一、二叉树
二叉树(Binary Tree)是n(n>=0)个结点的有限集合,该集合或者为空集(称为空二叉树),或者由一个根结点和两颗互不相交的,分别称为根结点的左子树和右子树的二叉树;
二、二叉树的性质
(1)性质1:在二叉树的第i层上至多有个结点
(2)性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有个结点(k≥1)
(3)性质3:对任何一颗二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则no=n2+1;
(4)性质4:具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为,([ ]表示不大于x的最大整数)
(5)性质5:如果对一颗有n个结点的完全二叉树)(其深度为)的结点按层序编号(从第1层到第层,每层从左到右),对任一结点i(1≤i≤n)有:
1.如果i=1,则结点i是二叉树的根,无双亲;如果i>1,则其双亲是结点[i/2];
2.如果2i>n,则结点i无左孩子(结点i为叶子结点);否则其左孩子是结点2i;
3.如果2i+1>n,则结点i无右孩子;否则其右孩子是结点2i+1.
三、二叉树的的存储结构
1、二叉树的顺序存储结构:用一维数组存储二叉树中的结点,并且结点的存储位置,也就是数组的下标要能体现结点之间的逻辑关系,比如双亲与孩子的关系。
下标:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
A | B | C | # | # | D | E | # | # | F | # | # | G | # | H | # | # |

