Linux内存管理10(基于6.1内核)---内存初始化-bootmem_init初始化
一、初始化内存管理数据结构概述
上一篇在memblock完成之后, 内存初始化开始进入第二阶段, 第二阶段是一个漫长的过程, 它执行了一系列复杂的操作, 从体系结构相关信息的初始化慢慢向上层展开, 其主要执行了如下操作:
1.特定于体系结构的设置
在完成了基础的内存结点和内存域的初始化工作以后, 我们必须克服一些硬件的特殊设置。
- 在初始化内存的结点和内存区域之前, 内核先通过pagging_init初始化了内核的分页机制, 这样我们的虚拟运行空间就初步建立, 并可以完成物理地址到虚拟地址空间的映射工作。
在arm64架构下, 内核在start_kernel()->setup_arch()中通过arm64_memblock_init( )完成了memblock的初始化之后, 接着通过setup_arch()->paging_init()开始初始化分页机制。
paging_init负责建立只能用于内核的页表, 用户空间是无法访问的. 这对管理普通应用程序和内核访问内存的方式,有深远的影响。
- 在分页机制完成后, 内核通过setup_arch()->bootmem_init开始进行内存基本数据结构(内存结点pg_data_t, 内存域zone和页帧)的初始化工作, 就是在这个函数中, 内核开始从体系结构相关的部分逐渐展开到体系结构无关的部分, 在zone_sizes_init->free_area_init_node中开始, 内核开始进行内存基本数据结构的初始化, 也不再依赖于特定体系结构无关的层次。
bootmem_init()
始化内存数据结构包括内存节点, 内存域和页帧page
|
|---->arm64_numa_init();
| 支持numa架构
|
|---->zone_sizes_init(min, max);
来初始化节点和管理区的一些数据项
|
|---->free_area_init_node
| 初始化内存节点
|
|---->free_area_init_core
| 初始化zone
|
|---->memmap_init
| 初始化page页面
|
|---->memblock_dump_all();
| 初始化完成, 显示memblock的保留的所有内存信息
2.建立内存管理的数据结构
对相关数据结构的初始化是从全局启动函数start_kernel中开始的, 该函数在加载内核并激活各个子系统之后执行. 由于内存管理是内核一个非常重要的部分, 因此在特定体系结构的设置步骤中检测并确定系统中内存的分配情况后, 会立即执行内存管理的初始化。
3.移交早期的分配器到内存管理器
最后我们的内存管理器已经初始化并设置完成, 可以投入运行了, 因此内核将内存管理的工作从早期的内存分配器(bootmem或者memblock)移交到我们的buddy伙伴系统。
二、Start Initialization
2.1 回到setup_arch函数
回到start_kernel()->setup_arch()函数
void __init setup_arch(char **cmdline_p)
{
/* 初始化memblock */
arm64_memblock_init( );
/* 分页机制初始化 */
paging_init();
bootmem_init();
}
-
memblock已经通过arm64_memblock_init完成了初始化, 至此系统中的内存可以通过memblock分配了。
-
paging_init完成了分页机制的初始化, 至此内核已经布局了一套完整的虚拟内存空间。
至此我们所有的内存都可以通过memblock机制来分配和释放, 尽管它实现的笨拙而简易, 但是已经足够我们初始化阶段使用了, 反正内核页不可能指着它过一辈子, 而我们也通过pagging_init创建了页表, 为内核提供了一套可供内核和进程运行的虚拟运行空间, 我们可以安全的进行内存的分配。是时候初始化强大的buddy系统。
内核接着setup_arch()->bootmem_init()函数开始执行。
体系结构相关的代码需要在启动期间建立如下信息。
- 系统中各个内存域的页帧边界,保存在max_zone_pfn数组。
早期的内核还需记录各结点页帧的分配情况,保存在全局变量early_node_map中。
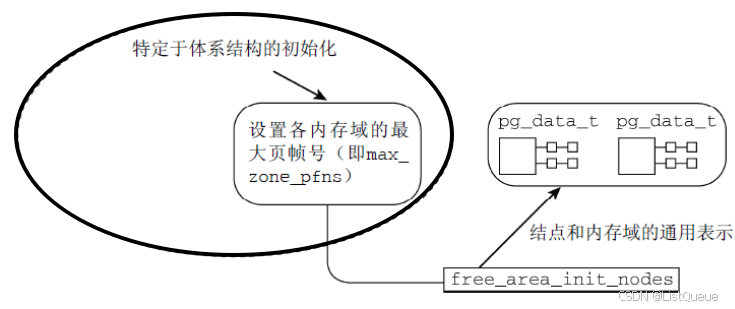
内核提供了一个通用的框架, 用于将上述信息转换为伙伴系统预期的节点和内存域数据结构, 但是在此之前各个体系结构必须自行建立相关结构。
2.2 bootmem_init函数初始化内存结点和管理域
arm64架构下, 在setup_arch中通过paging_init函数初始化内核分页机制之后, 内核通过bootmem_init()开始完成内存结点和内存区域的初始化工作。arch/arm64/mm/init.c
void __init bootmem_init(void)
{
unsigned long min, max;
min = PFN_UP(memblock_start_of_DRAM());
max = PFN_DOWN(memblock_end_of_DRAM());
early_memtest(min << PAGE_SHIFT, max << PAGE_SHIFT);
max_pfn = max_low_pfn = max;
min_low_pfn = min;
arch_numa_init();
/*
* must be done after arch_numa_init() which calls numa_init() to
* initialize node_online_map that gets used in hugetlb_cma_reserve()
* while allocating required CMA size across online nodes.
