目录
复习用tip
1、虚拟头节点非常好用!!所有涉及到头节点都会因为链表对象的存在与否有一定操作难度,如果设置虚拟头节点,可以将其视为普通结点一起处理
2、链表类内的结点结构体,非常好用。
3、c++需要注意主动删除结点(申请了内存)
4、循环列表可以解决约瑟夫环的问题
707.设计链表
题目链接
题意要求:
在链表类中实现这些功能:
- get(index):获取链表中第 index 个节点的值。如果索引无效,则返回-1。
- addAtHead(val):在链表的第一个元素之前添加一个值为 val 的节点。插入后,新节点将成为链表的第一个节点。
- addAtTail(val):将值为 val 的节点追加到链表的最后一个元素。
- addAtIndex(index,val):在链表中的第 index 个节点之前添加值为 val 的节点。如果 index 等于链表的长度,则该节点将附加到链表的末尾。如果 index 大于链表长度,则不会插入节点。如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点。
- deleteAtIndex(index):如果索引 index 有效,则删除链表中的第 index 个节点。
强烈建议使用结构体结点、虚拟节点,否则对头节点的处理非常麻烦
class MyLinkedList {
public:
// 定义链表节点结构体
struct LinkedNode {
int val;
LinkedNode* next;
LinkedNode(int val):val(val), next(nullptr){}
};
// 初始化链表
MyLinkedList() {
_dummyHead = new LinkedNode(0); // 这里定义的头结点 是一个虚拟头结点,而不是真正的链表头结点
_size = 0;
}
// 获取到第index个节点数值,如果index是非法数值直接返回-1, 注意index是从0开始的,第0个节点就是头结点
int get(int index) {
if (index > (_size - 1) || index < 0) {
return -1;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead->next;
while(index--){ // 如果--index 就会陷入死循环
cur = cur->next;
}
return cur->val;
}
// 在链表最前面插入一个节点,插入完成后,新插入的节点为链表的新的头结点
void addAtHead(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
newNode->next = _dummyHead->next;
_dummyHead->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在链表最后面添加一个节点
void addAtTail(int val) {
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(cur->next != nullptr){
cur = cur->next;
}
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 在第index个节点之前插入一个新节点,例如index为0,那么新插入的节点为链表的新头节点。
// 如果index 等于链表的长度,则说明是新插入的节点为链表的尾结点
// 如果index大于链表的长度,则返回空
// 如果index小于0,则在头部插入节点
void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
if(index > _size) return;
if(index < 0) index = 0;
LinkedNode* newNode = new LinkedNode(val);
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur->next;
}
newNode->next = cur->next;
cur->next = newNode;
_size++;
}
// 删除第index个节点,如果index 大于等于链表的长度,直接return,注意index是从0开始的
void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
if (index >= _size || index < 0) {
return;
}
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while(index--) {
cur = cur ->next;
}
LinkedNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
//delete命令指示释放了tmp指针原本所指的那部分内存,
//被delete后的指针tmp的值(地址)并非就是NULL,而是随机值。也就是被delete后,
//如果不再加上一句tmp=nullptr,tmp会成为乱指的野指针
//如果之后的程序不小心使用了tmp,会指向难以预想的内存空间
tmp=nullptr;
_size--;
}
// 打印链表
void printLinkedList() {
LinkedNode* cur = _dummyHead;
while (cur->next != nullptr) {
cout << cur->next->val << " ";
cur = cur->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
int _size;
LinkedNode* _dummyHead;
};
203.移除链表元素
遍历方法
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
if(head==nullptr) return head;
ListNode* node=new ListNode(-1);
node->next=head;
ListNode* cur=node;
/* 铭记:是对【下一个】结点进行操作
* 在“更换【下一个】结点”时,不可以切换到【再下一个】
*/
while(cur->next){//注意,需要判定下一个结点都存在
if(cur->next->val==val){
ListNode* tmp = cur->next;
cur->next=cur->next->next;
delete tmp;
}
else{//在这里分开
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return node->next;
}
递归方法
ListNode* removeElements(ListNode* head, int val) {
//递归方法
if (head == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
head->next = removeElements(head->next,val);
return head->val == val ? head->next : head;
}
206.反转链表
遍历法
要注意不要“提前”翻转
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
//遍历方法
ListNode* cur=head;
ListNode* pre=NULL;
ListNode* tmp=NULL;
while(cur){
tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;;
}
return pre;
}
递归方法
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head||!head->next){
return head;
}
ListNode* tmp=reverseList(head->next);
//现在tmp=head->next;
head->next->next=head;//tmp->next=head;
head->next=nullptr;//head<-tmp<-...
