Netty入门案例,讲解Netty的客户端 和服务器端的实现,Netty是NIO框架,同类型的还有Mina,不过Netty的使用,比Mina更容易简单。
官网地址:https://netty.io/
优快云的案例:http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/column/details/enjoynetty.html
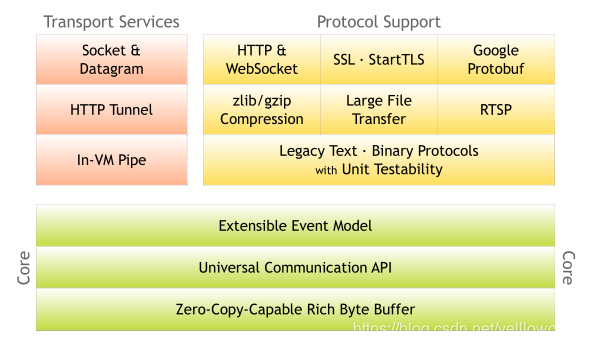
Netty的系统架构中,实现了Http,SSL,google Protobuf,websocket的协议。
代码地址
https://gitee.com/yellowcong/netty/tree/master/demo-helloword
案例
通过Netty实现客户端和服务器段消息的传递
实现效果
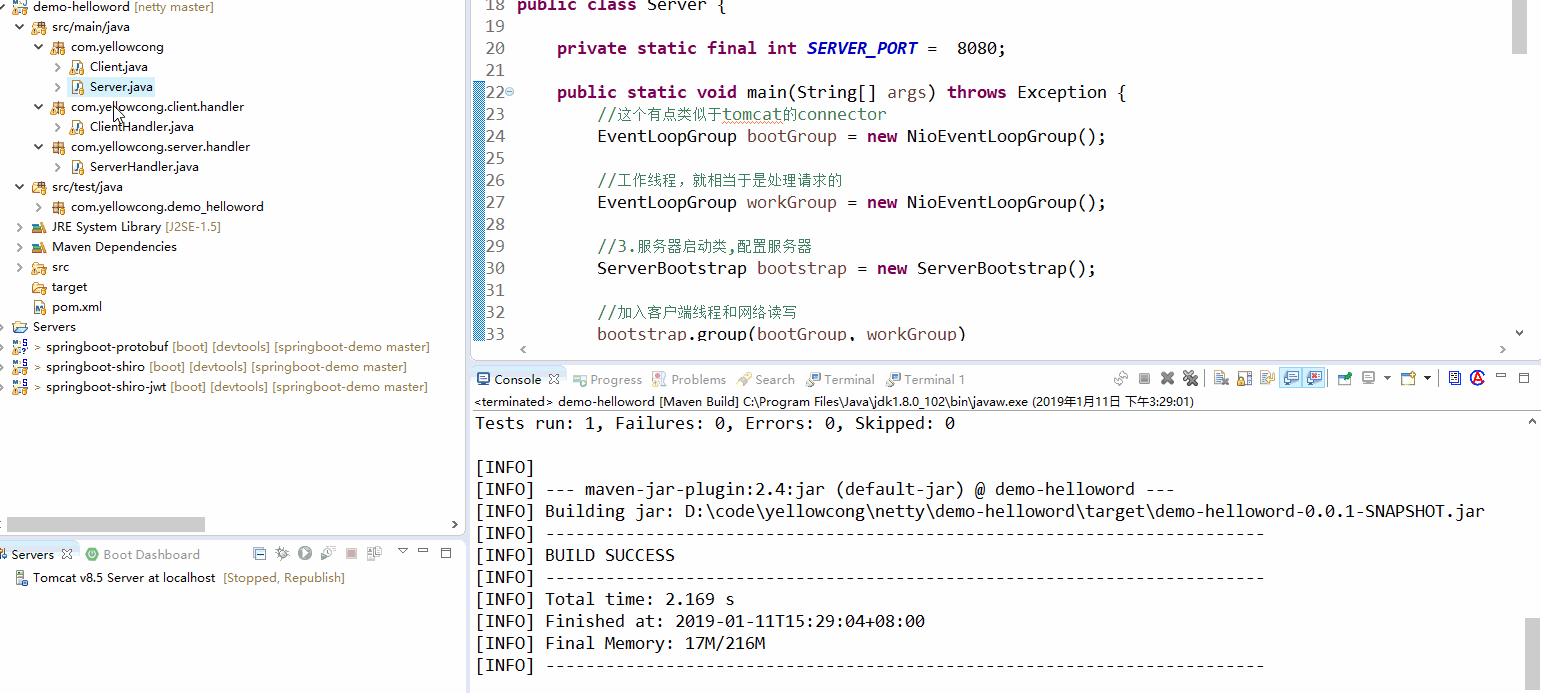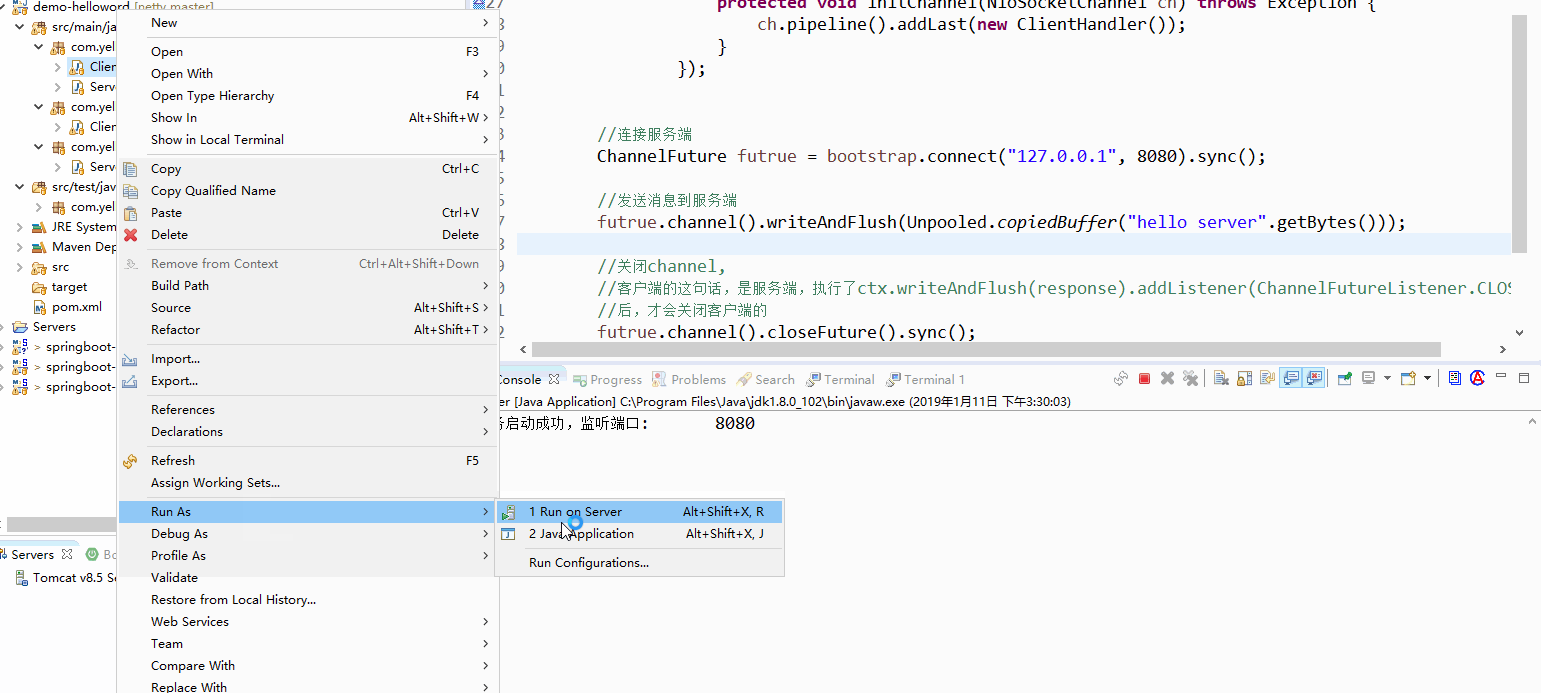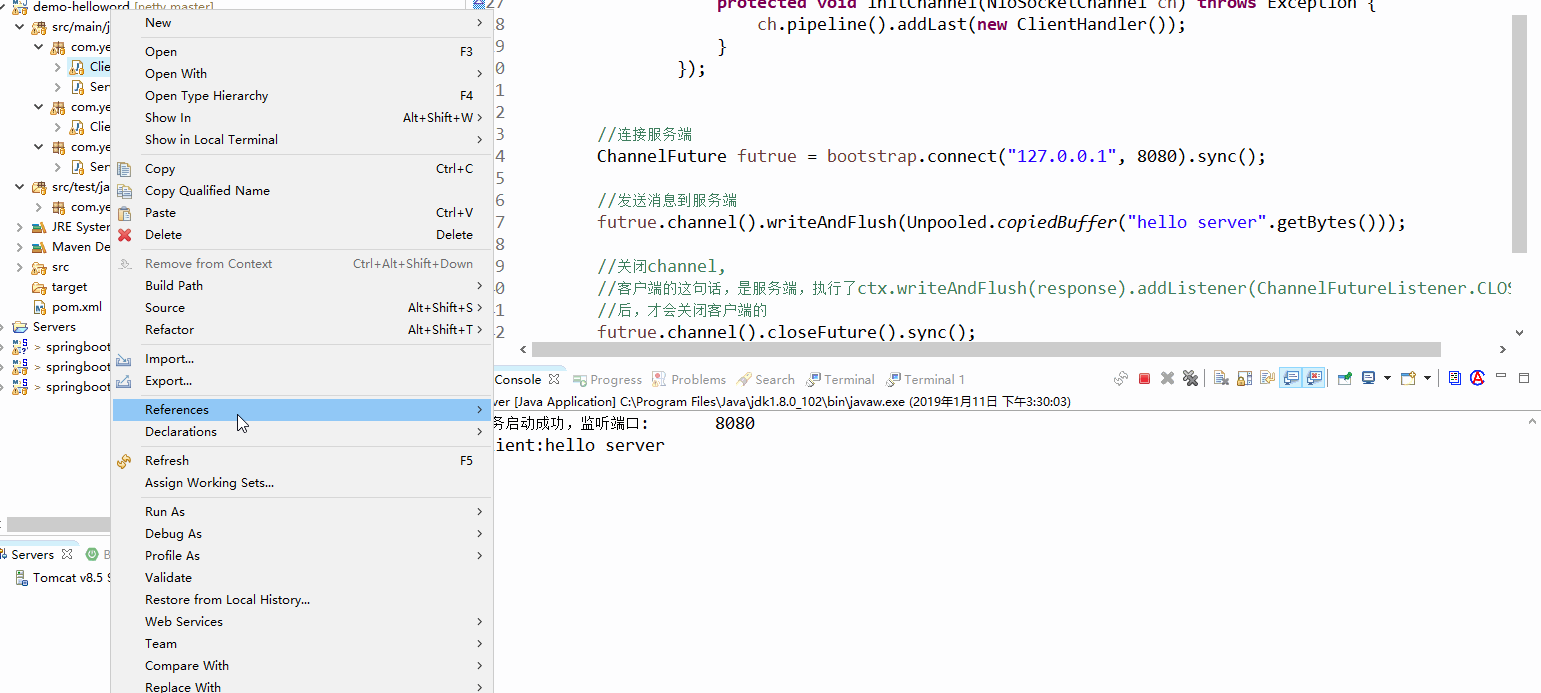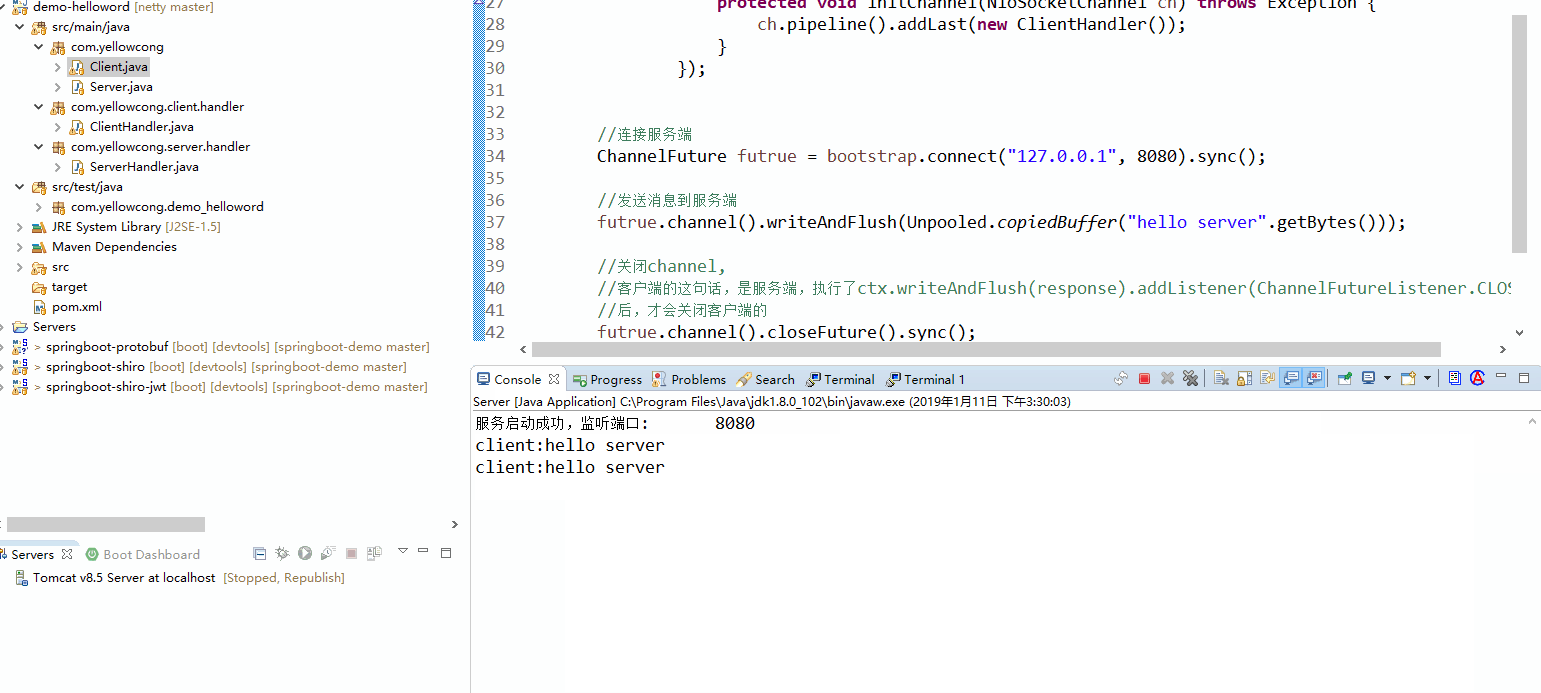
可以看到运行服务端后,一致监听8080 端口,然后,运行客户端,发送消息给服务端,我发送了两次消息,可以看到,服务端,收到了两次消息。
服务器端
服务器段,使用的是ServerBootstrap 类,而且需要有两个线程池,一个是客户端连接池(EventLoopGroup client),还有一个是网络传输线程池(EventLoopGroup work),设定服务器或客户端处理的Handlerd的时候SocketChannel 这个类是Netty包下的的,而不是NIO的。channel.channel().closeFuture().sync() 这端代码的阻塞的,用于等待管道来。如果不设定等待,服务器端就直接执行完毕,程序终止。
package yellowcong.socket.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
/**
* 创建日期:2017年10月8日 <br/>
* 创建用户:yellowcong <br/>
* 功能描述:
*/
public class Server {
public static final Integer PORT = 8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.第一个线程组 是用于接收Client端连接的
