一、背景
之前做过一个项目是需要将位图转换成矢量图,其中一个很重要的步骤,就是需要用贝塞尔曲线拟合一些散列点。了解贝塞尔曲线的同学都知道,如果贝塞尔曲线的控制点都明确的情况下,想算出来线上的点是很容易的,直接套公式就可以把点的坐标算出来。但是如果这个过程反过来,给你一些点的坐标,求出贝塞尔曲线的控制点,是很困难的。
三阶贝塞尔曲线的公式: P = P0*(1-t)**3 + 3*P1*t*(1-t)**2 + 3*P2*t**2*(1-t) + P3*t**3 (公式中*表示乘法运算,**表示幂运算)
二、思路
1、用圆拟合散点,再用三阶贝塞尔曲线拟合圆。优点算法简单,缺点,曲线很僵硬,放大看全是圆弧,失去了贝塞尔曲线的强大的表达能力。
2、用二阶贝塞尔曲线拟合散点,优点算法简单,运算效率高。缺点二阶贝塞尔曲线实际就是抛物线,表达能力有限和思路1类似。
3、用最小二乘法。优点运算可靠,速度快。缺点,公式推导复杂,理解很难。方法很可取,但是不是本文讲述的重点。
4、网上搜了很多,有用遗传算法的,各种。后来想想,目前这么火热的人工神经网络能否解决这个问题呢?本文带大家一起尝试一下。
三、尝试
试着用人工神经网络来搞定这个问题。就要考虑输入输出。
1、输入,输入肯定是散列点。但是怎么输入呢,人工神经网络大部分输入参数都是固定的,但是散列点根据线的长度,个数不固定。能否想办法固定下来呢?我们选一些代表性的点,起点、终点、三个四分之一点。总共5个点,10个值。
2、输出,输出控制点的坐标。起点、终点已知、那么就要两个控制点的坐标,总共4个数字。那么输出就是4个值。
四、网络搭建
本次网络不牵涉到图像运算,就采用双隐藏层的ANN网络即可解决问题。网络结构很简单,读者可自行搜索。这里不做详细介绍,后面直接上代码。
五、数据集
数据集自己写随机代码生成即可,放在训练过程中,可以做成无监督学习,省时省力。
六、实验效果。
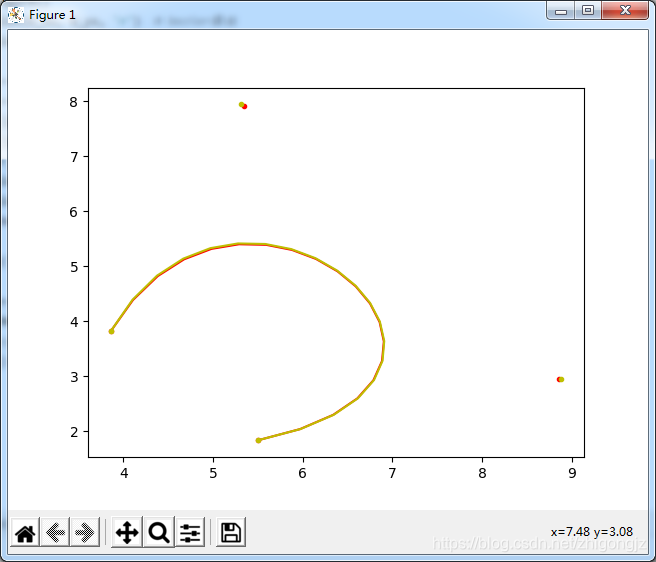
直接上图,图中红色点是实际控制点,黄色点是网络预测的点,几乎重合,曲线也几乎重合,效果很好:


七、代码
tensorflow 2.0+,如果对您有用,请帮忙点赞哈,文章是原创,转载请标明出处,沟通交流加我QQ306128847,。
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, models
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
b_xs = []
b_ys = []
# xs表示原始数据
# n表示阶数
# k表示索引
def one_bezier_curve(a, b, t):
return (1 - t) * a + t * b
def n_bezier_curve(xs, n, k, t):
if n == 1:
return one_bezier_curve(xs[k], xs[k + 1], t)
else:
return (1 - t) * n_bezier_curve(xs, n - 1, k, t) + t * n_bezier_curve(xs, n - 1, k + 1, t)
def bezier_curve(xs, ys, num, b_xs, b_ys):
n = 3 # 采用5次bezier曲线拟合
t_step = 1.0 / (num - 1)
# t_step = 1.0 / num
print(t_step)
t = np.arange(0.0, 1 + t_step, t_step)
print(len(t))
for each in t:
b_xs.append(n_bezier_curve(xs, n, 0, each))
b_ys.append(n_bezier_curve(ys, n, 0, each))
class AnnNet(object):
def __init__(self):
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(64, activation='sigmoid', input_shape=(10,)))
model.add(layers.Dense(32, activation='sigmoid'))
model.add(layers.Dense(4))
model.summary()
self.model = model
def GenerateArray(self):
while 1:
x= []
y= []
for i in range(10):
point = np.random.rand(8) * 10
times = np.random.rand(3)
times = [0.2, 0.5, 0.8]
pt1x = ((1 - times[0]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[0] * ((1 - times[0]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[0]) * point[4] + (times[0] ** 3) * point[6]
pt1y = ((1 - times[0]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[0] * ((1 - times[0]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[0]) * point[5] + (times[0] ** 3) * point[7]
pt2x = ((1 - times[1]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[1] * ((1 - times[1]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[1] ** 2) * (1 - times[1]) * point[4] + (times[1] ** 3) * point[6]
pt2y = ((1 - times[1]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[1] * ((1 - times[1]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[1] ** 2) * (1 - times[1]) * point[5] + (times[1] ** 3) * point[7]
pt3x = ((1 - times[2]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[2] * ((1 - times[2]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[2]) * point[4] + (times[2] ** 3) * point[6]
pt3y = ((1 - times[2]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[2] * ((1 - times[2]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[2]) * point[5] + (times[2] ** 3) * point[7]
x.append([point[0], point[1], pt1x, pt1y, pt2x, pt2y, pt3x, pt3y, point[6], point[7]])
y.append([point[2], point[3], point[4], point[5]])
X = np.array(x)
Y = np.array(y)
yield (X, Y)
def LossFunc(self, ytrue, ypred):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(ytrue-ypred))
return loss
def Train(self):
print('train start!')
self.check_path = 'save.ckpt'
if os.path.exists(self.check_path + '.index'):
self.model.load_weights(self.check_path)
self.model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss = self.LossFunc)
save_model_cb = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(self.check_path, save_weights_only=True, verbose=1, period=1)
back = self.model.fit_generator(self.GenerateArray(), steps_per_epoch=1000, epochs=100, callbacks=[save_model_cb])
print('train end!')
def Test(self):
print('test start!')
self.check_path = 'save.ckpt'
if os.path.exists(self.check_path + '.index'):
self.model.load_weights(self.check_path)
x= []
y= []
point = np.random.rand(8) * 10
times = [0.2, 0.5, 0.8]
pt1x = ((1 - times[0]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[0] * ((1 - times[0]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[0]) * point[4] + (times[0] ** 3) * point[6]
pt1y = ((1 - times[0]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[0] * ((1 - times[0]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[0]) * point[5] + (times[0] ** 3) * point[7]
pt2x = ((1 - times[1]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[1] * ((1 - times[1]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[1] ** 2) * (1 - times[1]) * point[4] + (times[1] ** 3) * point[6]
pt2y = ((1 - times[1]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[1] * ((1 - times[1]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[1] ** 2) * (1 - times[1]) * point[5] + (times[1] ** 3) * point[7]
pt3x = ((1 - times[2]) ** 3) * point[0] + 3 * times[2] * ((1 - times[2]) ** 2) * point[2] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[2]) * point[4] + (times[2] ** 3) * point[6]
pt3y = ((1 - times[2]) ** 3) * point[1] + 3 * times[2] * ((1 - times[2]) ** 2) * point[3] + 3 * (times[0] ** 2) * (1 - times[2]) * point[5] + (times[2] ** 3) * point[7]
x.append([point[0], point[1], pt1x, pt1y, pt2x, pt2y, pt3x, pt3y, point[6], point[7]])
y.append([point[2], point[3], point[4], point[5]])
X = np.array(x)
Y = np.array(y)
ypred = self.model.predict(X)
print(Y)
print(ypred)
num = 20
xs = [point[0], point[2], point[4], point[6]]
ys = [point[1], point[3], point[5], point[7]]
b_xs = []
b_ys = []
bezier_curve(xs, ys, num, b_xs, b_ys) # 将计算结果加入到列表中
plt.figure()
plt.plot(b_xs, b_ys, 'r') # bezier曲线
plt.plot(xs, ys, '.r') # 控制点
b_xs = []
b_ys = []
xs = [point[0], ypred[0][0], ypred[0][2], point[6]]
ys = [point[1], ypred[0][1], ypred[0][3], point[7]]
bezier_curve(xs, ys, num, b_xs, b_ys) # 将计算结果加入到列表中
plt.plot(b_xs, b_ys, 'y') # bezier曲线
plt.plot(xs, ys, '.y') # 控制点
plt.show()
print('test end!')
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = AnnNet()
net.Train()
net.Test()


























 971
971

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








