CompletableFuture学习的小例子
CompletableFuture<String> objectCompletableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "1";
});
// objectCompletableFuture.thenApply(r -> {
// System.out.println(r);
// return "2";
// });
// objectCompletableFuture.thenApply(r -> {
// System.out.println(r);
// return "2";
// });
objectCompletableFuture.thenApply(r -> {
System.out.println(r);
return "3";
}).whenComplete((result, t) -> {
System.out.println(result);
});
Thread.sleep(20000L);
任务执行
下面的分析都是假设CompletableFuture线程未执行完的情况
调用CompletableFuture#supplyAsync方法
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier); // 默认线程池
}
static <U> CompletableFuture<U> asyncSupplyStage(Executor e,
Supplier<U> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<U> d = new CompletableFuture<U>();// new一个CompletableFuture
e.execute(new AsyncSupply<U>(d, f));// 执行一个新线程
return d;
}
static final class AsyncSupply<T> extends ForkJoinTask<Void>
implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
CompletableFuture<T> dep; Supplier<T> fn;
AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture<T> dep, Supplier<T> fn) {
this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;
}
public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }
public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}
public final boolean exec() { run(); return true; }
public void run() {
CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<T> f;
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
dep = null; fn = null;
if (d.result == null) {
try {
d.completeValue(f.get()); // completeValue方法会把f的执行结果赋值到CompletableFuture#result
} catch (Throwable ex) {
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
d.postComplete(); // 通知完成(先跳过这步,假设在上边sleep了)
}
}
}
假设run方法没有跑完,则CompletableFuture#supplyAsync方法直接放回一个新CompletableFuture对象。
此时调用CompletableFuture#thenApply方法
public <U> CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(
Function<? super T,? extends U> fn) {
return uniApplyStage(null, fn);
}
private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(
Executor e, Function<? super T,? extends V> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<V> d = new CompletableFuture<V>(); // 又new一个CompletableFuture