EventLoopGroup bootGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //客户端
//2.第二个线程组 实际业务操作请求
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); //网络读写
//3.服务器启动类,配置服务器
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
//加入客户端线程和网络读写
bootstrap.group(bootGroup, workGroup)
//我要指定使用NioServerSocketChannel这种类型的通道 ,当我们是Http的时候,需要更换这个Channel的类型
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
// 指定处理SockerChannel 的处理器
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){ //一掉要注意这个 SocketChannel 是Netty封装的,不是NIO
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//将我们的服务器处理类传递进去
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ServerHandler());
}
})
//设定BackLog大小大小
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128) //生产环境中,最好配额制100多
//保持连接
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true)
;
System.out.println("服务器启动。。。。。。");
//绑定指定的端口 进行监听
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(PORT).sync();
//如果不休眠 ,直接就结束了
// Thread.sleep(1000000);
//关闭Channel
//这个是相当于程序是睡眠模式,线程阻塞在这个地方
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
//关闭线程组
bootGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
服务器端消息处理类
Netty的消息处理类,需要实现ChannelHandler 接口,但是我们可以直接继承NIO已经帮我们写好的ChannelHandlerAdapter类,然后复写里面的channelRead 和exceptionCaught 方法,channelRead 用于处理业务逻辑,exceptionCaught 用于处理异常捕获设定响应后就关闭程序.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE); 在服务器端,做断开连接操作
package yellowcong.socket.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFutureListener;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
/**
* 创建日期:2017年10月8日 <br/>
* 创建用户:yellowcong <br/>
* 功能描述:服务器请求
*/
//这个Handler需要继承 ChannelHandlerAdapter,这个是Netty实现的
public class ServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
//读取Message
ByteBuf buff = (ByteBuf) msg;
//建立一个数组用来存储读取的数据
byte [] data = new byte[buff.readableBytes()];
buff.readBytes(data);
System.out.println("Server:\t"+new String(data));
//回馈客户端
ctx.writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("Hello,Server get Data".getBytes()))
//设定响应后就关闭程序
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//用来处理Netty执行过程中的异常
cause.printStackTrace(); //打印错误
ctx.close(); //关闭容器
}
}
