红黑树总结
2-3树介绍2-3树插入元素- 红黑树由来(和
2-3树等价) - 红黑树性质的理解
- 红黑树中添加元素
- 添加中维护红黑树的代码
- 使用LeetCode804. Unique Morse Code Words测试红黑树
前言
2-3树介绍
2节点: 容纳1个元素,有2个孩子;3节点: 容纳2个元素,有3个孩子;4节点: 容纳3个元素,有4个孩子;- …


绝对平衡表示的是任意子树左右高度之差为0。
2-3树插入元素
一个原则: 添加节点将永远不会添加到一个空的位置(和二叉搜索树不同)、只会和最后找到的叶子节点做融合。
细分为四种情况:
- 向
2节点(2个孩子的节点)中添加1个元素,融合成一个3节点; - 向
3节点(3个孩子的节点)中添加1个元素,先融合成为一个4节点、如果这个4节点是根节点,直接分裂成含有三个2节点的一棵树; - 如果这个
4节点不是根节点,就不能分裂成含有三个2节点的一棵树;因为这样会破坏2-3树的绝对平衡性。正确的做法是向上和父亲节点做新的融合,这里又分为两种情况, 第一种情况: 父亲为2节点,直接融合到父亲,变成3节点; - 第二种情况: 父亲为
3节点,先融合到父亲,变成4节点,然后父亲分散,全部变成2节点;
下图的层次关系可能会比较清楚:

看具体的细分的四种情况:
1).最简单的情况:

2).插入3节点且是根:

3).插入3节点且不是根且父亲是2节点:

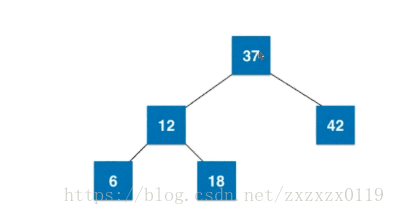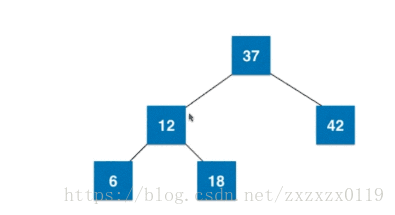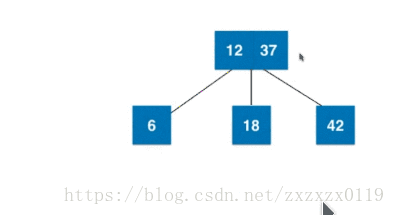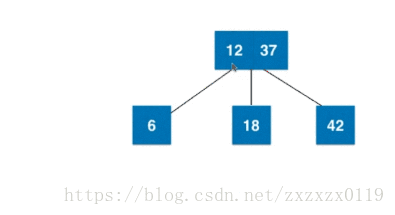
4).插入3节点且不是根且父亲是3节点:

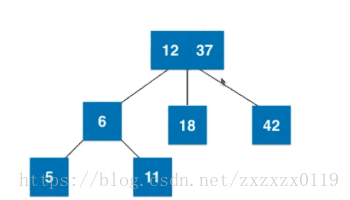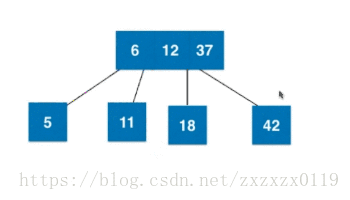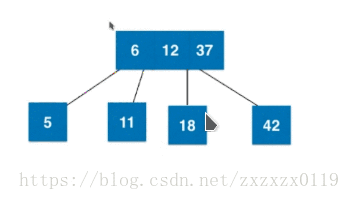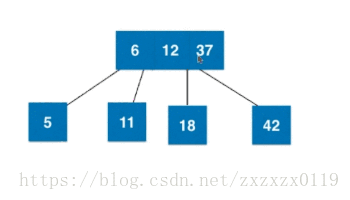
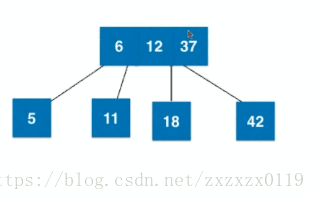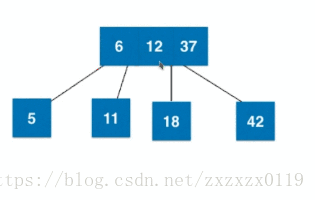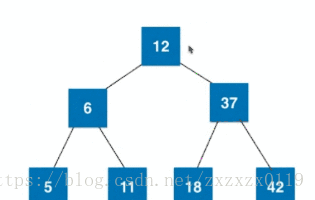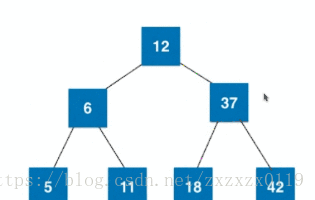
红黑树由来(和2-3树等价)
<<算法4>>中提到2-3树和红黑树是等价的,则其中2节点和3节点对应红黑树的关系有两种:
1) . 第一种 : 2节点转换成红黑树节点:

2) . 第二种 : 3节点转换成红黑树节点:
- 由于一般树结构一个节点只表示一个值,所以要将3节点用一种特殊的方式转换,即转换成红黑树节点;

- 上面的摆放只是直观的摆放,我们需要将b节点作为c节点的左孩子,但是又需要去标识b和c的对应关系(是一个3节点而且b < c) 所以我们将b、c中间的线绘制成红色;并且还原成二分搜索树的样子:
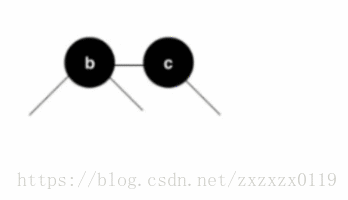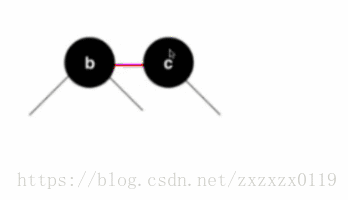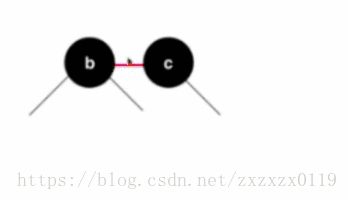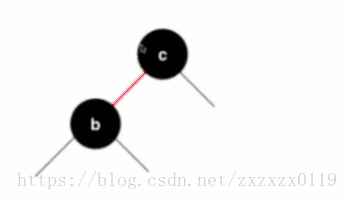
- 但是在二叉树的实现中没有使用相应的类来表示那条边是红色的,所以我们使用节点来表示这个特性,由于每一个节点只有一个父亲,也就是每一个节点和它父亲相连的边只有一条边,所以我们可以把这条边(红色)的信息存放在结点上,也就是把b描绘成红色,所以这就是红色节点的由来:这个红色的节点b表示的是这个节点之前在2-3树中是在一个3节点中,而且和它的父亲是存放在一起的(并列),而且它的值比它父亲小。

然后再看一个2-3树和红黑树转换的例子:

更加直观的看:

红黑树性质的理解

- 第一条: 这个很简单,是红黑树的定义;
- 第二条: 由于在2-3树中根节点或者是2节点,或者是3节点,这两种节点转换成红黑树节点之后根节点都是黑色的;

- 第三条: 与其说是性质,不如说是定义,不过要注意这里的叶子节点指的是最后的空节点,都指定为黑色的节点,如果是空树,则同时满足2、3条性质;
- 第四条: 也是和2-3树密切关系,一个红色节点,在2-3树中是3节点的左边节点,它的左右孩子在2-3树中都要么是2节点,要么是3节点,但是他们的根都是黑色的;

- 第五条: 是最重要的一条性质,最主要的原因是2-3树是绝对平衡的,如果途中经过的是一个3节点也不要紧,反正都是有一个黑色节点,所以经过的黑色节点的数量是一样多的;所以红黑树是保持"黑平衡"的二叉树,本质就是2-3树是绝对平衡的;

红黑树中添加元素
一个原则: 新插入的结点永远是红色

有几个子过程步骤以及相关需要维护的地方:
- 第一个:维护根节点为黑色,因为我们第二条性质是根节点永远为黑色,所以我们在插入完节点之后,要维护根节点为黑色;
1). 新插入:
2). 更一般的情况对于根的维护:

- 第二个:也是插入的第二种情况,这个很简单,也不需要维护,直接插入就好 :

- 第三个:也是插入的第三种情况,也就是带插入的红色结点比根节点大(插在右边),这个需要维护,和AVL中一样,类似RR型,需要进行左旋转:

过程如下:

但是这样还不够,我们还需要维护颜色: 此时x成为了新的根节点,所以x.color = node.color(x颜色变成之前根节点的颜色); 而node.color = RED,因为形成的还是3节点:(注意之前的node.color有可能是红色,但是后续还要处理 )