*/
#if defined(CONFIG_HUGETLB_PAGE) && defined(CONFIG_CMA)
arm64_hugetlb_cma_reserve();
#endif
kvm_hyp_reserve();
/*
* sparse_init() tries to allocate memory from memblock, so must be
* done after the fixed reservations
*/
sparse_init();
zone_sizes_init();
/*
* Reserve the CMA area after arm64_dma_phys_limit was initialised.
*/
dma_contiguous_reserve(arm64_dma_phys_limit);
/*
* request_standard_resources() depends on crashkernel's memory being
* reserved, so do it here.
*/
reserve_crashkernel();
memblock_dump_all();
}
2.3 zone_sizes_init函数
在初始化内存结点和内存域之前, 内核首先通过setup_arch()–>bootmem_init()–>zone_sizes_init()来初始化节点和管理区的一些数据项, 其中关键的是初始化了系统中各个内存域的页帧边界,保存在max_zone_pfn数组。arch/arm64/mm/init.c
static void __init zone_sizes_init(void)
{
unsigned long max_zone_pfns[MAX_NR_ZONES] = {0};
unsigned int __maybe_unused acpi_zone_dma_bits;
unsigned int __maybe_unused dt_zone_dma_bits;
phys_addr_t __maybe_unused dma32_phys_limit = max_zone_phys(32);
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA
acpi_zone_dma_bits = fls64(acpi_iort_dma_get_max_cpu_address());
dt_zone_dma_bits = fls64(of_dma_get_max_cpu_address(NULL));
zone_dma_bits = min3(32U, dt_zone_dma_bits, acpi_zone_dma_bits);
arm64_dma_phys_limit = max_zone_phys(zone_dma_bits);
max_zone_pfns[ZONE_DMA] = PFN_DOWN(arm64_dma_phys_limit);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ZONE_DMA32
max_zone_pfns[ZONE_DMA32] = PFN_DOWN(dma32_phys_limit);
if (!arm64_dma_phys_limit)
arm64_dma_phys_limit = dma32_phys_limit;
#endif
if (!arm64_dma_phys_limit)
arm64_dma_phys_limit = PHYS_MASK + 1;
max_zone_pfns[ZONE_NORMAL] = max_pfn;
free_area_init(max_zone_pfns);
}
在获取了三个管理区的页面数后,通过free_area_init()->free_area_init_node()来完成后续工作, 其中核心函数为free_area_init()->free_area_init_node(),用来针对特定的节点进行初始化。
截至到目前为止, 体系结构相关的部分已经结束了, 各个体系结构已经自行建立了自己所需的一些底层数据结构, 这些结构建立好以后, 内核将繁重的内存数据结构创建和初始化的工作交给free_area_init_node()函数来完成.
