论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.00752
注:无监督看的第一篇
Abstract
有监督学习在现实世界的应用中由于数据标注的缺失和领域空白,使其具有局限性。而无监督学习通过领域适应去学习,这对人很有吸引力,但是却充满挑战。现阶段的无监督学习方法在通过距离正确辩别正样本和负样本的方法下,经常失败。因为这两种样本往往具有很大的重叠性,不容易分开。为了解决这个问题,我们提出了一种叫做GDS的方法,我们从全局的角度区分开正样本和负样本。我们对两个全局距离以高斯分布的方法进行建模并且在无监督的训练过程中,将两者分开,同时鼓励它们在无监督的学习过程中保持锐度。尤其是,从全局的视野对其分布建模并且及时促进分布以及GDS相关损失的更新。我们使用动量更新机制来建立和维持参数分布并且计算在训练过程中fly的损失。为了进一步推进两种分布的距离,我们采用了以分布为基础的hard mining。
1 Introduction
Many efforts have been made to develop unsupervised domain adaptation for person re-identification (UDA-ReID)[21,37,35,25,27,7,46,42,47,48].
Pseudo label based approaches usually pre-train the network with source domain data and predict pseudo labels for the unlabeled target images,
by clustering, followed by fine-tuning with the pseudo labels [44,45,7,31,49,9,41].
基于伪标签的方法通常使用源域数据对网络进行预训练,并对未标记的目标图像进行伪标签预测,通过集群,然后使用伪标签进行微调。
Transfer-based approaches often transfer the labeled source images to have the style of the target domain [39,5,25]
基于转移的方法通常将标记的源图像转移到具有目标域风格的图像[39,5,25]
Transfer-basedapproaches often transfer the labeled source images to have the style of the tar-get domain [39,5,25]. These approaches suffer from either noisy labels or noisyimages due to incorrect pseudo labels or unrealisticness of the transferred images [41].
由于不正确的伪标签或传输图像的不真实感,这些方法要么受到噪声标签的影响,要么受到噪声图像的影响[41]
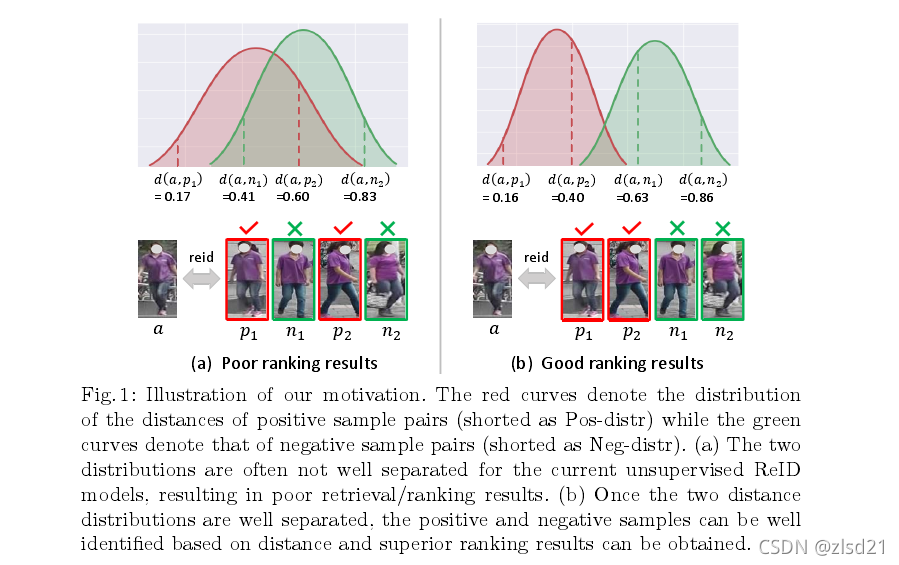
a,b两图对比展示了由于数据分布带来的检索情况的差异,例如a图d(a,n1)的距离小于d(a,p2)的距离,这样分割的时候就会带来错误。改善过后的b图可以有效的避免上述所说的问题。
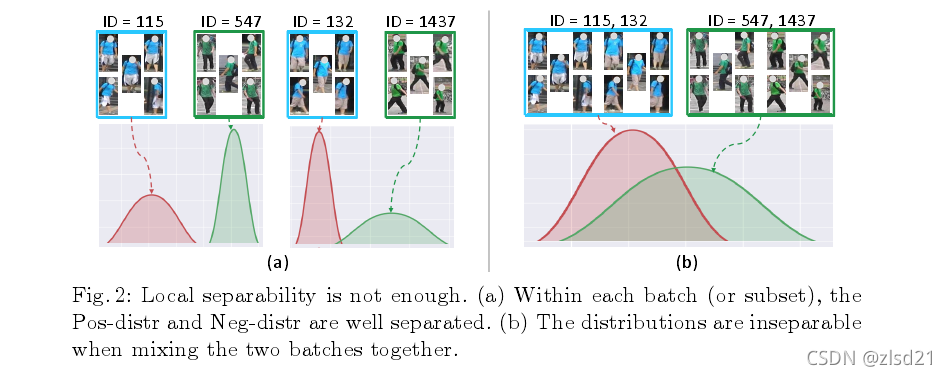
下文又继续说了一个问题:
as illustrated in Fig. 2, being still a local solution, the separation is easily broken across batches and still cannot guarantee the superiority of the global retrieval performance.
