Summary
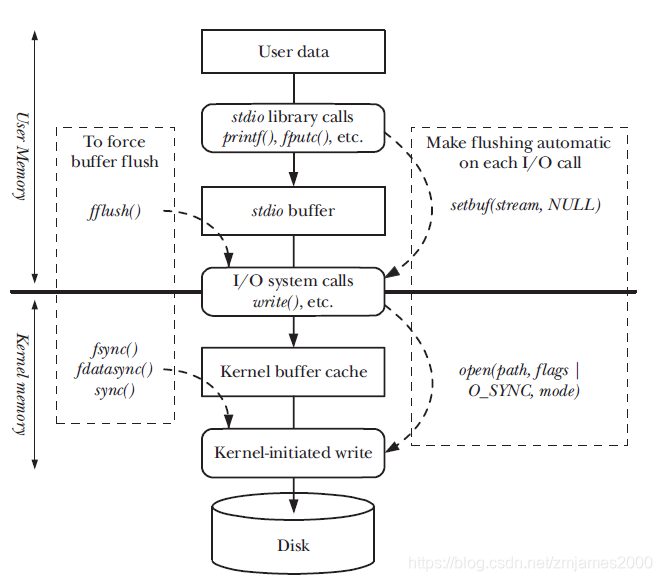
Buffering of input and output data is performed by the kernel, and also by the stdio library. In some cases, we may wish to prevent buffering, but we need to be aware of the impact this has on application performance. Various system calls and library
functions can be used to control kernel and stdio buffering and to perform one-off buffer flushes.
A process can use posix_fadvise() to advise the kernel of its likely pattern for accessing data from a specified file.
The kernel may use this information to optimize the use of the buffer cache, thus improving I/O performance.
The Linux-specific open() O_DIRECT flag allows specialized applications to bypass the buffer cache.
The fileno() and fdopen() functions assist us with the task of mixing system calls and standard C library functions to perform I/O on the same file. Given a stream, fileno() returns the corresponding file descriptor; fdopen() performs the converse operation, creating a new stream that employs a specified open file descriptor.





 本文探讨了Linux环境下输入输出缓冲机制,包括内核及标准I/O库如何进行缓冲,以及如何通过系统调用和库函数控制缓冲行为,实现性能优化。文章还介绍了通过posix_fadvise()和open()的O_DIRECT标志来提升I/O性能的方法。
本文探讨了Linux环境下输入输出缓冲机制,包括内核及标准I/O库如何进行缓冲,以及如何通过系统调用和库函数控制缓冲行为,实现性能优化。文章还介绍了通过posix_fadvise()和open()的O_DIRECT标志来提升I/O性能的方法。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








