A. Hotelier
sb模拟,直接按题意模拟就可以了。
B. Block Adventure
Gildong is playing a video game called Block Adventure. In Block Adventure, there are n columns of blocks in a row, and the columns are numbered from 1 to n. All blocks have equal heights. The height of the i-th column is represented as hi, which is the number of blocks stacked in the i-th column.
Gildong plays the game as a character that can stand only on the top of the columns. At the beginning, the character is standing on the top of the 1-st column. The goal of the game is to move the character to the top of the n-th column.
The character also has a bag that can hold infinitely many blocks. When the character is on the top of the i-th column, Gildong can take one of the following three actions as many times as he wants:
if there is at least one block on the column, remove one block from the top of the i-th column and put it in the bag;
if there is at least one block in the bag, take one block out of the bag and place it on the top of the i-th column;
if i<n and |hi−hi+1|≤k, move the character to the top of the i+1-st column. k is a non-negative integer given at the beginning of the game. Note that it is only possible to move to the next column.
In actions of the first two types the character remains in the i-th column, and the value hi changes.
The character initially has m blocks in the bag. Gildong wants to know if it is possible to win the game. Help Gildong find the answer to his question.
Input
Each test contains one or more test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases t (1≤t≤1000). Description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains three integers n, m, and k (1≤n≤100, 0≤m≤106, 0≤k≤106) — the number of columns in the game, the number of blocks in the character’s bag at the beginning, and the non-negative integer k described in the statement.
The second line of each test case contains n integers. The i-th integer is hi (0≤hi≤106), the initial height of the i-th column.
Output
For each test case, print “YES” if it is possible to win the game. Otherwise, print “NO”.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
题意,感觉表达有点乱。站在一个h[i]个方块垒起来的地方,可以无限拿方块,也可以放方块,当 abs(h[i]-h[i+1]) <= K的时候可以进到下一个。否则无法过去。
做法:直接贪心就可以了,拿当前最多能拿的方块,放当前最少需要的方块。模拟能不能到达最后一层就可以了。
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAX = 110;
ll h[MAX];
ll N,M,K;
bool solve(){
for(int i=1;i<N;++i){
if(h[i] >= h[i+1]-K){//当前方块多,即可不断的拿
M += h[i]-max(0LL,(h[i+1]-K));//注意最少也是0,不能出现负数
}
else{
if(h[i]+M >= h[i+1]-K){
M -= ((h[i+1]-K)-h[i]);//最少需要补得方块。
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
int main(void){
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&N,&M,&K);
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i){
scanf("%lld",&h[i]);
}
if(solve()){
cout << "YES" << endl;
}
else{
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Round Corridor
Amugae is in a very large round corridor. The corridor consists of two areas. The inner area is equally divided by n sectors, and the outer area is equally divided by m sectors. A wall exists between each pair of sectors of same area (inner or outer), but there is no wall between the inner area and the outer area. A wall always exists at the 12 o’clock position.
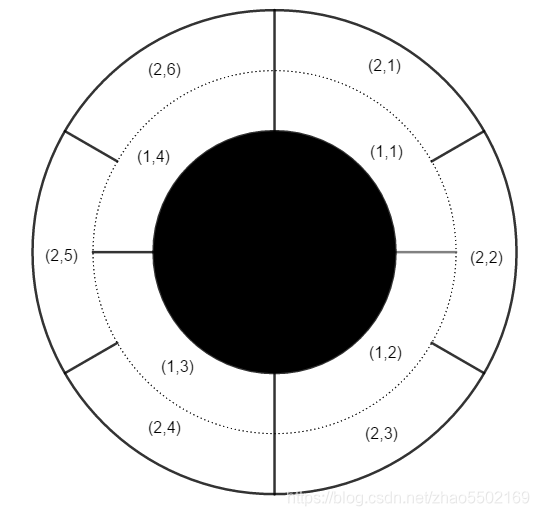
The inner area’s sectors are denoted as (1,1),(1,2),…,(1,n) in clockwise direction. The outer area’s sectors are denoted as (2,1),(2,2),…,(2,m) in the same manner. For a clear understanding, see the example image above.
Amugae wants to know if he can move from one sector to another sector. He has q questions.
For each question, check if he can move between two given sectors.
Input
The first line contains three integers n, m and q (1≤n,m≤1018, 1≤q≤104) — the number of sectors in the inner area, the number of sectors in the outer area and the number of questions.
