目录
前言:
前面我们学习了顺序表和链表,今天学习栈和列队,为什么栈和列队要在顺序表和链表后面讲呢,因为站和队列的实现就要依靠于顺序表和链表,本文介绍了栈和队列的结构功能以及代码实现,最后还有博主手记的笔记,大家可以参考一下思路,希望能帮助到大家。下面我们一起来看看吧。
一、栈
1.栈的概念与结构
栈:⼀种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的⼀端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插⼊和删除操作的⼀端称为栈顶,另⼀端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
入栈:栈的插⼊操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶。
栈的结构如图所示:
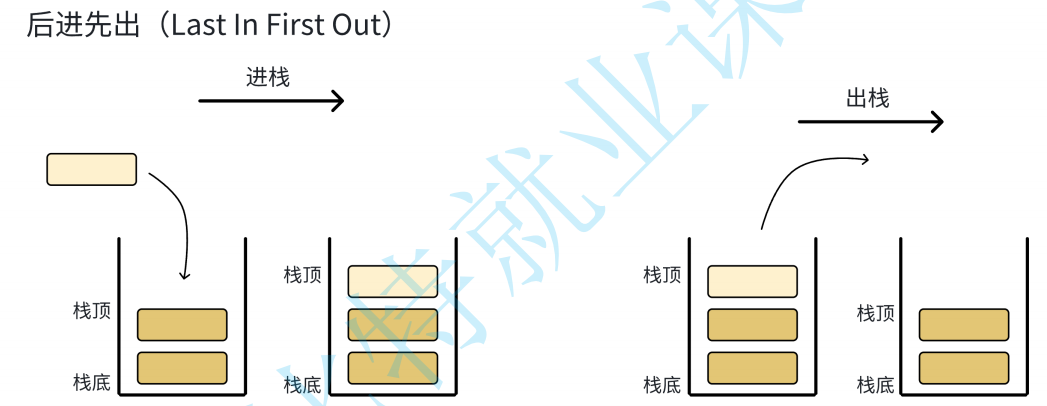
栈是用数组(顺序表)来实现的,入栈和出栈都在数组尾部实现。原因如下:
数组进行进栈出栈的时间复杂度为O(1);
数组每入栈一个数据只需要一个类型大小的空间,而链表则需要一整个节点大小的空间。
2.栈的实现
1)定义栈的结构
//定义栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct stack {
STDataType* arr;
int top; //栈顶
int capacity;
}stack;2)初始化
//初始化
void STInit(stack* ps)
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}3)销毁
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(stack* ps)
{
if (ps->arr != NULL)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}4)入栈
入栈需要先判断空间是否足够,然后再进行入栈。
//入栈
void STPush(stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//判断空间是否足够
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//空间足够
ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}5)出栈
出栈之前需要断言一下传入的ps中是否为空,是否值为NULL。我们用下面这个函数来解决
//判断栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}//出栈
void STPop(stack* ps)
{
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}6)取栈顶元素
//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(stack* ps)
{
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}7)获取栈中有效元素个数
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int STSize(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}3.栈的完整代码
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//定义栈的结构
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct stack {
STDataType* arr;
int top;
int capacity;
}stack;
//初始化栈
void STInit(stack* ps);
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(stack* ps);
//入栈
void STPush(stack* ps, STDataType x);
//栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(stack* ps);
//出栈
void STPop(stack* ps);
//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(stack* ps);
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int STSize(stack* ps);Stack.c
#include"Stack.h"
//初始化
void STInit(stack* ps)
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//销毁栈
void STDestroy(stack* ps)
{
if (ps->arr != NULL)
{
free(ps->arr);
}
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(stack* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//判断空间是否足够
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* temp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (temp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc");
exit(1);
}
ps->arr = temp;
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
//空间足够
ps->arr[ps->top++] = x;
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool STEmpty(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
//出栈
void STPop(stack* ps)
{
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
ps->top--;
}
//取栈顶数据
STDataType STTop(stack* ps)
{
assert(!STEmpty(ps));
return ps->arr[ps->top - 1];
}
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int STSize(stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}test.c
#include"Stack.h"
void test1()
{
stack st;
STInit(&st);
STPush(&st, 1);
STPush(&st, 2);
STPush(&st, 3);
STPush(&st, 4);
STPush(&st, 5);
printf("%d\n", STSize(&st));
while (!STEmpty(&st))
{
STDataType top = STTop(&st);
printf("%d ", top);
STPop(&st);
}
printf("\n");
printf("%d\n", STSize(&st));
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}二、队列
1.队列的概念与结构
概念:只允许在⼀端进行插入数据操作,在另⼀端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出FIFO(First In First Out)的特点。
⼊队列:进行插入操作的⼀端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的⼀端称为队头
队列的结构如图所示:
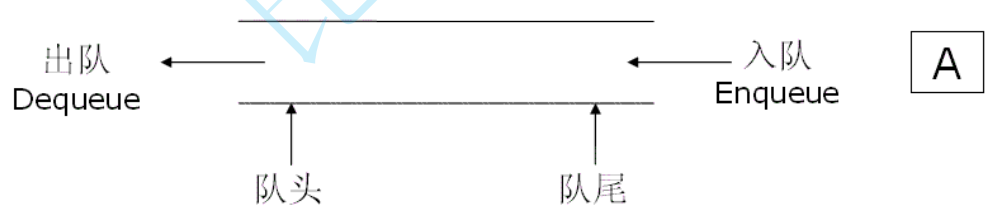
队列是用链表来实现的,在链表中使用phead和ptail分别表示队头和队尾,原因如下:
用链表以及两个指针phead和ptail来实现入队出队时间复杂度只为O(1);
而数组头部的插入和删除时间复杂度均为O(n),出队列在数组头上出数据效率比较低。
2.队列的实现
1)定义队列的结构
先定义队列的节点的结构
//创建队列的节点
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode {
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;再定义队列的结构
//创建队列的结构
typedef struct Queue {
QueueNode* phead;
QueueNode* ptail;
}Queue;2)初始化
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}3)入队列,队尾
入队列之前要先为x创建新节点,然后再入队列。
//入队列,队尾
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
//创建值为x的节点
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//插入队列
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else {
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = pq->ptail->next;
}
}4)出队列,队头
出队列之前要先判断一下传入的值是否为空,以及队列元素是否为空。这里用函数来判断:
//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}//出队列,队头
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead == pq->ptail)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else {
QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
}5)取队头元素
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}6)取队尾元素
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}7)队列有效元素个数
//队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur!=NULL)
{
size++;
pcur = pcur->next;
}
return size;
}也可以在队列结构Queue中再加入一个size来记录该队列里的有效元素个数,就不用再遍历链表查数了,时间复杂度从O(n)变成了O(1)。
8)销毁队列
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur)
{
QueueNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}3.队列的完整代码
Queue.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
//创建队列的节点
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode {
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QueueNode;
//创建队列的结构
typedef struct Queue {
QueueNode* phead;
QueueNode* ptail;
}Queue;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//入队列,队尾
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
//出队列,队头
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);Queue.c
#include"Queue.h"
//初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
//入队列,队尾
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
//创建值为x的节点
QueueNode* newnode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc");
exit(1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//插入队列
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else {
pq->ptail->next = newnode;
pq->ptail = pq->ptail->next;
}
}
//队列判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead == NULL;
}
//出队列,队头
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead == pq->ptail)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}
else {
QueueNode* next = pq->phead->next;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
}
//取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
//取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
//队列有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur!=NULL)
{
size++;
pcur = pcur->next;
}
return size;
}
//销毁队列
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QueueNode* pcur = pq->phead;
while (pcur)
{
QueueNode* next = pcur->next;
free(pcur);
pcur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}test.c
#include"Queue.h"
void test1()
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
QueuePush(&q, 1);
QueuePush(&q, 2);
QueuePush(&q, 3);
QueuePush(&q, 4);
printf("size = %d\n",QueueSize(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
printf("size = %d\n", QueueSize(&q));
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("size = %d\n", QueueSize(&q));
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}三、博主手记


结语:
栈和队列的分享到这里就结束了,他们的结构虽有不同,但是也可以互相转换,这就需要我们进一步学习这块的知识了,下篇文章我会分享栈和队列的精选算法题目,欢迎大家来捧场,感谢支持!
 栈与队列详解及C实现
栈与队列详解及C实现
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