代码:
/**左旋转
node x
/ \ --> / \
T1 x node T3
/ \ / \
T2 T3 T1 T2
*/
private Node leftRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.right;
Node T2 = x.left;
x.left = node;
node.right = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
- 第四个: 也是插入的第四种情况,也是另一种维护情况: 颜色反转, 在根节点的右侧插入: 其实相当于在2-3树中的
3节点中插入元素,然后分散:
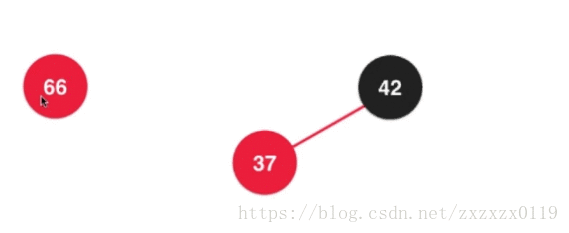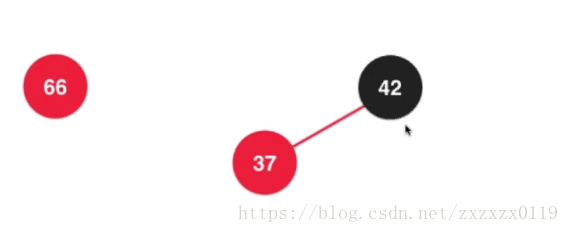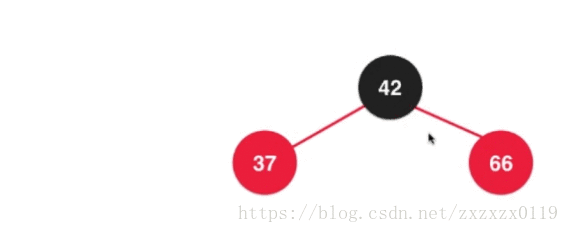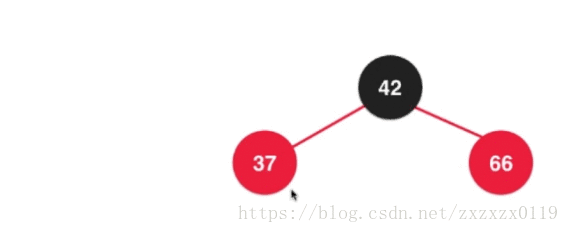
在2-3树中散开之后都成为了2节点,所以需要变成全都是黑色节点:
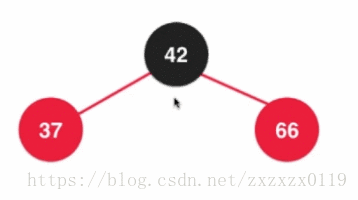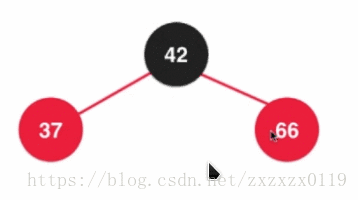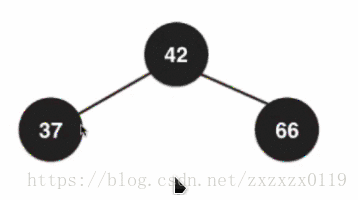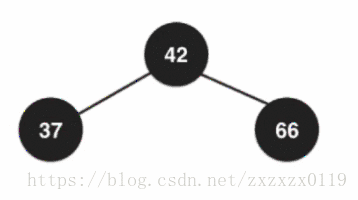
最后融合,根节点又需要变回红色,因为这个根节点要向上去和它的父亲节点去融合:
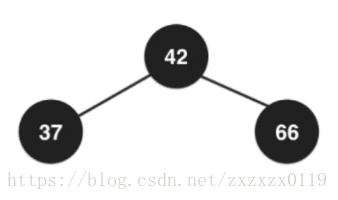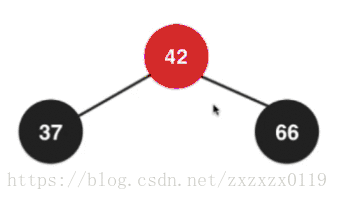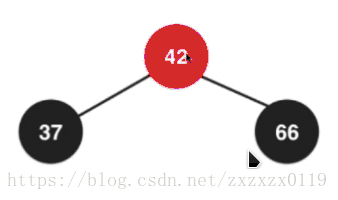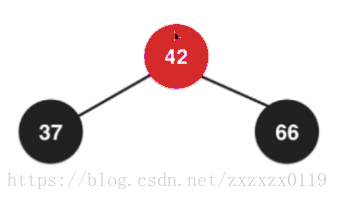
整体如下图 (需要经过两次换色);