Each of the next q lines contains four integers sx, sy, ex, ey (1≤sx,ex≤2; if sx=1, then 1≤sy≤n, otherwise 1≤sy≤m; constraints on ey are similar). Amague wants to know if it is possible to move from sector (sx,sy) to sector (ex,ey).
Output
For each question, print “YES” if Amugae can move from (sx,sy) to (ex,ey), and “NO” otherwise.
You can print each letter in any case (upper or lower).
Example
inputCopy
4 6 3
1 1 2 3
2 6 1 2
2 6 2 4
outputCopy
YES
NO
YES
Note
Example is shown on the picture in the statement.
做法:
内部每个扇形的度数是 (360/n),外部的每个扇形角度是 (360/m)。设内部第a个扇形和外部第b个扇形刚好度数和相等,即构成一个封闭的门。a* (360/n) = b*(360/m) 化简后可以知道。a/b = n/m;也就是a 和n是对应成比例的,b 和m是对应成比例的。
n 和 m 除以二者最大gcd后记为 n’ m’,则可以通过py,ey求出对应在第几个门前面,判断两个坐标在不在同一个门当中即可。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
ll N,M,Q;
ll sx,sy,ex,ey;
ll get(ll num,bool inner){
if(inner){
if(num % N == 0)
return num/N;
else
return num/N+1;
}
else{
if(num % M == 0)
return num/M;
else
return num/M+1;
}
}
bool solve(){
ll ps,pe;
ps = get(sy,sx == 1);
pe = get(ey,ex == 1);
if(ps == pe)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main(void){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&N,&M,&Q);
ll GCD = __gcd(N,M);
N/=GCD;M/=GCD;
for(int i=1;i<=Q;++i){
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld",&sx,&sy,&ex,&ey);
if(solve()){
printf("YES\n");
}
else{
printf("NO\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
E. Compress Words
Amugae has a sentence consisting of n words. He want to compress this sentence into one word. Amugae doesn’t like repetitions, so when he merges two words into one word, he removes the longest prefix of the second word that coincides with a suffix of the first word. For example, he merges “sample” and “please” into “samplease”.
Amugae will merge his sentence left to right (i.e. first merge the first two words, then merge the result with the third word and so on). Write a program that prints the compressed word after the merging process ends.
Input
The first line contains an integer n (1≤n≤105), the number of the words in Amugae’s sentence.
The second line contains n words separated by single space. Each words is non-empty and consists of uppercase and lowercase English letters and digits (‘A’, ‘B’, …, ‘Z’, ‘a’, ‘b’, …, ‘z’, ‘0’, ‘1’, …, ‘9’). The total length of the words does not exceed 106.
Output
In the only line output the compressed word after the merging process ends as described in the problem.
Examples
inputCopy
5
I want to order pizza
outputCopy
Iwantorderpizza
inputCopy
5
sample please ease in out
outputCopy
sampleaseinout
题意:把相同的前后缀去重,然后从左到右合并单词。问你最后压缩出来的串是多少。
做法:很显然需要一个算法能O(N)的求出相同前后缀的长度即可。我用的是字符串哈希的方法。
比赛过了,赛后却挂了。。。哎,自己最开始只用了一个base,以及用的自然溢出。当时猜想到可以回出现哈希碰撞。哎,可惜时间不太够了。。这次用了三个base,加mod 不用自然溢出,过了。似乎用两个就可以通过。
代码如下:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef long long ll;
ll Mod1 = 1e9+7,Mod2 = 998244353,Mod3 = 19971205;
ll B1 = 131,B2 = 13131,B3 = 1331;
int overlap(string &a,string &b){
int al = a.length(),bl = b.length();
int ans = 0;
ll ah1 = 0,ah2 = 0,ah3 = 0;
ll bh1 = 0,bh2 = 0,bh3 = 0;
ll t1= 1,t2 = 1,t3 = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=min(al,bl);++i){
ah1 = ah1 + a[al-i]*t1;ah1 %= Mod1;
ah2 = ah2 + a[al-i]*t2;ah2 %= Mod2;
ah3 = ah3 + a[al-i]*t3;ah3 %= Mod3;
bh1 = bh1*B1 + b[i-1];bh1 %= Mod1;
bh2 = bh2*B2 + b[i-1];bh2 %= Mod2;
bh3 = bh3*B3 + b[i-1];bh3 %= Mod3;
if(ah1 == bh1 && ah2 == bh2 && ah3 == bh3)
ans = i;
t1 = t1*B1%Mod1;
t2 = t2*B2%Mod2;
t3 = t3*B3%Mod3;
}
return ans;
}
int main(void){
int N;
string res = "";
string last = "";
string str;
cin >> N;
for(int i=1;i<=N;++i){
cin >> str;
if(i == 1){
res = str;
}
else{
int len = overlap(res,str);
res += str.substr(len);
}
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}





 本文精选三道算法竞赛题目,包括模拟酒店经营策略、解决走廊迷宫问题以及压缩字符串序列,详细解析题目的核心思想与高效算法实现。
本文精选三道算法竞赛题目,包括模拟酒店经营策略、解决走廊迷宫问题以及压缩字符串序列,详细解析题目的核心思想与高效算法实现。
















 853
853

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