如上图所阐述的,仍然只是一个局部的解决方案,对于a来说从local的角度能使其很好的分离开pos和neg样本,而从global的角度即将batch混在一起时,没办法的有效分开pos和neg样本。
再描述完不足后,本文提出了自己的核心解决方案
– We are the first to propose to optimize unsupervised person ReID from aglobal distance-distribution perspective by encouraging the global separation of positive and negative samples. We address the problem of inseparability of distance distributions in existing unsupervised ReID models by introducing aglobal distance-distributions separation (GDS) constraint.
– We maintain and update the distribution variables through a momentum up-date mechanism, enabling the timely update of the distribution variables and accurate estimation of the loss for each batch.
– To further promote the separation of the Pos-distr and Neg-distr, we introduce a distribution-based hard mining mechanism in GDS.
1.我们首次提出了以全局距离分布的角度,通过鼓励全局正负样本的分离来优化无监督学习。我们通过引入GDS方法解决了现存无监督学习中距离分布的问题。
2.我们通过动量更新机制,使其能够及时的更新变量分布,以及准确的估计每个batch的损失。
3.为了更好的促进pos样本和neg样本的分离,我们在GDS中引入了distribution-based hard mining mechanism
2 Related Work
2.1 Unsupervised Person Re-identification
Unsupervised domain adaptive person ReID aims to learn a ReID model from alabeled source domain and an unlabeled target domain. It is attractive for real-word deployments as it does not require the expensive annotation efforts whileexploiting the source domain knowledge. The domain gap between datasets re-sults in poor generalization of a source domain trained model to another domain.
无监督领域适应re-id的目标是通过从带标签的源域和不带标签的目标域,来学习到一个re-id模型。这对现实世界来说很好用,因为它不需要大量的提前标注。但是不同域之间的差异,导致域之间的泛化能力特别差。为了解决这个问题,目前提出了很多方法,总结下来有如下几种:
style transfer, attribute recognition,and clustering-based pseudo label estimation.
style transfer :基于风格转移的方法是利用图像风格翻译技术(如Cycle-GAN[61])将源标记图像转换为具有目标域风格的图像,进行自适应[39,5,25]。