So :顺序结构一般适合用于完全二叉树,才不会造成存储空间的浪费
2、二叉链表结构:由于顺序存储适用性不强,所以提出链式存储结构。二叉树每个结点最多有2个孩子,所以设计如下的结构:
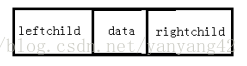
所以二叉树链表的结点结构定义为:
typedef char ElemType;
#define END '#'typedef struct BtNode //二叉树定义结点
{
ElemType data;
BtNode* leftchild;
BtNode* rightchild;
}BtNode,*BinaryTree;3、遍历二叉树: 从根结点出发,按照某种次序依次访问二叉树中的所有结点,使得每个结点被访问一次且仅被访问一次;
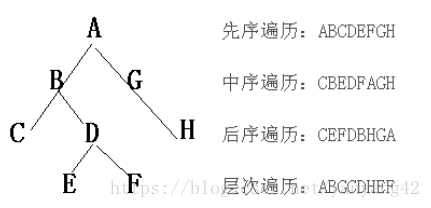
(1)先序遍历:先访问根结点,然后前序左子树,再前序右子树;
void PreOrder(BtNode* p) //先序遍历
{
if (p!=NULL)
{
cout << " " << p->data;
PreOrder(p->leftchild);
PreOrder(p->rightchild);
}
}(2)中序遍历:从根结点开始(注意并不是先访问根结点),中序遍历根结点的左子树,然后访问根结点,最后中序遍历右子树;
void InOrder(BtNode* p)//中序遍历
{
if (p!= NULL)
{
InOrder(p->leftchild);
cout << " " << p->data;
InOrder(p->rightchild);
}
}(3)后序遍历:从左到右先叶子后结点的方式访问左右子树,最后访问根结点;
void PastOrder(BtNode* p)//后序遍历
{
if (p != NULL)
{
PastOrder(p->leftchild);
PastOrder(p->rightchild);
cout << " " << p->data;
}
}(4)层次遍历:从根结点开始访问,从上而下逐层遍历,在同一层中,按从左到右的顺序对结点逐个访问;
void LevelOrder(BtNode* ptr)//层次遍历
{
if (ptr==NULL)
{
return;
}
queue<BtNode*> d1;
d1.push(ptr);
while (!d1.empty())
{
ptr = d1.front();
cout << ptr->data << " ";
d1.pop();
if (ptr->leftchild)
{
d1.push(ptr->leftchild);
}
if (ptr->rightchild)
{
d1.push(ptr->rightchild);
}
}
cout << endl;
} 根据二叉树的先、中、后序列,可以得到两个二叉树遍历的性质
根据二叉树的先、中、后序列,可以得到两个二叉树遍历的性质
(1)已知先序遍历和中序遍历,可以唯一确定一颗二叉树;
(2)已知后序遍历和中序遍历,可以唯一确定一颗二叉树;
4、二叉树的建立
附:创建结点、释放结点
BtNode* BuyNode() //购买结点
{
BtNode* node = (BtNode*)malloc(sizeof(BtNode));
assert(node!=NULL);
memset(node, 0, sizeof(BtNode));
return node;
}
void free_node(BtNode* p)//释放结点
{
free(p);
}(1)根据输入字符创建树
BtNode* CreateTree1()//根据输入创建二叉树(in:ABC##DE##F##G#H##)
{
ElemType x;
BtNode* s = NULL;
cin >> x;
if (x!=END)
{
s = BuyNode();
s->data = x;
s->leftchild = CreateTree1();
s->rightchild = CreateTree1();
}
return s;
}(2)根据字符串数组创建二叉树
BtNode* CreateTree2(ElemType* &str)//根据字符数组创建二叉树
{
BtNode* s = NULL;
if (str != NULL && *str != END)
{
s = BuyNode();
s->data = *str;
s->leftchild = CreateTree2(++str);
s->rightchild = CreateTree2(++str);
}
return s;
}(3)根据先序、中序遍历创建二叉树
BtNode*CreateTreePI(ElemType* ps, ElemType* is,unsigned len)//根据先序、中序遍历创建二叉树
{
if (ps==NULL||is==NULL||len<1)
{
return NULL;
}
BtNode* s = BuyNode();
s->data = *ps;
int n = 0;
while (n<len)
{
if (*(is+n)==*ps)
{
break;
}
++n;
}
s->leftchild = CreateTreePI(ps + 1, is, n);
s->rightchild = CreateTreePI(ps + n + 1, is + n + 1, len - n - 1);
return s;
}(4)根据中序、后序遍历创建二叉树
int Find_Node(ElemType e,ElemType* is, unsigned len)//在中序中找到根结点的位置
{
if (is!=NULL&&len>0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len;++i)
{
if (e==*(is+i))
{
return i;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
BtNode*CreateTreeIL(ElemType* is, ElemType* ls, unsigned len)//根据中序、后序遍历创建二叉树
{
if (is == NULL || ls == NULL || len<1)
{
return NULL;
}
BtNode* s = BuyNode();
s->data = *(ls + len-1);
int pos = Find_Node(*(ls + len-1),is, len);//在中序中找到根结点的位置
if (pos==-1)
{
return NULL;
}
s->leftchild = CreateTreeIL(is, ls, pos);
s->rightchild = CreateTreeIL(is+pos+1, ls+pos, len-pos-1);
return s;
}(5)根据已存在的链式二叉树转为顺序存储形式的二叉树结构
void CreateTree_br(BtNode* node, ElemType* br, int len, int pos)//根据链式二叉树建立数组形式的二叉树
{
if (node == NULL || br == NULL || len<1) //pos:在数组中的下标位置
{
return;
}
br[pos] = node->data;
if (pos*2+1<len)
{
CreateTree_br(node->leftchild, br, len, pos * 2 + 1);
}
if (pos * 2 + 2<len)
{
CreateTree_br(node->rightchild, br, len, pos * 2 + 2);
}
}(6)根据已存在的顺序存储形式的二叉树结构转为链式二叉树
BtNode* Create_tree(ElemType *ar, int n,int pos)//int
{
if (ar!=NULL&&pos<n)
{
BtNode* s = BuyNode();
s->data = ar[pos];
s->leftchild = Create_tree(ar, n, pos * 2 + 1);
s->rightchild = Create_tree(ar, n, pos * 2 + 2);
return s;
}
return NULL;
}








 本文详细介绍了二叉树的概念、性质及存储方式,并深入探讨了遍历方法及其应用,包括先序、中序、后序及层次遍历。此外,还介绍了如何通过不同方式构建二叉树。
本文详细介绍了二叉树的概念、性质及存储方式,并深入探讨了遍历方法及其应用,包括先序、中序、后序及层次遍历。此外,还介绍了如何通过不同方式构建二叉树。
















 1065
1065

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