代码:
//三个节点的颜色反转 根->RED 两个孩子->BLACK
private void flipColors(Node node){
node.color = RED;
node.left.color = BLACK;
node.right.color = BLACK;
}
- 第五个:也是插入的第五种情况,在根节点的左边的左边,也就是向
2-3树中的3结点的左边添加元素:
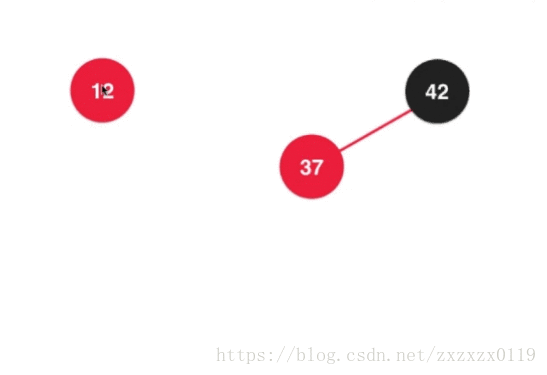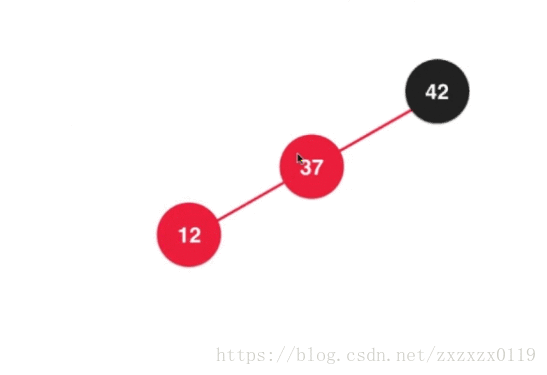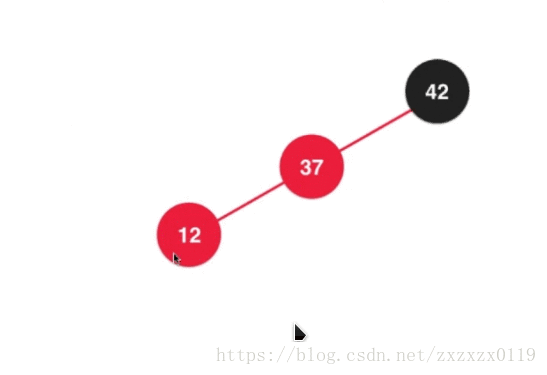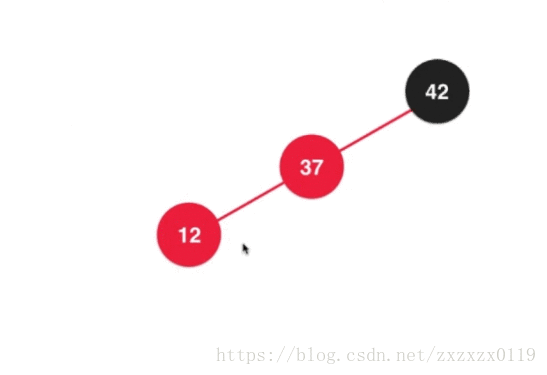
等价于在2-3树中这样插入:

然后需要进行右旋转:

/**右旋转
node x
/ \ / \
x T1 --> y node
/ \ / \ / \
y T2 T4 T3 T2 T1
/ \
T4 T3
*/
private Node rightRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = node;
node.left = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
然后又需要维护颜色(前两部同左旋转,最后一步是颜色翻转(filpColors))

