引用简介
引用(Reference)是 C++语言相对于 C语言的又一个扩充,类似于指针,只是在声明的时候用&取代了*。
引用可以看做是被引用对象的一个别名,在声明引用时,必须同时对其进行初始化。引用的声明方法如下:
类型标识符 &引用名 = 被引用对象
引用心法:
1.被引用对象与原对象是一种申明关系。
2.引用时对其进行初始化。
3.不单独开辟空间。
4.被引用对象与原对象数据类型要相同。
例如 拷贝构造函数:
A &(const A& a)
A a1;
A a2(a1); //必须先初始化引用类
值引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
// 声明简单的变量
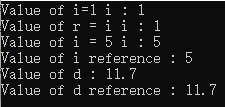
int i=1;
double d;
cout << "Value of i=1 i : " << i << endl;
// 声明引用变量
int& r = i;
double& s = d;
cout << "Value of r = i i : " << i << endl;
i = 5;
cout << "Value of i = 5 i : " << i << endl;
cout << "Value of i reference : " << r << endl;
d = 11.7;
cout << "Value of d : " << d << endl;
cout << "Value of d reference : " << s << endl;
return 0;
}
函数引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 函数声明
void swap(int &x, int &y);
int swap1(int& a, int& b);
int main ()
{
// 局部变量声明
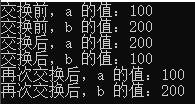
int a = 100;
int b = 200;
cout << "交换前,a 的值:" << a << endl;
cout << "交换前,b 的值:" << b << endl;
/* 调用函数来交换值 */
swap(a, b);
cout << "交换后,a 的值:" << a << endl;
cout << "交换后,b 的值:" << b << endl;
swap1(a, b);
cout << "再次交换后,a 的值:" << a << endl;
cout << "再次交换后,b 的值:" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
void swap(int &x, int &y)
{
int temp;
temp = x; /* 保存地址 x 的值 */
x = y; /* 把 y 赋值给 x */
y = temp; /* 把 x 赋值给 y */
return;
}
int swap1(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp;
temp = a ^ b;
a = temp ^ a;
b = temp ^ b;
return 0;
}
类对象的引用
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class book
{
public:
book(){}
~book(){}
public:
void setprice(double a);
double getprice();
void settitle(char* a);
char * gettitle();
private:
double price;
char * title;
};
void book::setprice(double a)
{
price = a;
}
double book::getprice()
{
return price;
}
void book::settitle(char* a)
{
title = a;
}
char * book::gettitle()
{
return title;
}
void display(book & b)
{
cout<<"The price of "<<b.gettitle()<<" is $"<<b.getprice()<<endl;
}
book & init(char *t, double p)
{
static book b;
b.settitle(t);
b.setprice(p);
return b;
}
int main()
{
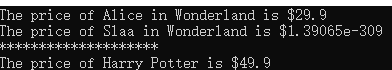
book Alice;
Alice.settitle("Alice in Wonderland");
Alice.setprice(29.9);
display(Alice);
book Harry;
Harry.settitle("Slaa in Wonderland");
display(Harry);
cout << "********************" <<endl;
Harry = init("Harry Potter", 49.9);
display(Harry);
return 0;
}
可以看到
Harry = init("Harry Potter", 49.9);
//被调用后,是通过自己创建book,赋值后返回book
book & init(char *t, double p)
{
static book b;
b.settitle(t);
b.setprice(p);
return b;
}
引用的本质
扩展变量作用域





 本文详细解读C++中的引用,包括值引用、函数引用和类对象引用的使用,以及引用的本质——扩展变量作用域。通过实例演示了引用在数据交换、函数参数传递和类对象操作中的优势。
本文详细解读C++中的引用,包括值引用、函数引用和类对象引用的使用,以及引用的本质——扩展变量作用域。通过实例演示了引用在数据交换、函数参数传递和类对象操作中的优势。



















 1539
1539

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










