AXI provides access permissions signals, AWPROT and ARPROT, that can protect against illegal
transactions downstream in the system. For example, if a transaction does not have the correct
level of protection, a memory controller could refuse read or write access by using these signals.
This is useful for security solutions like Arm TrustZone, where a processor has two separate states,
Secure and Non-secure.
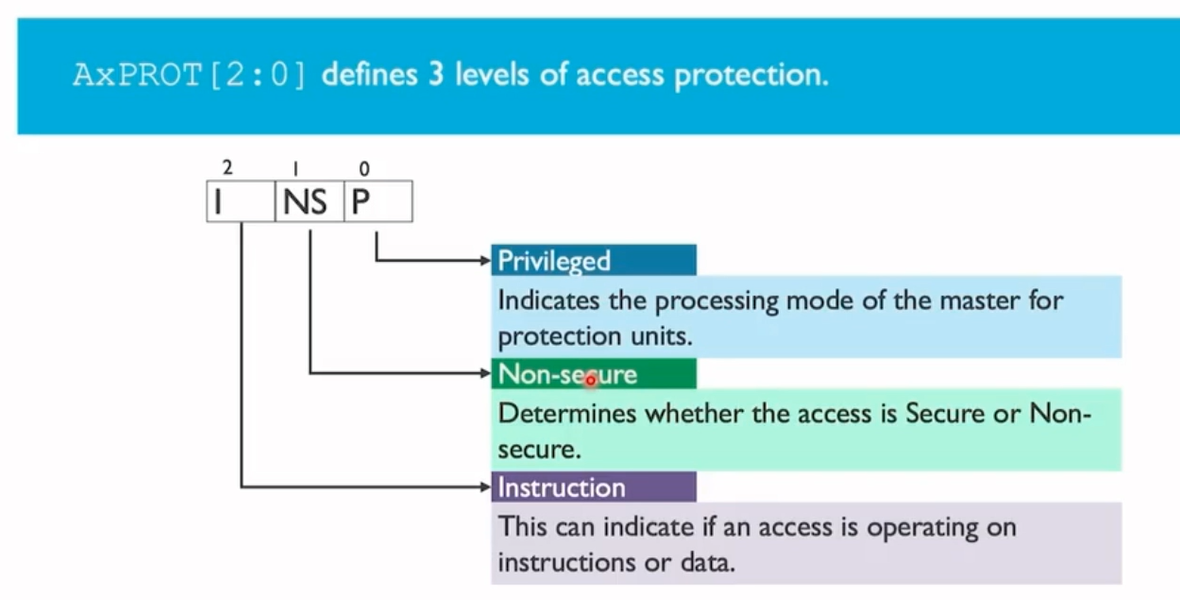
AxPROT defines three levels of access protection, as shown in the following diagram:
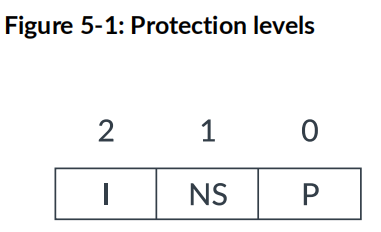
The AxPROT bit allocations specify the following attributes:
• AxPROT[0] § identifies an access as unprivileged or privileged:
◦ 1 indicates privileged access.
◦ 0 indicates unprivileged access.
Although some processors support multiple levels of privil





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 3293
3293

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








