一、密封类
密封类可以用来限制扩展性,如果密封了某个类,则其他类不能从 该类继承。
如果密封了某个成员,则派生类不能重写该成员的实现。
默认情况下,不应该密封类和成员。
密封可以防止对库的类型和成员进行自定义。
C#中使用密封类时,如果类满足以下条件,则应将其密封:
1.静态类。
2.类包含带有安全敏感信息的继承的受保护成员。
3.类继承多个虚成员,并且密封每个成员的开发和测试开销明显大于密封整个类。
4.类是一个要求使用反射进行快速搜索的属性。密封属性可提高反射在检查属性时的性能。
密封类需要使用sealed关键字,语法如下:
访问修饰符 sealed class 类名:基类或接口
{
//继承非必须要写
//类成员
}
密封类特性:
1.密封类不能作为基类被继承,但它可以继承别的类或者实现接 口。
2.在密封类中不能声明受保护成员或虚成员,因为受保护成员只 能从派生类进行访问,而虚成员只能在派生类中重写。
3.由于密封类的不可继承性,因此密封类不能声明为抽象的,即 sealed修饰符不能与abstact修饰符同时使用。
二、密封方法
密封方法只能用于对基类的虚方法(virtual)进行实现,并提供具体 的实现。
所以,声明密封方法时,sealed修饰符总是和override修饰符同时 使用。
密封方法语法如下:
public sealed override 方法名()
{
//方法体
}
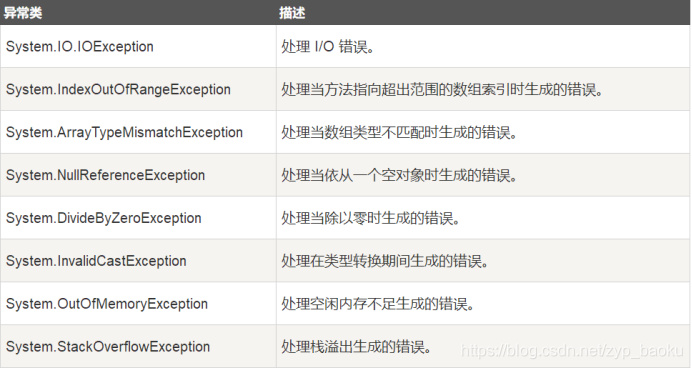
三、异常
异常是在程序执行期间出现的问题。
C# 中的异常是对程序运行时出现的特殊情况的一种响应。
异常提供了一种把程序控制权从某个部分转移到另一个部分的方式。
C# 异常处理时建立在四个关键词之上的:try、catch、finally 和 throw。
try:一个 try 块标识了一个将被激活的特定的异常的代码块。后跟一个或多个 catch 块。
catch:程序通过异常处理程序捕获异常。catch 关键字表示异常的捕获。
finally:finally 块用于执行给定的语句,不管异常是否被抛出都会执行。
throw:当问题出现时,程序抛出一个异常。使用 throw 关键字来完成。
1.try...catch:
try
{
//执行代码
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
//捕获异常
}
2.try...catch(多):
try
{
//执行代码
}
catch (....Exception ex)
{
//捕获异常
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
//捕获异常
}
3.try...catch...finally
try
{
//执行代码
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
//捕获异常
}
finally
{
//执行代码
}
4.自定义异常
//可写在catch 也可作为单独代码进行编写
throw (new Exception("报错啦"));
四、案例
Event类库
Cat类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Event
{
public class Cat
{
private string name;
public Cat(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public delegate void MouseRun();
public event MouseRun CatRun;
public void Showt()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是{0}",name);
if (CatRun != null)
{
CatRun();
}
}
}
}
Mouse类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Event
{
public class Mouse
{
private string name;
public Mouse(string name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public void Run()
{
Console.WriteLine("猫来了,{0}快跑",name);
}
}
}
Program类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Event
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Cat c = new Event.Cat("加菲猫");
Mouse m = new Mouse("米老鼠");
c.CatRun += new Cat.MouseRun(m.Run);
c.Showt();
c.CatRun -= new Cat.MouseRun(m.Run);
c.Showt();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
Temp类库
Program类
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Temp
{
class Program
{
delegate void Show();
delegate void Show1(string str);
delegate string returnStr();
delegate string returnStr2(string str);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//Show s = new Show(Show1);
//s();
Show1 s1 = new Show1(Show2);
s1("zs");
//returnStr rs = new returnStr(returnStr1);
//string str = rs();
//Console.WriteLine(str);
returnStr2 rs2 = new returnStr2(returnStr3);
string str = rs2("1234");
Console.WriteLine(str);
Console.ReadKey();
}
//public static void Show1()
//{
// Console.WriteLine("SHOW1");
//}
public static void Show2(string s)
{
Console.WriteLine("SHOW1");
}
public static string returnStr1()
{
return "str";
}
public static string returnStr3(string str)
{
if (str.Length > 3)
{
return str;
}return "1";
}
}
}





 本文深入解析C#中的密封类与密封方法,探讨其在限制继承、增强安全性和提升性能方面的作用。同时,介绍了异常处理机制及自定义异常的创建,最后通过案例展示委托和事件的使用。
本文深入解析C#中的密封类与密封方法,探讨其在限制继承、增强安全性和提升性能方面的作用。同时,介绍了异常处理机制及自定义异常的创建,最后通过案例展示委托和事件的使用。
















 11万+
11万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