if (e != null || !d.uniApply(this, f, null)) { // e默认为空,后面的uniApply会判断this(也就是supplyAsync方法new的第一个CompletableFuture)是否执行完(result是否null),为空就走这个if
UniApply<T,V> c = new UniApply<T,V>(e, d, this, f);// new一个UniApply对象,把this和新new的CompletableFuture封装一下
push(c);// push到this的stack中
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
return d;// 返回新new的CompletableFuture
}
此时的supplyAsync返回的CompletableFuture结构。CompletableFuture#stack存了封装了两个CompletableFuture对象的UniApply对象。
类图只是为了展示结构,不标准的哈
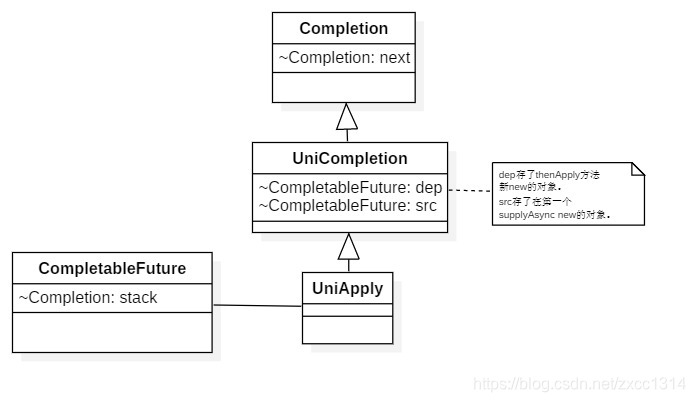
thenApply返回新new的CompletableFuture,再调用CompletableFuture#whenComplete方法。和CompletableFuture#supplyAsync方法类似,只是封装类变成了UniWhenComplete。
public CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action) {
return uniWhenCompleteStage(null, action);
}
private CompletableFuture<T> uniWhenCompleteStage(
Executor e, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<T> d = new CompletableFuture<T>();
if (e != null || !d.uniWhenComplete(this, f, null)) {
UniWhenComplete<T> c = new UniWhenComplete<T>(e, d, this, f);
push(c);
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
return d;
}
类图只是为了展示结构,不标准的哈
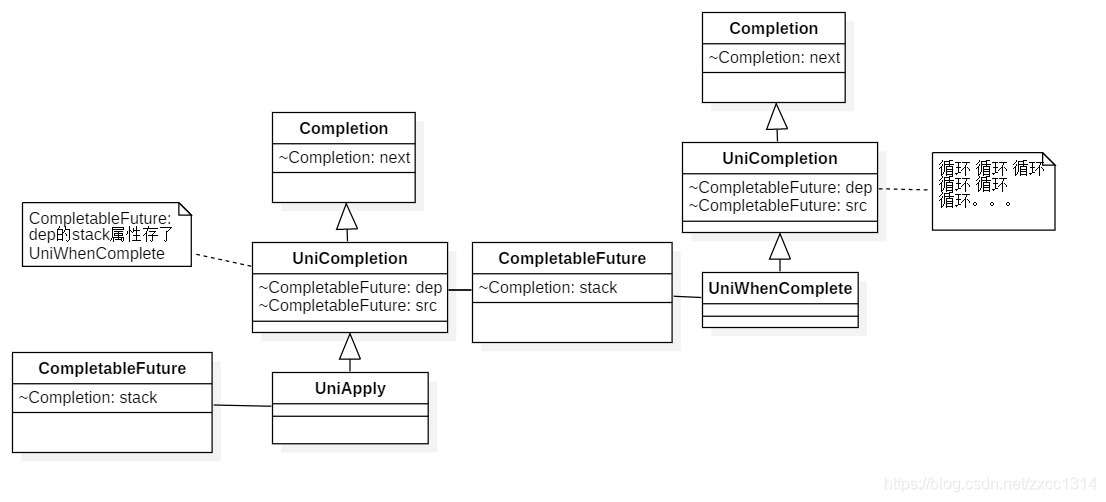
现在把文章开头的注释打开,这样会把新new的CompletableFuture的封装类添加到CompletableFuture.Completion#next中,变成一个链表。
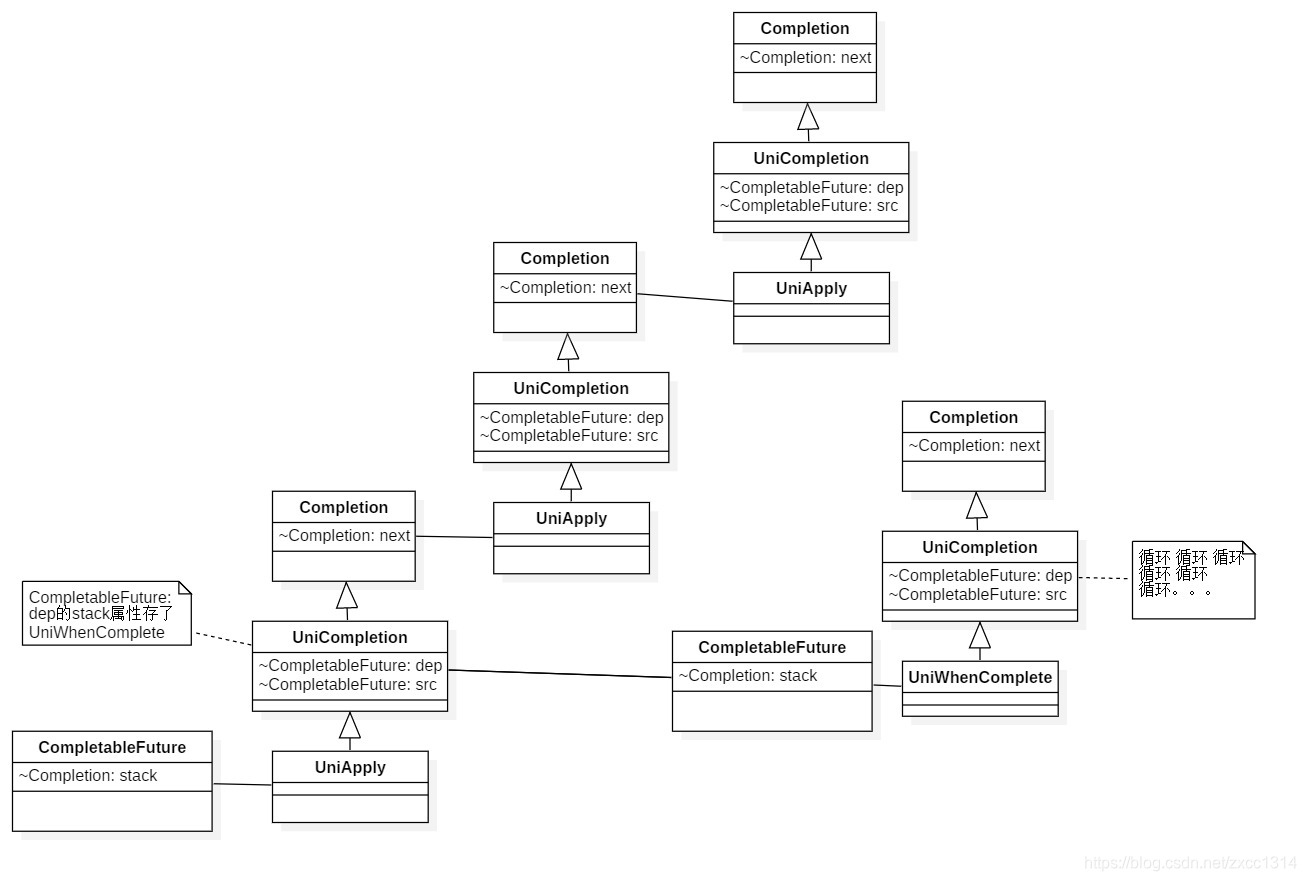
next存储的是使用同一个对象执行thenApply等方法形成的链表,而dep存储的是使用每个thenApply等方法返回的CompletableFuture形成的stack?(看起来像链表)。
异步任务执行结果回调
回到CompletableFuture#supplyAsync方法execute的Runnable,当任务执行完会调用CompletableFuture#postComplete方法。这个方法逻辑比较绕,不想看可以跳过,功能是执行上面添加的所有的lambda回调。
final void postComplete() {
/*
* 在每个步骤中,变量f将当前依赖项保存为弹出和运行。 它一次只沿一条路径扩展,推动其他路径以避免无限制的递归。
*/
CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;
while ((h = f.stack) != null || // h临时存放了this stack
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) { // 将next链表cas到stack中
if (t != null) {
if (f != this) { // 如果f不等于this,则将添加到当前的stack中
pushStack(h); // 这样操作会使得,之前多级结构,变成同一个Stack
continue;
}
h.next = null; // detach
}
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d; // tryFire会执行上述添加的所有lambda回调
}
}
}
Dubbo 2.7.x 全链路异步
http://dubbo.apache.org/zh-cn/docs/user/demos/async-execute-on-provider.html
NettyServerHandler#channelRead方法,Netty IO线程接收到请求。
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
