1、例子2
先构造结构,再初始化这个结构,让它们活动起来
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
x_data=np.random.rand(100).astype(np.float32)
y_data=x_data*0.1+0.3
#create tensorflow structure start
Weights=tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([1],-1.0,1.0))
biases=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
y=Weights*x_data+biases
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_data))
optimizer=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5)
train=optimizer.minimize(loss)
init=tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess=tf.Session()
sess.run(init) #很重要
for step in range(201):
sess.run(train)
if step%20==0:
print(step,sess.run(Weights),sess.run(biases))#每隔20次,输出权重W和B
输出的结果是:
0 [0.6654811] [0.00397022]
20 [0.24498683] [0.22517873]
40 [0.13706154] [0.2808742]
60 [0.10947368] [0.29511106]
80 [0.10242166] [0.2987503]
100 [0.10061904] [0.29968056]
120 [0.10015826] [0.29991835]
140 [0.10004047] [0.29997912]
160 [0.10001035] [0.29999468]
180 [0.10000264] [0.29999864]
200 [0.10000066] [0.29999965]
2、Session会话控制
session:执行命令,对话的控制,实现创造好的结构上的特定点的功能
每次run一下,才执行(tensorflow结构)
其中:sess.close()有和没有差不多,有的话,更为整洁和系统一点
import tensorflow as tf
matrix1=tf.constant([[3,3]])
matrix2=tf.constant([[2],[2]])
product=tf.matmul(matrix1,matrix2) #matrix multiply np.dot()
#method1
sess=tf.Session()
result=sess.run(product)
print(result)
sess.close()
#method2
with tf.Session() as sess:
result2=sess.run(product)
print(result2)###这个方法会自动close,即,sess.close()
运行结果
[[12]]
[[12]]
3、Variable变量
一定要定义成是一个变量,他才是一个变量
import tensorflow as tf
state = tf.Variable(0,name='counter') # our first variable in the "global_variable" set
#print(state.name)
one=tf.constant(1)
new_value = tf.add(state, one)
update = tf.assign(state, new_value)
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# once define variables, you have to initialize them by doing this
sess.run(init)
for i in range(3):
sess.run(update)
print(sess.run(state))
#如果有定义,variable,一定要有init,再run
#如果有定义,variable,一定要有init,再run
4、placeholder传入值
variable 已经规定好初始自,placeholder是运行时才传入初始值,先占坑,然后每一次从外界传入一个值
import tensorflow as tf
x1 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
y1 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=None)
z1 = x1 + y1
x2 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[2, 1])
y2 = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[1, 2])
z2 = tf.matmul(x2, y2)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# when only one operation to run
z1_value = sess.run(z1, feed_dict={x1: 1, y1: 2})
print(z1_value)
# when run multiple operations
z1_value, z2_value = sess.run(
[z1, z2], # run them together
feed_dict={
x1: 3, y1: 2,
x2: [[2], [2]], y2: [[3, 3]]
})
print(z1_value)
print(z2_value)
结果是:
3.0
5.0
[[6. 6.]
[6. 6.]]
5、什么是激励函数(深度学习)
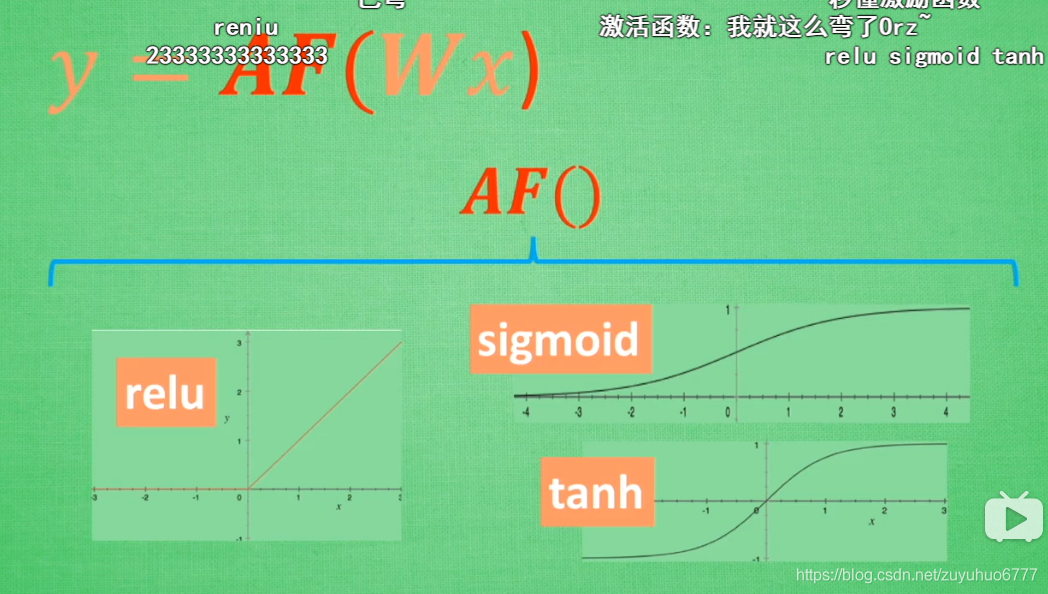
非线性=激活函数(掰弯)
曲线性化
卷积网络使用Relu,RNN使用Relu或者Tanh
6、激励函数 Activation function
让一些神经元先激活起来,让这些信息传递给后面(数值提高)
7、添加层

emmm,中间断了一层,之前写的没有了
16、分类学习
输出概率值
17、什么是过拟合(overfitting)
过拟合=自负
解决方法:1、增加数据量
2、正则化:

w为学习的参数,再过拟合中,w一般会变化较大。如果w变化太大,cost也跟着变大
3、Dropout regularization
每一次都随机忽略一些神经元连接,
让每一次训练的结果,都不依赖其中一些特定的神经元(就像L1和L2一样,过度依赖的参数W会很大,L1和L2会惩罚这些大的参数),而droupout从根本上让神经网络,无法过度依赖
18、Dropout 解决overfitting





















 3210
3210

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