三、free_area_init_nodes初始化数据结构
3.1 free_area_init_node
mm/mm_init.c
static void __init free_area_init_node(int nid)
{
pg_data_t *pgdat = NODE_DATA(nid);
unsigned long start_pfn = 0;
unsigned long end_pfn = 0;
/* pg_data_t should be reset to zero when it's allocated */
WARN_ON(pgdat->nr_zones || pgdat->kswapd_highest_zoneidx);
get_pfn_range_for_nid(nid, &start_pfn, &end_pfn);
pgdat->node_id = nid;
pgdat->node_start_pfn = start_pfn;
pgdat->per_cpu_nodestats = NULL;
if (start_pfn != end_pfn) {
pr_info("Initmem setup node %d [mem %#018Lx-%#018Lx]\n", nid,
(u64)start_pfn << PAGE_SHIFT,
end_pfn ? ((u64)end_pfn << PAGE_SHIFT) - 1 : 0);
calculate_node_totalpages(pgdat, start_pfn, end_pfn);
} else {
pr_info("Initmem setup node %d as memoryless\n", nid);
reset_memoryless_node_totalpages(pgdat);
}
alloc_node_mem_map(pgdat);
pgdat_set_deferred_range(pgdat);
free_area_init_core(pgdat);
lru_gen_init_pgdat(pgdat);
}
free_area_init函数中通过循环遍历各个节点,循环中调用了free_area_init函数初始化该节点对应的pg_data_t和zone、page的数据.
3.2 设置可使用的页帧编号
free_area_init_nodes首先必须分析并改写特定于体系结构的代码提供的信息。其中,需要对照在zone_max_pfn和zone_min_pfn中指定的内存域的边界,计算各个内存域可使用的最低和最高的页帧编号。使用了两个全局数组来存储这些信息:mm/mm_init.c
static unsigned long arch_zone_lowest_possible_pfn[MAX_NR_ZONES] __initdata;
static unsigned long arch_zone_highest_possible_pfn[MAX_NR_ZONES] __initdata;
static unsigned long zone_movable_pfn[MAX_NUMNODES] __initdata;
通过max_zone_pfn传递给free_area_init_core的信息记录了各个内存域包含的最大页帧号。
free_area_init_core将该信息转换为一种更方便的表示形式,即以[low, high]形式描述各个内
存域的页帧区间,存储在前述的全局变量中:mm/mm_init.c
/**
* free_area_init - Initialise all pg_data_t and zone data
* @max_zone_pfn: an array of max PFNs for each zone
*
* This will call free_area_init_node() for each active node in the system.
* Using the page ranges provided by memblock_set_node(), the size of each
* zone in each node and their holes is calculated. If the maximum PFN
* between two adjacent zones match, it is assumed that the zone is empty.
* For example, if arch_max_dma_pfn == arch_max_dma32_pfn, it is assumed
* that arch_max_dma32_pfn has no pages. It is also assumed that a zone
* starts where the previous one ended. For example, ZONE_DMA32 starts
* at arch_max_dma_pfn.
*/
void __init free_area_init(unsigned long *max_zone_pfn)
{
unsigned long start_pfn, end_pfn;
int i, nid, zone;
bool descending;
/* Record where the zone boundaries are */
memset(arch_zone_lowest_possible_pfn, 0,
sizeof(arch_zone_lowest_possible_pfn));
memset(arch_zone_highest_possible_pfn, 0,
sizeof(arch_zone_highest_possible_pfn));
start_pfn = PHYS_PFN(memblock_start_of_DRAM());
descending = arch_has_descending_max_zone_pfns();
for (i = 0; i < MAX_NR_ZONES; i++) {
if (descending)
zone = MAX_NR_ZONES - i - 1;
else
zone = i;
if (zone == ZONE_MOVABLE)
continue;
end_pfn = max(max_zone_pfn[zone], start_pfn);
arch_zone_lowest_possible_pfn[zone] = start_pfn;
arch_zone_highest_possible_pfn[zone] = end_pfn;
start_pfn = end_pfn;
}
/* Find the PFNs that ZONE_MOVABLE begins at in each node */
memset(zone_movable_pfn, 0, sizeof(zone_movable_pfn));
find_zone_movable_pfns_for_nodes();
...
}
3.3 构建其他内存域的页帧区间
接下来构建其他内存域的页帧区间,方法很直接:第n个内存域的最小页帧,即前一个(第n-1个)内存域的最大页帧。当前内存域的最大页帧由max_zone_pfn给出mm/mm_init.c
void __init free_area_init(unsigned long *max_zone_pfn)
{
unsigned long start_pfn, end_pfn;
int i, nid, zone;
bool descending;
...
/* Find the PFNs that ZONE_MOVABLE begins at in each node */
memset(zone_movable_pfn, 0, sizeof(zone_movable_pfn));
/* 用于计算进入ZONE_MOVABLE的内存数量 */
find_zone_movable_pfns_for_nodes();
...