NettyChannel channel = NettyChannel.getOrAddChannel(ctx.channel(), url, handler);
try {
handler.received(channel, msg);
} finally {
NettyChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(ctx.channel());
}
}
经过几层调用后会调用到AllChannelHandler#received方法。会把请求分发到Dubbo内部的Executor。直接返回释放Netty的IO线程。
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
ExecutorService executor = getExecutorService();
try {
executor.execute(new ChannelEventRunnable(channel, handler, ChannelState.RECEIVED, message));
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 异常处理,省略
}
}
dubbo内部线程执行后,再经过几层调用后会调用HeaderExchangeHandler#handleRequest方法。
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException {
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
/**
* 参数校验,省略
*/
Object msg = req.getData();
try {
// handle data.
CompletableFuture<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg); // 最终会调用自己实现的Service
if (future.isDone()) {
res.setStatus(Response.OK);
res.setResult(future.get());
channel.send(res);
return;
}
future.whenComplete((result, t) -> {
try {
if (t == null) {
res.setStatus(Response.OK);
res.setResult(result);
} else {
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
}
channel.send(res);
} catch (RemotingException e) {
logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + e);
} finally {
// HeaderExchangeChannel.removeChannelIfDisconnected(channel);
}
});
} catch (Throwable e) {
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e));
channel.send(res);
}
}
如果Service实现了CompletableFuture,则可以把业务处理放到业务线程,释放掉Dubbo线程。
public class AsyncServiceImpl implements AsyncService {
@Override
public CompletableFuture<String> sayHello(String name) {
RpcContext savedContext = RpcContext.getContext();
// 建议为supplyAsync提供自定义线程池,避免使用JDK公用线程池
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(savedContext.getAttachment("consumer-key1"));
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "async response from provider.";
});
}
}
优秀!~










 本文深入探讨了Java中CompletableFuture的使用,包括supplyAsync、thenApply和whenComplete方法的工作原理,展示了如何通过CompletableFuture实现全链路异步处理,提高程序效率。
本文深入探讨了Java中CompletableFuture的使用,包括supplyAsync、thenApply和whenComplete方法的工作原理,展示了如何通过CompletableFuture实现全链路异步处理,提高程序效率。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








