){
int t=find(p[x]);
d[x]^=d[p[x]];
p[x]=t;
}
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
n=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)p[i]=i;
int res=m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
string type;
cin>>a>>b>>type;
a=get(a-1),b=get(b);
int t=0;
if(type=="odd")t=1;
int pa=find(a),pb=find(b);
if(pa==pb){
if((d[a]^d[b])!=t){
res=i-1;
break;
}
}else{
p[pa]=pb;
d[pa]=d[a]^d[b]^t;
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}2. 扩展域方式
枚举思想
1) 如果x,y是同类,若 x 奇则 y 奇,若 x 偶则 y 偶
( 1 )合并x+n , y+n ( 2 )合并x , y
2) 如果异类 ,若 x 奇则 y 偶,若 x 偶则 y 奇
( 1 )合并x+n , y ( 2 )合并x , y+n
//并查集 + 离散化
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=20010,M=N/2;
int n,m;
int p[N];
unordered_map<int,int> S;
int get(int x){
if(S.count(x)==0)S[x]=++n;
return S[x];
}
int find(int x){
if(x!=p[x])p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
void solve(){
cin>>n>>m;
n=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)p[i]=i;
int res=m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int a,b;
string type;
cin>>a>>b>>type;
a=get(a-1),b=get(b);
if(type=="even"){
if(find(a+M)==find(b)){
res=i-1;
break;
}
p[find(a)]=find(b);
p[find(a+M)]=find(b+M);
}else{
if(find(a)==find(b)){
res=i-1;
break;
}
p[find(a)]=find(b+M);
p[find(a+M)]=find(b);
}
}
cout<<res<<endl;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
t=1;
//cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}




















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








