构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(){}
Person(int id);
~Person(){}
void display();
private:
int m_ID;
};
Person::Person(int id)
{
m_ID = id;
}
void Person::display()
{
cout << "hello world" <<endl;
cout << "hello world ID:" << m_ID <<endl;
}
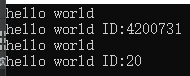
int main()
{
Person p;
p.display();
Person pID(20);
pID.display();
return 0;
}
构造函数是类中一种特殊的成员函数,其特殊之处有三点:
构造函数的函数名必须与类名相同;
构造函数无返回值;
当我们创建类对象的时候,构造函数会被自动调用,而无需我们主动调用。
一个类中可以有多个构造函数,构造函数之间构成函数重载的关系。
构造函数初始化赋值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(){}
Person(int id):m_ID(id){}
~Person(){}
void display();
private:
int m_ID;
};
void Person::display()
{
cout << "hello world" <<endl;
cout << "hello world ID:" << m_ID <<endl;
}
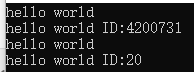
int main()
{
Person p;
p.display();
Person pID(20);
pID.display();
return 0;
}
通知构造函数构造时赋值,比构造完成后赋值更好一些
Person(int id):m_ID(id){}
利用构造函数限制对象创建
不申明默认构造函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
//Person(){}
Person(int id):m_ID(id){}
~Person(){}
void display();
private:
int m_ID;
};
void Person::display()
{
cout << "hello world" <<endl;
cout << "hello world ID:" << m_ID <<endl;
}
int main()
{
//Person p;
//p.display();
Person pID(20);
pID.display();
return 0;
}
直接注释掉
//Person(){}
将默认构造函数声明为 private
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
//Person(){}
Person(int id):m_ID(id){}
~Person(){}
void display();
private:
Person(){}
private:
int m_ID;
};
void Person::display()
{
cout << "hello world" <<endl;
cout << "hello world ID:" << m_ID <<endl;
}
int main()
{
//Person p;
//p.display();
Person pID(20);
pID.display();
return 0;
}
请记住,将默认构造函数声明为 private很常用,一定要记住。





 本文详细介绍了构造函数的使用,包括如何进行初始化赋值、如何通过构造函数控制对象创建,并探讨了不声明默认构造函数和将其设为private的实践。
本文详细介绍了构造函数的使用,包括如何进行初始化赋值、如何通过构造函数控制对象创建,并探讨了不声明默认构造函数和将其设为private的实践。


















 3389
3389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