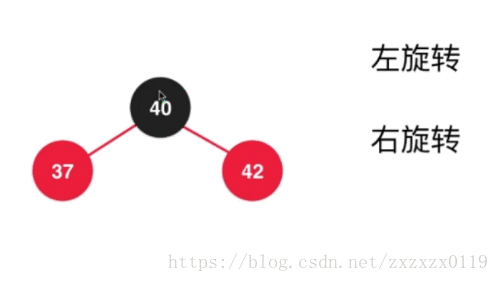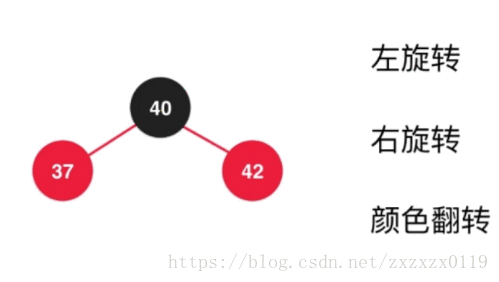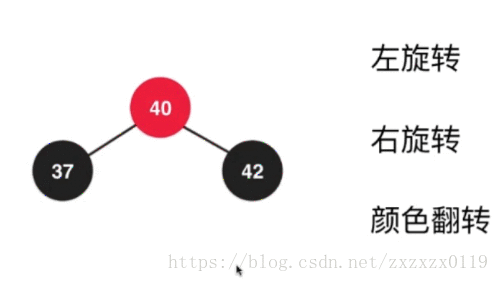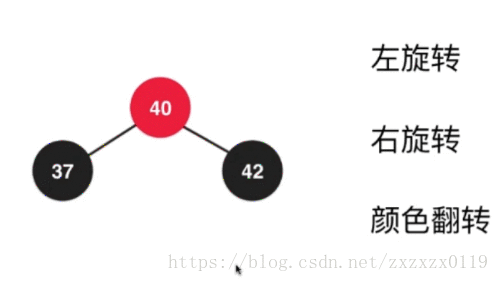
- 第六个: 在根节点的左孩子的右边添加,类似2-3树中添加在3节点的中间,这个只需要运用前面的那些步骤综合即可完成:
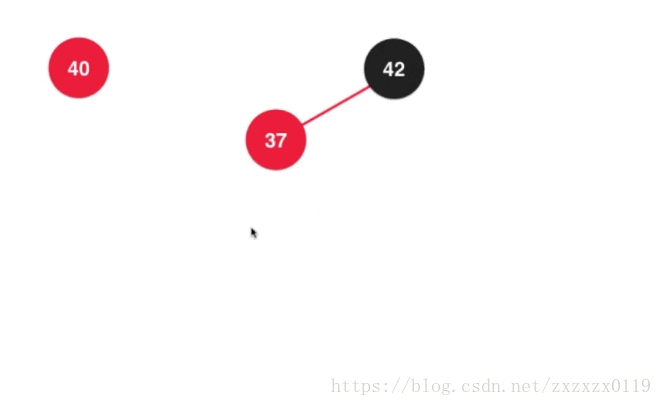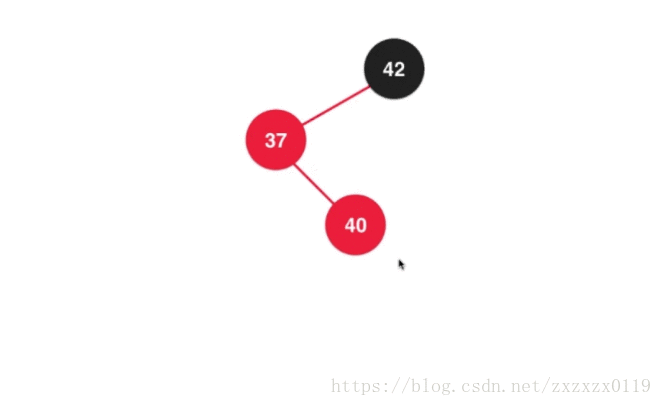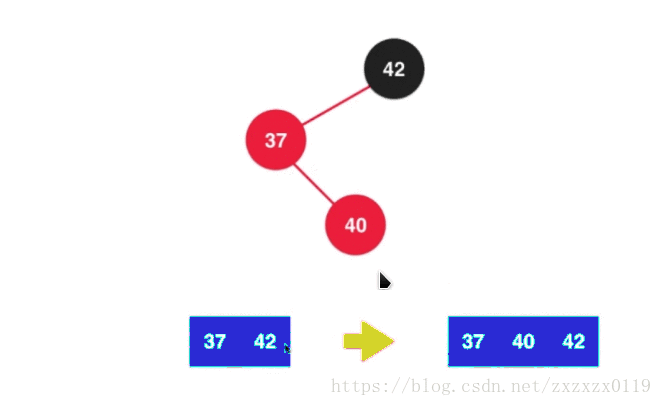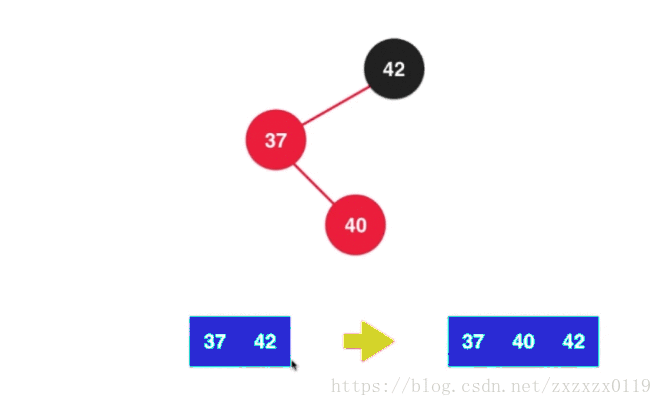
a.先对37进行左旋转 :