客户端
Client端,使用的启动类是Bootstrap,只需要一个工作线程组就可以了,然后调用 Bootstrap的connect() 进行服务器连接.
package yellowcong.socket.netty;
import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
/**
* 创建日期:2017年10月8日 <br/>
* 创建用户:yellowcong <br/>
* 功能描述:
*/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
EventLoopGroup workGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
//客户端启动
Bootstrap boot = new Bootstrap();
boot.group(workGroup)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class) //客户端的Socker
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>(){ //一掉要注意这个 SocketChannel 是Netty封装的,不是NIO
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
//将我们的服务器处理类传递进去
ch.pipeline().addLast(new ClientHandler());
}
});
//绑定指定的端口 进行监听
ChannelFuture channel = boot.connect("127.0.0.1", 8080).sync();
//发送数据
channel.channel().writeAndFlush(Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello Client".getBytes()));
//这个相当于没有关闭Channel,注释
channel.channel().closeFuture().sync();
//关闭线程组
workGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
客户端消息处理类
客户端消息和服务端的消息处理相同,就是继承了ChannelHandlerAdapter 类,复写里面channelRead 和exceptionCaught 方法
package yellowcong.socket.netty;
import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerAdapter;
import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
import io.netty.util.ReferenceCountUtil;
/**
* 创建日期:2017年10月8日 <br/>
* 创建用户:yellowcong <br/>
* 功能描述:客户端请求的处理
*/
public class ClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
//打印错误
cause.printStackTrace();
//关闭容器
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
try {
//获取message
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
//将数据写到字节数组中
byte [] data = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(data);
//打印数据
System.out.println("Client:\t"+new String(data));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//释放消息
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
}










 本文介绍了一个简单的Netty应用案例,包括客户端与服务器端的搭建流程。Netty是一种高性能的NIO框架,支持HTTP、SSL等多种协议。文章详细展示了如何通过Netty实现客户端与服务器之间的消息传递。
本文介绍了一个简单的Netty应用案例,包括客户端与服务器端的搭建流程。Netty是一种高性能的NIO框架,支持HTTP、SSL等多种协议。文章详细展示了如何通过Netty实现客户端与服务器之间的消息传递。

















 514
514

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