}
由于ZONE_MOVABLE是一个虚拟内存域,不与真正的硬件内存域关联,该内存域的边界总是设置为0。回忆前文,可知只有在指定了内核命令行参数kernelcore或movablecore之一时,该内存域才会存在.
该内存域一般开始于各个结点的某个特定内存域的某一页帧号。相应的编号在find_zone_movable_pfns_for_nodes里计算。
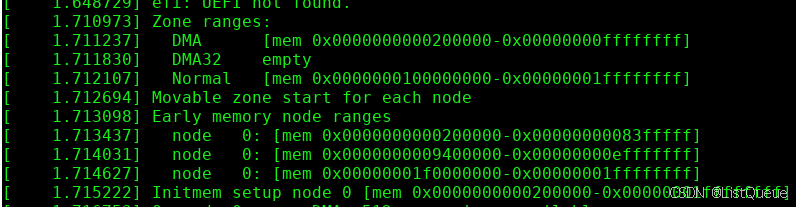
现在可以向用户提供一些有关已确定的页帧区间的信息。例如:arm64:
3.4 建立结点数据结构
free_area_init_nodes剩余的部分遍历所有结点,分别建立其数据结构
void __init free_area_init(unsigned long *max_zone_pfn)
{
unsigned long start_pfn, end_pfn;
int i, nid, zone;
bool descending;
...
for_each_node(nid) {
pg_data_t *pgdat;
if (!node_online(nid)) {
pr_info("Initializing node %d as memoryless\n", nid);
/* Allocator not initialized yet */
pgdat = arch_alloc_nodedata(nid);
if (!pgdat)
panic("Cannot allocate %zuB for node %d.\n",
sizeof(*pgdat), nid);
arch_refresh_nodedata(nid, pgdat);
free_area_init_node(nid);
/*
* We do not want to confuse userspace by sysfs
* files/directories for node without any memory
* attached to it, so this node is not marked as
* N_MEMORY and not marked online so that no sysfs
* hierarchy will be created via register_one_node for
* it. The pgdat will get fully initialized by
* hotadd_init_pgdat() when memory is hotplugged into
* this node.
*/
continue;
}
pgdat = NODE_DATA(nid);
free_area_init_node(nid);
/* Any memory on that node */
if (pgdat->node_present_pages)
node_set_state(nid, N_MEMORY);
check_for_memory(pgdat);
}
...
}
代码遍历所有活动结点,并分别对各个结点调用free_area_init_node建立数据结构。
四、free_area_init_core初始化内存域zone
初始化内存域数据结构涉及的繁重工作由free_area_init_core执行,它会依次遍历结点的所有内存域, 该函数定义mm/mm_init.c
4.1 free_area_init_core函数代码注释
/*
* Set up the zone data structures:
* - mark all pages reserved
* - mark all memory queues empty
* - clear the memory bitmaps
*
* NOTE: pgdat should get zeroed by caller.
* NOTE: this function is only called during early init.
*/
static void __init free_area_init_core(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
enum zone_type j;
int nid = pgdat->node_id;
pgdat_init_internals(pgdat);
pgdat->per_cpu_nodestats = &boot_nodestats;
for (j = 0; j < MAX_NR_ZONES; j++) {
struct zone *zone = pgdat->node_zones + j;
unsigned long size, freesize, memmap_pages;
size = zone->spanned_pages;
freesize = zone->present_pages;
/*
* Adjust freesize so that it accounts for how much memory
* is used by this zone for memmap. This affects the watermark
* and per-cpu initialisations
*/
memmap_pages = calc_memmap_size(size, freesize);
if (!is_highmem_idx(j)) {
if (freesize >= memmap_pages) {
freesize -= memmap_pages;
if (memmap_pages)
pr_debug(" %s zone: %lu pages used for memmap\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages);
} else
pr_warn(" %s zone: %lu memmap pages exceeds freesize %lu\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages, freesize);
}
/* Account for reserved pages */
if (j == 0 && freesize > dma_reserve) {
freesize -= dma_reserve;
pr_debug(" %s zone: %lu pages reserved\n", zone_names[0], dma_reserve);
}
if (!is_highmem_idx(j))
nr_kernel_pages += freesize;
/* Charge for highmem memmap if there are enough kernel pages */
else if (nr_kernel_pages > memmap_pages * 2)
nr_kernel_pages -= memmap_pages;
nr_all_pages += freesize;
/*
* Set an approximate value for lowmem here, it will be adjusted
* when the bootmem allocator frees pages into the buddy system.