return tmp;
}
24.两两交换链表中的结点
题目链接
分奇偶确认终止循环的条件、及时保存可能改变的结点
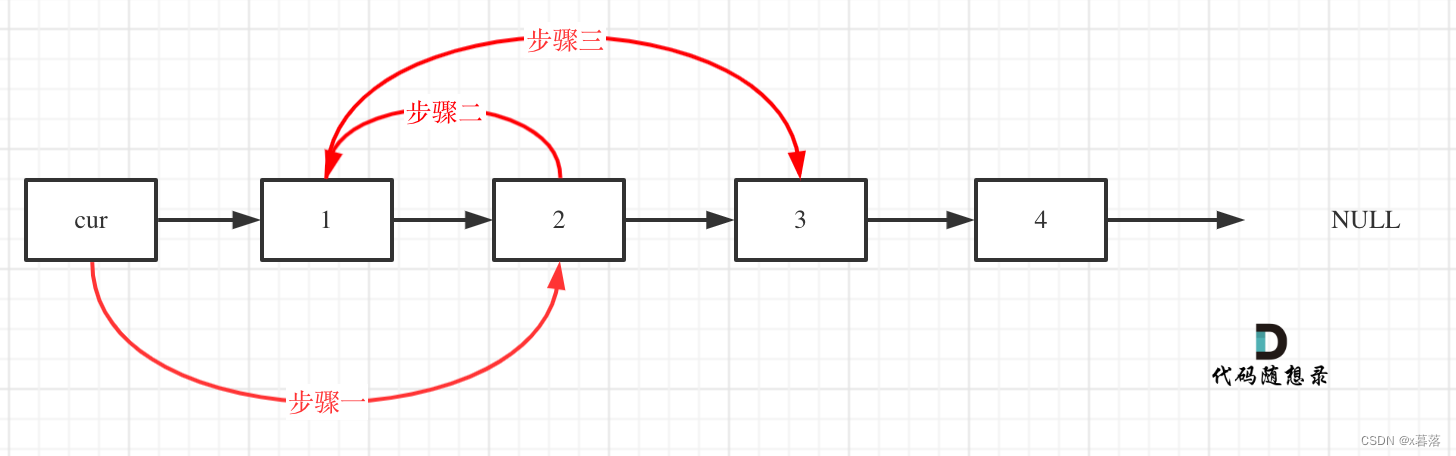
进步:看完卡哥的视频一遍AC了
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next=head;//虚拟头指针
ListNode* curr=dummy;
while(curr->next&&curr->next->next){
ListNode* tmp1=curr->next;
ListNode* tmp2=curr->next->next->next;
curr->next=curr->next->next;
curr->next->next=tmp1;
tmp1->next=tmp2;
curr=curr->next->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next=head;
ListNode* fast=dummy;
ListNode* slow=dummy;
while(n--&&fast!=nullptr){
fast=fast->next;
}
fast=fast->next;
while(fast){//fast比slow快n个结点
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
slow->next=slow->next->next;
return dummy->next;
}
面试题 02.07. 链表相交
题目链接
思路:先怼到末尾位对齐,如果全部相同则返回,如果有不同则退出
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
ListNode* curA{headA},*curB{headB};
int lenA{0},lenB{0};
//求A,B的长度
while(curA){
curA=curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB){
curB=curB->next;
lenB++;
}
int gap=lenA-lenB;
curA=headA; curB=headB;
if(gap>0){ //A长
while(gap--){
curA=curA->next;
}
}else if(gap<0){ //B长
while(gap++){
curB=curB->next;
}
}
//要注意对返回值的初始化
ListNode * ans;
if(curA==curB){
ans=curA;
}
else{
ans=curA->next;
}
while(curB&&curA){
if(curB!=curA){
ans=curA->next;
}
curB=curB->next;
curA=curA->next;
}
return ans;
}
142.环形链表II
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
//环应至少【2】结点
if(!head||!head->next||!head->next->next)//正常判空、指针/循环有效性、快指针循环有效性
return NULL;
ListNode* fast=head;
ListNode* slow=head;
while(1){
if(fast==NULL||fast->next==NULL){
return NULL;
}
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
if(slow==fast) break;//s+l
}
fast=head;//s+l=n*r
while(fast!=slow){
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return fast;
}







 本文详细介绍了链表的设计与操作,包括添加、删除、反转、交换节点以及检测链表的特定问题如倒数第N个节点和环形链表。通过实例演示了如何使用虚拟头节点简化头节点处理,并提供了遍历和递归的方法实现各种链表操作。
本文详细介绍了链表的设计与操作,包括添加、删除、反转、交换节点以及检测链表的特定问题如倒数第N个节点和环形链表。通过实例演示了如何使用虚拟头节点简化头节点处理,并提供了遍历和递归的方法实现各种链表操作。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