attribute recognition:基于属性的方法[37,24]旨在通过学习某些线索,如人的身体属性,将源领域知识与目标领域共享,使特征学习规范化。
clustering-based pseudo label estimation:其基本思路是通过特征聚类,利用未标记样本的相似性预测伪标记,然后利用伪标记进行微调
但是这些无监督ReID模型通常会受到伪标签或生成图像的干扰。正负对距离分布的不可分性严重,类间距离小,类内距离大(见上文第一图(a))。
2.2 Metric Learning for Person Re-identification
分别阐述了目前常用的三种损失:Id Loss,metric Loss,Histogram Loss
并阐述了三者的问题,再又说了Zhang 再[49]中提出的方法:
Besides capturing the local structure of data with triplet-based loss, Zhanget al. [49] use global information by appending a changeable classification layerto the model with the number of classes being the number of clusters. This en-courages the separability of clustered centers but is less effective in encouragingthe separation of distance distributions of positive pairs and negative pairs. Be-sides, the classification layer needs to be re-trained together with the change ofclustering results which may result in a slow and unstable convergence
除了利用基于三重损失的数据的局部结构,zhang等人还利用全局信息,在模型中添加一个可变的分类层,类的数量为簇的数量。这促进了聚集中心的可分离性,但在促进正负距离分布的分离方面效果较差。此外,分类层需要重新训练,聚类结果也会发生变化,这可能会导致收敛缓慢且不稳定。
为了解决上述存在的所有问题,我们提出了GDS的方法,有效的解决了上述问题。
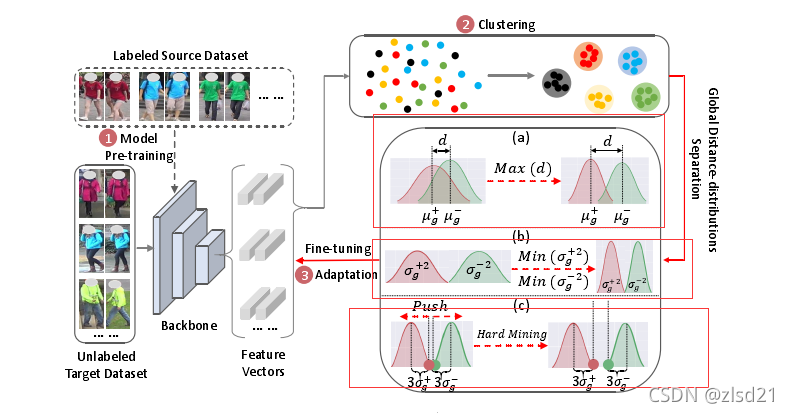
3 Unsupervised ReID with GDS Constraint
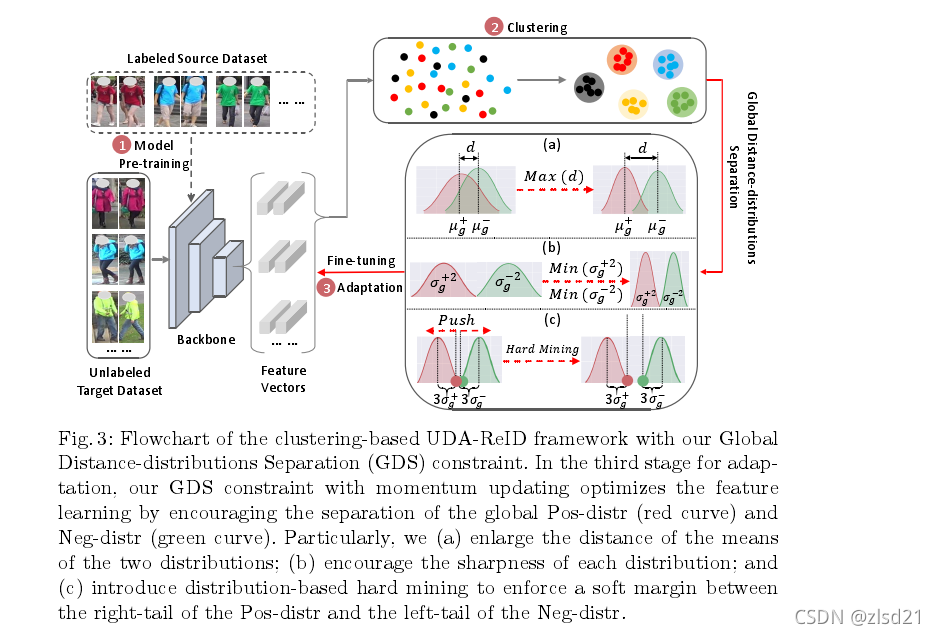
Clustering-based approaches in general consist of three stages with the lasttwo stages executed alternatively for many iterations [31,7,42,49,9,41]
基于聚类的方法通常包括三个阶段,最后两个阶段在多次迭代时交替执行[31,7,42,49,9,41]
如上图所示:
第一阶段是模型预训练,用源域标记的数据对ReID网络进行预训练,进行特征学习。
第二阶段是聚类阶段,目的是通过聚类结果给未标记的目标域数据分配伪标签。
在第三阶段的自适应中,利用伪标签对网络进行微调,进行域自适应,其中基于三元组的损失函数常用于优化。在第三阶段我们将GDS算法应用于更有效的特征学习。GDS鼓励分离正样本对和负样本对的全局距离分布。
3.1 Global Distance-distribution Modeling with Momentum Update
我们从ReID模型(包括无监督和有监督的方法)中观察了正样本对和负样本对在数据集上的距离分布,发现它们呈类高斯分布。