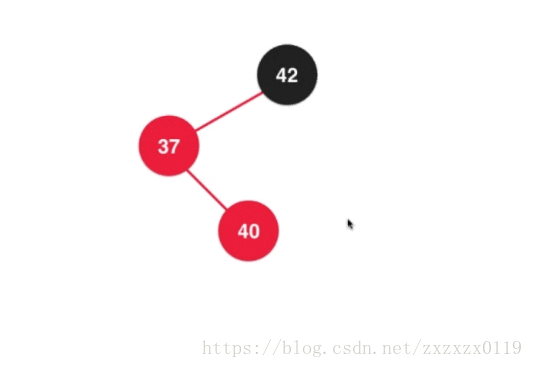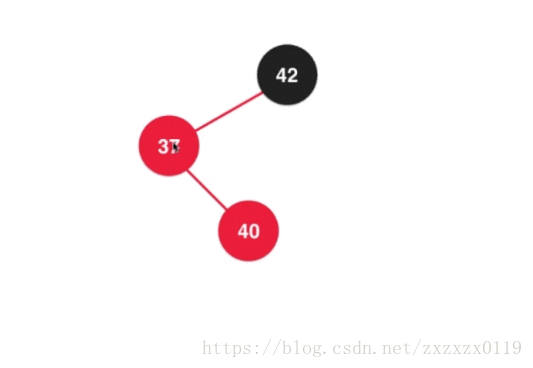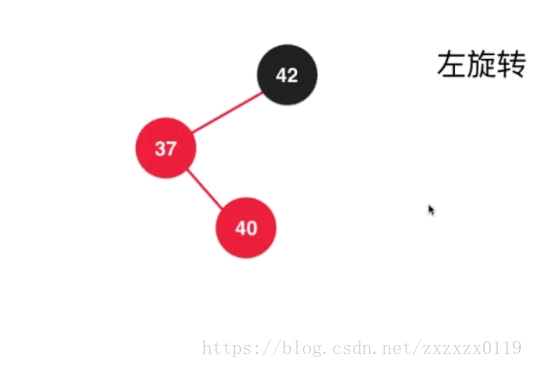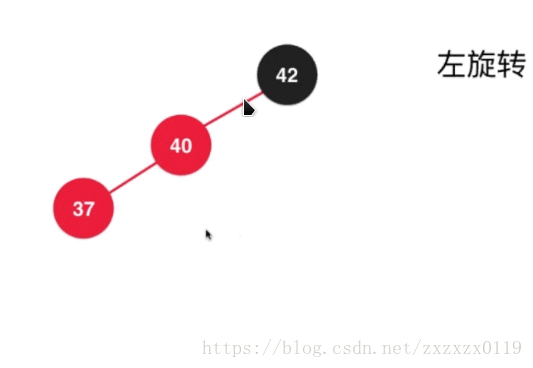
b.对上面的结果进行右旋转,并且调整颜色 :
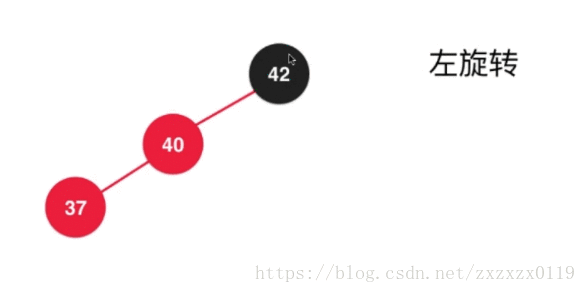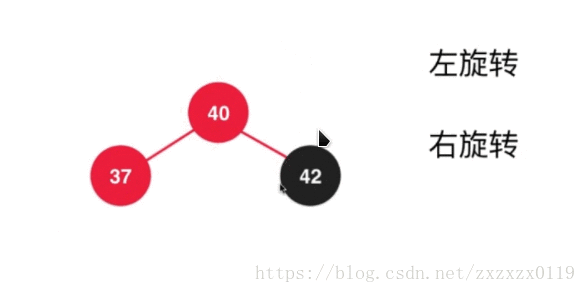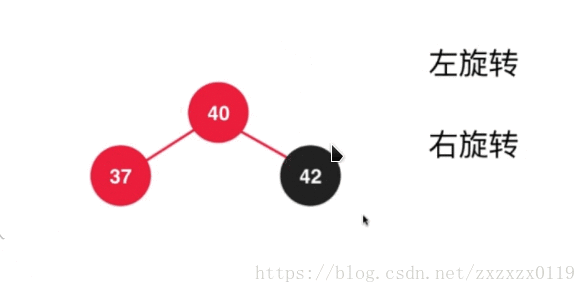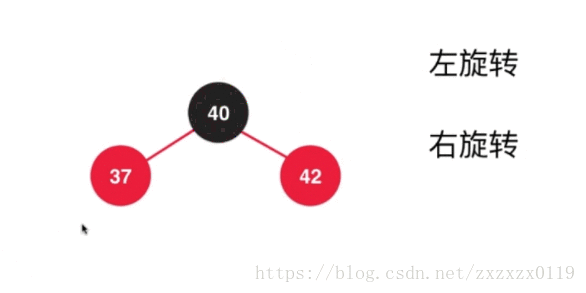
c.最后进行之前的颜色翻转(filpColors):
- 总结 : 所以我们发现,其实就是三种基本操作: 左旋转,右旋转,颜色翻转的结合