* And all highmem pages will be managed by the buddy system.
*/
zone_init_internals(zone, j, nid, freesize);
if (!size)
continue;
setup_usemap(zone);
init_currently_empty_zone(zone, zone->zone_start_pfn, size);
}
}
4.2 流程讲解
初始化内存域数据结构涉及的繁重工作由free_area_init_core执行,它会依次遍历结点的所有内存域
static void __init free_area_init_core(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
enum zone_type j;
int nid = pgdat->node_id;
...
/* 遍历每个管理区 */
for (j = 0; j < MAX_NR_ZONES; j++) {
struct zone *zone = pgdat->node_zones + j;
unsigned long size, freesize, memmap_pages;
/* size为该管理区中的页框数,包括洞 */
size = zone->spanned_pages;
/* realsize为管理区中的页框数,不包括洞 /
realsize = freesize = zone->present_pages;
...
}
内存域的真实长度,可通过跨越的页数减去空洞覆盖的页数而得到。其复杂性实质上取决于内存模型和所选定的配置选项,但所有变体最终都没有什么意外之处。
static void __init free_area_init_core(struct pglist_data *pgdat)
{
enum zone_type j;
int nid = pgdat->node_id;
...
if (!is_highmem_idx(j)) {
if (freesize >= memmap_pages) {
freesize -= memmap_pages;
if (memmap_pages)
pr_debug(" %s zone: %lu pages used for memmap\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages);
} else
pr_warn(" %s zone: %lu memmap pages exceeds freesize %lu\n",
zone_names[j], memmap_pages, freesize);
}
/* Account for reserved pages */
if (j == 0 && freesize > dma_reserve) {
freesize -= dma_reserve;
pr_debug(" %s zone: %lu pages reserved\n", zone_names[0], dma_reserve);
}
if (!is_highmem_idx(j))
nr_kernel_pages += freesize;
/* Charge for highmem memmap if there are enough kernel pages */
else if (nr_kernel_pages > memmap_pages * 2)
nr_kernel_pages -= memmap_pages;
nr_all_pages += freesize;
/*
* Set an approximate value for lowmem here, it will be adjusted
* when the bootmem allocator frees pages into the buddy system.
* And all highmem pages will be managed by the buddy system.
*/
zone_init_internals(zone, j, nid, freesize);
if (!size)
continue;
setup_usemap(zone);
init_currently_empty_zone(zone, zone->zone_start_pfn, size);
...
}
内核使用两个全局变量跟踪系统中的页数。nr_kernel_pages统计所有一致映射的页,而nr_all_pages还包括高端内存页在内free_area_init_core始化为0
free_area_init_core()->zone_init_internals()->zone_pcp_init()
-
zone_pcp_init尝试初始化该内存域的per-CPU缓存。
-
init_currently_empty_zone初始化free_area列表,并将属于该内存域的所有page实例都设置为初始默认值。
所有页属性起初都设置MIGRATE_MOVABLE。
五、memmap_init初始化page页面
在free_area_init_core初始化内存管理区zone的过程中, 通过memmap_init函数对每个内存管理区zone的page内存进行了初始化
memmap_init函数定义mm/mm_init.c
static void __init memmap_init(void)
{
unsigned long start_pfn, end_pfn;
unsigned long hole_pfn = 0;
int i, j, zone_id = 0, nid;
for_each_mem_pfn_range(i, MAX_NUMNODES, &start_pfn, &end_pfn, &nid) {
struct pglist_data *node = NODE_DATA(nid);
for (j = 0; j < MAX_NR_ZONES; j++) {
struct zone *zone = node->node_zones + j;
if (!populated_zone(zone))
continue;
memmap_init_zone_range(zone, start_pfn, end_pfn,
&hole_pfn);
zone_id = j;
}
}
#ifdef CONFIG_SPARSEMEM
/*
* Initialize the memory map for hole in the range [memory_end,
* section_end].
* Append the pages in this hole to the highest zone in the last
* node.