因此,我们采用高斯分布来模拟样本对的距离分布。我们将正样本对的距离分布表示为N(µ+,σ+2),负样本对的距离分布表示为N(µ−,σ−2)。我们的目标是设计优化指标和策略,以鼓励两种数据集(全局)分布的分离,以指导特征学习。
我们的卷积神经网络不是同时探索所有样本,而是在小批量层面上进行优化,其中从批次计算的损失反向传播,以优化网络,以促进及时更新,避免大内存的要求。
基于此,我们维护数据集分布参数,并在每批中更新它们。这样可以及时更新估计的分布变量和对应的gds损失,其中分布随特征提取网络的更新而变化。
给出了正对距离的全局距离分布的动量更新为:
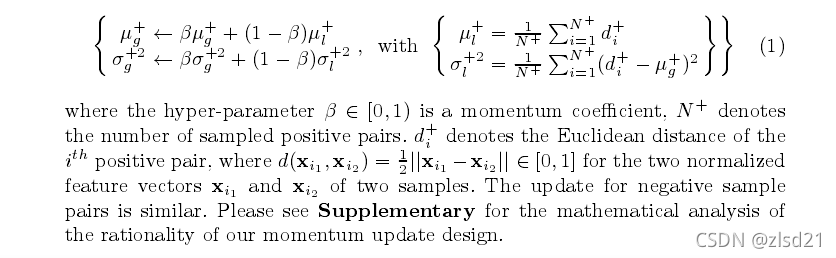
其中超参数β∈[0,1]为动量系数,N+表示采样正负对的个数。d+表示正对的欧氏距离,其中对于两个样本的两个归一化特征向量xi1和xi2, d(xi1, xi2) =12||xi1−xi2||∈[0,1]。对负样本配对的更新是类似的。
3.2 Global Distance-distributions Separation (GDS) Constraint
在3.1中我们详细描述了动量更新机制能够维护数据之间的高斯分布情况。接下来我们来详细描述GDS如何使数据分离。
为了分离正样本对和负样本对的全局距离分布,我们设计了一种基于分布的hard mining的GDS损失,即GDS- h损失,它在每个最小batch中优化网络。它使有基本的GDS损失,和分布为基础的hard mining 损失 构成的:
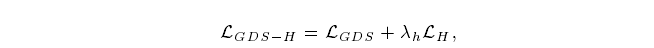
where λh is a hyper-parameter that balances their importance.
GDS损失的定义:
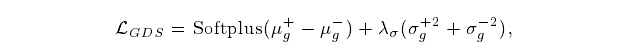
where λσ is another hyper-parameter that balances the importance of mean andvariance (please see the study on λh and λσ in the experiment).
如图上图所示:
第一项Softplus(µ+g−µ−g)促进了两种分布的中心分离。
第二项(σ+2 g+ σ−2 g)通过使两种分布的方差最小,来鼓励它们的锐度。(使其分布变得更高,即更集中化)
我们期望位于潜在重叠区域的难以挖掘的样本也能被分离出来。我们通过引入基于分布的hard mining 损失HLoss来实现这一点
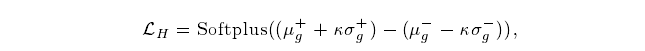
where κ is a hyper-parameter which controls the strength of hard mining。k越大,分布覆盖的面积越大。HLoss的实际意义就是使正负样本的边界有一个合适的margin,这个合适的margin能使其训练效果更好。
下文详细描述了u,σ的前后变化公式:
给出了GDS-H损失函数的梯度更新公式:
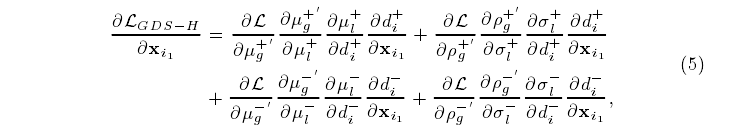





 本文提出了一种全局距离分布分离(GDS)方法来优化无监督行人重识别(ReID)。现有的无监督ReID方法在区分正负样本对的距离分布时面临困难,GDS通过高斯分布建模解决这一问题,利用动量更新机制保持分布变量的及时更新,并通过分布基的难例挖掘促进正负样本对的分离。该方法在每个小批量中优化网络,提高了特征学习的效率和准确性。
本文提出了一种全局距离分布分离(GDS)方法来优化无监督行人重识别(ReID)。现有的无监督ReID方法在区分正负样本对的距离分布时面临困难,GDS通过高斯分布建模解决这一问题,利用动量更新机制保持分布变量的及时更新,并通过分布基的难例挖掘促进正负样本对的分离。该方法在每个小批量中优化网络,提高了特征学习的效率和准确性。
















 1480
1480

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








