Accumulation Degree
Description
Trees are an important component of the natural landscape because of their prevention of erosion and the provision of a specific ather-sheltered ecosystem in and under their foliage. Trees have also been found to play an important role in producing oxygen and reducing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, as well as moderating ground temperatures. They are also significant elements in landscaping and agriculture, both for their aesthetic appeal and their orchard crops (such as apples). Wood from trees is a common building material.
Trees also play an intimate role in many of the world’s mythologies. Many scholars are interested in finding peculiar properties about trees, such as the center of a tree, tree counting, tree coloring. A(x) is one of such properties.
A(x) (accumulation degree of node x) is defined as follows:
Each edge of the tree has an positive capacity.
The nodes with degree of one in the tree are named terminals.
The flow of each edge can’t exceed its capacity.
A(x) is the maximal flow that node x can flow to other terminal nodes.
Since it may be hard to understand the definition, an example is showed below:
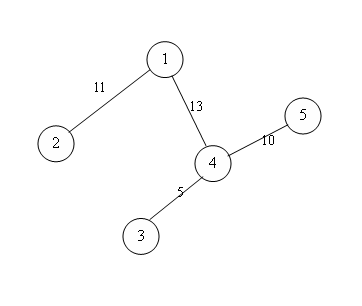
A(1)=11+5+8=24
Details:
1->2 11
1->4->3 5
1->4->5 8(since 1->4 has capacity of 13)
A(2)=5+6=11
Details:
2->1->4->3 5
2->1->4->5 6
A(3)=5
Details:
3->4->5 5
A(4)=11+5+10=26
Details:
4->1->2 11
4->3 5
4->5 10
A(5)=10
Details:
5->4->1->2 10
The accumulation degree of a tree is the maximal accumulation degree among its nodes. Here your task is to find the accumulation degree of the given trees.
Input
The first line of the input is an integer T which indicates the number of test cases. The first line of each test case is a positive integer n. Each of the following n - 1 lines contains three integers x, y, z separated by spaces, representing there is an edge between node x and node y, and the capacity of the edge is z. Nodes are numbered from 1 to n.
All the elements are nonnegative integers no more than 200000. You may assume that the test data are all tree metrics.
Output
For each test case, output the result on a single line.
Sample Input
1
5
1 2 11
1 4 13
3 4 5
4 5 10
Sample Output
26
题意:给一棵无根树,求出最大流量。
分析:设d[x]表示在以x为根的子树中,把x作为源点的最大流量,这个方程很简单,d[x]=∑min(d[son],w(x,son)),当son为叶子节点时,d[x]=d[x]+w(x,y),这样可以算出以其中一个点为源点时的最大流量,但是我们要计算以每个点为源点的最大值,朴素想法当然是枚举每个点计算。这里我们可以用二次扫描与换根法代替源点的枚举,设f[x]表示把x作为源点时,整个水系的最大流量,于是我们可以通过d来计算f。显然f[root]=d[root],若想把根从x变为y,
f[y]=min(d[x]-min(d[y],w(x,y)),w(x,y)),当x为叶子节点时f[y]=f[x]+w(x,y)。
代码
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#define N 400005
using namespace std;
struct arr
{
int to, nxt, w;
}a[N];
int f[N],d[N],du[N],ls[N*2],l,n,T;
bool v[N];
void add(int x, int y, int z)
{
a[++l].to = y;
a[l].nxt = ls[x];
a[l].w = z;
ls[x] = l;
}
int min(int x, int y){return x<y?x:y;}
void dp(int x)
{
v[x] = true;
for (int i = ls[x]; i; i = a[i].nxt)
if (!v[a[i].to])
{
dp(a[i].to);
d[x]+=du[a[i].to]==1?a[i].w:min(d[a[i].to],a[i].w);
}
}
void dfs(int x)
{
v[x] = true;
for (int i = ls[x]; i; i = a[i].nxt)
if (!v[a[i].to])
{
//f[a[i].to] = d[a[i].to] + du[x]==1?a[i].w:min(f[x] - min(d[a[i].to],a[i].w),a[i].w);
if (du[x] == 1) f[a[i].to] = d[a[i].to] + a[i].w;
else f[a[i].to] = d[a[i].to] +min(f[x] - min(d[a[i].to],a[i].w),a[i].w);
dfs(a[i].to);
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &T);
while (T--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
v[i] = false;
f[i] = d[i] = du[i] = 0;
}
memset(ls, 0, sizeof(ls));
l = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
int x, y, z;
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &y, &z);
add(x, y, z);
add(y, x, z);
du[x]++;
du[y]++;
}
dp(1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
v[i] = false;
f[1] = d[1];
dfs(1);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (f[i] > ans) ans = f[i];
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
}




 本文介绍了一种计算树中节点积累度的算法,通过定义积累度为从节点流向其他终端节点的最大流量,采用二次扫描与换根法高效计算每一点为根时的积累度,并找出最大值。
本文介绍了一种计算树中节点积累度的算法,通过定义积累度为从节点流向其他终端节点的最大流量,采用二次扫描与换根法高效计算每一点为根时的积累度,并找出最大值。
















 631
631

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