* The call to init_unavailable_range() is outside the ifdef to
* silence the compiler warining about zone_id set but not used;
* for FLATMEM it is a nop anyway
*/
end_pfn = round_up(end_pfn, PAGES_PER_SECTION);
if (hole_pfn < end_pfn)
#endif
init_unavailable_range(hole_pfn, end_pfn, zone_id, nid);
}
memmap_init_zone函数完成了page的初始化工作, 该函数定义mm/mm_init.c。节点和管理区的关键数据已完成初始化,内核在后面为内存管理做得一个准备工作就是将所有节点的管理区都链入到zonelist中,便于后面内存分配工作的进行。
内核在start_kernel()–>mm_core_init()->build_all_zonelist()中完成zonelist的初始化。
六、bootmem_init总结
6.1 start_kernel启动流程
init/main.c
start_kernel()
|---->page_address_init()
| 考虑支持高端内存
| 业务:初始化page_address_pool链表;
| 将page_address_maps数组元素按索引降序插入
| page_address_pool链表;
| 初始化page_address_htable数组.
|
|---->setup_arch(&command_line);
| 初始化特定体系结构的内容
|---->arm64_memblock_init( ); [参见memblock和bootmem]
| 初始化引导阶段的内存分配器memblock
|
|---->paging_init(); [参见分页机制初始化paging_init]
| 分页机制初始化
|
|---->bootmem_init(); [与build_all_zonelist共同完成内存数据结构的初始化]
| 初始化内存数据结构包括内存节点和内存域
|
|---->setup_per_cpu_areas();
| 为per-CPU变量分配空间
|
|---->mm_core_init---->build_all_zonelist() [bootmem_init初始化数据结构, 该函数初始化zonelists]
| 为系统中的zone建立后备zone的列表.
| 所有zone的后备列表都在
| pglist_data->node_zonelists[0]中;
|
| 期间也对per-CPU变量boot_pageset做了初始化.
|
|---->mm_core_init---->page_alloc_init()
|---->hotcpu_notifier(page_alloc_cpu_notifier, 0);
| 不考虑热插拔CPU
|
|
|---->vfs_caches_init_early()
|---->dcache_init_early()
| dentry_hashtable空间,d_hash_shift, h_hash_mask赋值;
| 同pidhash_init();
| 区别:
| 散列度变化了(13 - PAGE_SHIFT);
| 传入alloc_large_system_hash的最后参数值为0;
|
|---->inode_init_early()
| inode_hashtable空间,i_hash_shift, i_hash_mask赋值;
| 同pidhash_init();
| 区别:
| 散列度变化了(14 - PAGE_SHIFT);
| 传入alloc_large_system_hash的最后参数值为0;
|
6.2 build_all_zonelists初始化每个内存节点的zonelists
mm/page_alloc.c
void build_all_zonelists(void)
|---->set_zonelist_order()
|---->build_all_zonelists_init->current_zonelist_order = ZONELIST_ORDER_ZONE;
|
|---->__build_all_zonelists(NULL);
| Memory不支持热插拔, 为每个zone建立后备的zone,
| 每个zone及自己后备的zone,形成zonelist
|
|---->pg_data_t *pgdat = NULL;
| pgdat = &contig_page_data;(单node)
|
|---->build_zonelists(pgdat);
| 为每个zone建立后备zone的列表
|
|---->struct zonelist *zonelist = NULL;
| enum zone_type j;
| zonelist = &pgdat->node_zonelists[0];
|
|---->j = build_zonelists_node(pddat, zonelist, 0, MAX_NR_ZONES - 1);
| 为pgdat->node_zones[0]建立后备的zone,node_zones[0]后备的zone
| 存储在node_zonelist[0]内,对于node_zone[0]的后备zone,其后备的zone
| 链表如下(只考虑UMA体系,而且不考虑ZONE_DMA):
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[0].zone = &node_zones[2];
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[0].zone_idx = 2;
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[1].zone = &node_zones[1];
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[1].zone_idx = 1;
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[2].zone = &node_zones[0];
| node_zonelist[0]._zonerefs[2].zone_idx = 0;
|
| zonelist->_zonerefs[3].zone = NULL;
| zonelist->_zonerefs[3].zone_idx = 0;
|
|---->build_zonelist_cache(pgdat);
|---->pdat->node_zonelists[0].zlcache_ptr = NULL;
| UMA体系结构
|
|---->for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
| setup_pageset(&per_cpu(boot_pageset, cpu), 0);
|详见下文
|---->vm_total_pages = nr_free_pagecache_pages();
| 业务:获得所有zone中的present_pages总和.
|
|---->page_group_by_mobility_disabled = 0;
| 对于代码中的判断条件一般不会成立,因为页数会最够多(内存较大)





















 1809
1809

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