所以这是一个维护链,放在add中代码如下:
/** 向红黑树中添加新的元素(key, value) */
public void add(K key, V value) {//相当于JDK的put操作
root = add(root, key, value);
root.color = BLACK; /**子过程一: 保持最终根节点为黑色 --> 第二条性质 */
}
// 向以node为根的红黑树树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法,返回插入新节点后红黑树树的根
private Node add(Node node, K key, V value) {
if (node == null) {
size++;
return new Node(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
node.value = value;
/**维护链: 注意三个if不是互斥的 就是一个维护链的关系 */
if(isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)){ //右红,左黑 -> 左旋
node = leftRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)){ //左红 左左红 -> 右旋
node = rightRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)){//左红右红自己黑 -->颜色翻转
flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
重点在这段代码,就是三种基本的维护组成的维护链:
/**维护链: 注意三个if不是互斥的 就是一个维护链的关系 */
if(isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)){ //右红,左黑 -> 左旋
node = leftRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)){ //左红 左左红 -> 右旋
node = rightRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)){//左红右红自己黑 -->颜色翻转
flipColors(node);
}
添加中维护红黑树的代码
这里完成了左倾红黑树的add操作 : ,没有实现remove(),完整测试源码如下:
package DataStructure.Tree.RB;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* 红黑树实现 BSTMap中拷贝过来的
*/
public class RBTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private final static boolean RED = true;
private final static boolean BLACK = false;
private class Node {
public K key;
public V value;
public Node left, right;
public boolean color;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
left = null;
right = null;
// 一开始添加的时候都是红结点
color = RED; //为什么一开始是红色,因为在2-3结点中添加一个结点,永远是和叶子结点进行融合,所以是3节点,所以设置成红色
}
}
private Node root;
private int size;
public RBTree() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/** 判断节点node的颜色 */
private boolean isRed(Node node){
if(node == null) return BLACK;
return node.color;
}
/**左旋转
node x
/ \ --> / \
T1 x node T3
/ \ / \
T2 T3 T1 T2
*/
private Node leftRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.right;
Node T2 = x.left;
x.left = node;
node.right = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
/**右旋转
node x
/ \ / \
x T1 --> y node
/ \ / \ / \
y T2 T4 T3 T2 T1
/ \
T4 T3
*/
private Node rightRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = node;
node.left = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
/**三个节点的颜色反转 根->RED 两个孩子->BLACK */
private void flipColors(Node node){
node.color = RED;
node.left.color = BLACK;
node.right.color = BLACK;
}
/** 向红黑树中添加新的元素(key, value) */
public void add(K key, V value) {//相当于JDK的put操作
root = add(root, key, value);
root.color = BLACK; /**子过程一: 保持最终根节点为黑色 --> 第二条性质 */
}
// 向以node为根的红黑树树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法,返回插入新节点后红黑树树的根
private Node add(Node node, K key, V value) {
if (node == null) {
size++;
return new Node(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
node.value = value;
/**维护链: 注意三个if不是互斥的 就是一个维护链的关系 */
if(isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)){ //右红,左黑 -> 左旋
node = leftRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)){ //左红 左左红 -> 右旋
node = rightRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)){
flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
// 返回以node为根节点的红黑树中,key所在的节点
private Node getNode(Node node, K key) {
if (node == null)
return null;
if (key.equals(node.key))
return node;
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
return getNode(node.left, key);
else // if(key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
return getNode(node.right, key);
}
public boolean contains(K key) {
return getNode(root, key) != null;
}
public V get(K key) {
Node node = getNode(root, key);
return node == null ? null : node.value;
}
public void set(K key, V newValue) {
Node node = getNode(root, key);
if (node == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
node.value = newValue;
}
// 返回以node为根的红黑树的最小值所在的节点
private Node minimum(Node node) {
if (node.left == null)
return node;
return minimum(node.left);
}
// 删除掉以node为根的红黑树中的最小节点,返回删除节点后新的红黑树的根
private Node removeMin(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
size--;
return rightNode;
}
node.left = removeMin(node.left);
return node;
}
//没有实现remove中的调整
public V remove(K key) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No remove in RBTree!");
}
public void printTree(){
printTree(root,0,"H",8);
}
public void printTree(Node head,int height,String to,int len){
if(head == null)return;
printTree(head.right,height + 1,"v",len);
String val = to + head.key + to; //两边指示的字符
int lenV = val.length();
int lenL = (len - lenV)/2; //左边的空格(分一半)
int lenR = len - lenV - lenL; // 右边的空格
System.out.println( getSpace(len * height) + getSpace(lenL) + val + getSpace(lenR));
printTree(head.left,height + 1,"^",len);
}
public static String getSpace(int len){
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) str.append(" ");
return str.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer[] arr = {42,33,50,17,37,48,88,12,18,66,6};
// Arrays.sort(arr); //排序后插入也会保持平衡 但是BST会退化成链表
RBTree<Integer,Integer>rbTree = new RBTree<>();
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
rbTree.add(arr[i],null);
}
rbTree.printTree();
}
}
测试结果:

和这颗红黑树是一样的:

二叉树打印见这里。
使用LeetCode804. Unique Morse Code Words测试红黑树
题目链接
题目

解析
题目很简单,就是要你解析字符串之后看有多少种不同的翻译,使用HashSet和TreeSet都可以做,这里用RBTree改装的Set来测试(类似JDK中的TreeSet):
class Solution {
public int uniqueMorseRepresentations(String[] words) {
String[] codes = {".-","-...","-.-.","-..",".","..-.","--.","....","..",".---","-.-",".-..","--","-.","---",".--.","--.-",".-.","...","-","..-","...-",".--","-..-","-.--","--.."};
RBTree<String, Object> set = new RBTree<>();
for(String word: words){
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for(int i = 0 ; i < word.length() ; i ++)
res.append(codes[word.charAt(i) - 'a']);
set.add(res.toString(), null);
}
return set.getSize();
}
private class RBTree<K extends Comparable<K>, V> {
private final static boolean RED = true;
private final static boolean BLACK = false;
private class Node {
public K key;
public V value;
public Node left, right;
public boolean color;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
left = null;
right = null;
// 一开始添加的时候都是红结点
color = RED; //为什么一开始是红色,因为在2-3结点中添加一个结点,永远是和叶子结点进行融合,所以是3节点,所以设置成红色
}
}
private Node root;
private int size;
public RBTree() {
root = null;
size = 0;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
/** 判断节点node的颜色 */
private boolean isRed(Node node){
if(node == null) return BLACK;
return node.color;
}
/**左旋转
node x
/ \ --> / \
T1 x node T3
/ \ / \
T2 T3 T1 T2
*/
private Node leftRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.right;
Node T2 = x.left;
x.left = node;
node.right = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
/**右旋转
node x
/ \ / \
x T1 --> y node
/ \ / \ / \
y T2 T4 T3 T2 T1
/ \
T4 T3
*/
private Node rightRotate(Node node){
Node x = node.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = node;
node.left = T2;
//update color
x.color = node.color;
node.color = RED;
return x;
}
/**三个节点的颜色反转 根->RED 两个孩子->BLACK */
private void flipColors(Node node){
node.color = RED;
node.left.color = BLACK;
node.right.color = BLACK;
}
/** 向红黑树中添加新的元素(key, value) */
public void add(K key, V value) {//相当于JDK的put操作
root = add(root, key, value);
root.color = BLACK; /**子过程一: 保持最终根节点为黑色 --> 第二条性质 */
}
// 向以node为根的红黑树树中插入元素(key, value),递归算法,返回插入新节点后红黑树树的根
private Node add(Node node, K key, V value) {
if (node == null) {
size++;
return new Node(key, value);
}
if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
node.left = add(node.left, key, value);
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
node.right = add(node.right, key, value);
else // key.compareTo(node.key) == 0
node.value = value;
/**维护链: 注意三个if不是互斥的 就是一个维护链的关系 */
if(isRed(node.right) && !isRed(node.left)){ //右红,左黑 -> 左旋
node = leftRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.left.left)){ //左红 左左红 -> 右旋
node = rightRotate(node);
}
if(isRed(node.left) && isRed(node.right)){
flipColors(node);
}
return node;
}
// 返回以node为根节点的红黑树中,key所在的节点
private Node getNode(Node node, K key) {
if (node == null)
return null;
if (key.equals(node.key))
return node;
else if (key.compareTo(node.key) < 0)
return getNode(node.left, key);
else // if(key.compareTo(node.key) > 0)
return getNode(node.right, key);
}
public boolean contains(K key) {
return getNode(root, key) != null;
}
public V get(K key) {
Node node = getNode(root, key);
return node == null ? null : node.value;
}
public void set(K key, V newValue) {
Node node = getNode(root, key);
if (node == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
node.value = newValue;
}
// 返回以node为根的红黑树的最小值所在的节点
private Node minimum(Node node) {
if (node.left == null)
return node;
return minimum(node.left);
}
// 删除掉以node为根的红黑树中的最小节点,返回删除节点后新的红黑树的根
private Node removeMin(Node node) {
if (node.left == null) {
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = null;
size--;
return rightNode;
}
node.left = removeMin(node.left);
return node;
}
//没有实现remove中的调整
public V remove(K key) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("No remove in RBTree!");
}
}
}





 本文深入讲解了红黑树的基本概念,包括其与2-3树的关系、性质理解、添加元素的过程及代码实现,并通过LeetCode题例进行了测试验证。
本文深入讲解了红黑树的基本概念,包括其与2-3树的关系、性质理解、添加元素的过程及代码实现,并通过LeetCode题例进行了测试验证。
















 515
515

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








