1 回顾
在Ascend的aclgraph(一)aclgraph是什么?torchair又是怎么成图的?中提到了AclConcreteGraph的概念,
if self.config.mode.value == "max-autotune":
from torchair._ge_concrete_graph.fx2ge_converter import GeConcreteGraph
graph = GeConcreteGraph(self.config, name="graph_" + str(_next_unique_graph_id()))
elif self.config.mode.value == "reduce-overhead":
from torchair._acl_concrete_graph.fx2acl_converter import AclConcreteGraph
graph = AclConcreteGraph(self.config)
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported npu backend mode: {self.config.mode.value}.")
GeConcreteGraph先暂且不讨论,后续在花一个篇章去探讨。
2 AclConcreteGraph
先给出代码中定义(部分片段):
class AclConcreteGraph(ConcreteGraphBase):
def __init__(self, config: CompilerConfig, pool=None, stream=None, capture_error_mode: str = "global",
num_warmup_iters=0):
try:
import torch_npu
except ImportError as e:
raise RuntimeError(
"Couldn't import torch_npu. When the CompilerConfig.mode is reduce-overhead, "
"it is necessary to use torch_npu.npu.NPUGraph(), so importing torch_npu is essential.") from e
self._config = config
self._npugraph = torch_npu.npu.NPUGraph()
self._mempool = torch_npu.npu.graph_pool_handle() if pool is None else pool
self._stream = stream
self._capture_error_mode = capture_error_mode
self._num_warmup_iters = num_warmup_iters
self._captured = False
self._fx_graph = None
self._replay_func: Callable = None
self._capture_inputs = []
self._capture_outputs = []
self._user_inputs_list = []
self._meta_inputs = []
self._meta_outputs = []
关注到,上述__init__过程中提到了NPUGraph和graph_pool_handle两个概念。这2个概念都来自于torch_npu,而torch_npu又涉及到另外一个开源仓库,地址如下:
https://gitee.com/ascend/pytorch
先将代码clone下来,看下NPUGraph的定义。
git clone https://gitee.com/ascend/pytorch.git
2.1 NPUGraph
先看NPUGraph的定义。
class NPUGraph(torch_npu._C._NPUGraph):
r"""Wrapper around a NPU graph.
.. warning::
This API is in beta and may change in future releases.
"""
def __new__(cls):
return super().__new__(cls)
def capture_begin(self, pool=None, capture_error_mode="global"):
r"""Begin capturing NPU work on the current stream.
Typically, you shouldn't call ``capture_begin`` yourself.
Use :class:`~torch.npu.graph` or :func:`~torch.npu.make_graphed_callables`,
which call ``capture_begin`` internally.
Arguments:
pool (optional): Token (returned by :func:`~torch.npu.graph_pool_handle` or
:meth:`other_Graph_instance.pool()<torch.npu.NPUGraph.pool>`) that hints this graph may share memory
with the indicated pool. See :ref:`Graph memory management<graph-memory-management>`.
capture_error_mode (str, optional): specifies the aclmdlRICaptureMode for the graph capture stream.
Can be "global", "thread_local" or "relaxed". During npu graph capture, some actions, such as npuMalloc,
may be unsafe. "global" will error on actions in other threads, "thread_local" will only error for
actions in the current thread, and "relaxed" will not error on these actions. Do NOT change this setting
unless you're familiar with `aclmdlRICaptureMode`_
""" # noqa: B950
super().capture_begin(pool=pool, capture_error_mode=capture_error_mode)
def capture_end(self):
r"""End NPU graph capture on the current stream.
After ``capture_end``, ``replay`` may be called on this instance.
Typically, you shouldn't call ``capture_end`` yourself.
Use :class:`~torch.npu.graph` or :func:`~torch.npu.make_graphed_callables`,
which call ``capture_end`` internally.
"""
super().capture_end()
def replay(self):
r"""Replay the NPU work captured by this graph."""
super().replay()
def reset(self):
r"""Delete the graph currently held by this instance."""
super().reset()
def pool(self):
r"""Return an opaque token representing the id of this graph's memory pool.
This id can optionally be passed to another graph's ``capture_begin``,
which hints the other graph may share the same memory pool.
"""
return super().pool()
NPUGraph类型是经过pybind绑定的,定义7个对外接口:
- capture_begin
- capture_end
- replay
- reset
- pool
- debug_dump
- enable_debug_mode
功能代码实现在torch_npu._C._NPUGraph中。其定义如下:
shared_ptr_class_<c10_npu::NPUGraph>(torch_N_m, "_NPUGraph")
.def(py::init<>())
.def(
"capture_begin",
[](c10_npu::NPUGraph& self,
std::optional<c10_npu::MempoolId_t> pool_opt,
std::string capture_error_mode) {
aclmdlRICaptureMode capture_mode;
c10_npu::MempoolId_t pool = pool_opt.has_value()
? pool_opt.value() : c10_npu::MempoolId_t{0, 0};
if (capture_error_mode == "global") {
capture_mode = aclmdlRICaptureMode::ACL_MODEL_RI_CAPTURE_MODE_GLOBAL;
} else if (capture_error_mode == "thread_local") {
capture_mode = aclmdlRICaptureMode::ACL_MODEL_RI_CAPTURE_MODE_THREAD_LOCAL;
} else if (capture_error_mode == "relaxed") {
capture_mode = aclmdlRICaptureMode::ACL_MODEL_RI_CAPTURE_MODE_RELAXED;
} else {
TORCH_CHECK(
false,
"Unknown capture error mode. Expected `global`, `thread_local`, or `relaxed`, got ",
capture_error_mode);
}
return self.capture_begin(pool, capture_mode);
},
py::arg("pool"),
py::arg("capture_error_mode"),
py::call_guard<py::gil_scoped_release>())
.def(
"capture_end",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::capture_end))
.def(
"replay",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::replay))
.def(
"reset",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::reset))
.def(
"pool",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::pool))
.def(
"debug_dump",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::debug_dump))
.def(
"enable_debug_mode",
torch::wrap_pybind_function_no_gil(&c10_npu::NPUGraph::enable_debug_mode));
这是典型的pybind11的代码逻辑。
先不深入讲这些接口是如何实现的,还是从调用逻辑上看,这些接口都是什么时候被调用的。
2.2 AclConcreteGraph中的compile实现
AclConcreteGraph调用时执行的就是__call__函数,其中调用了self.compile函数。
def __call__(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
self.compile(*args, **kwargs)
# input process
for idx in self._user_inputs_list:
if self._capture_inputs[idx].data_ptr() != args[idx].data_ptr():
self._capture_inputs[idx].copy_(args[idx])
# run
with record_function("acl_graph_replay"):
self._replay_func(*args, **kwargs)
return self._capture_outputs
self.compile函数是aclgraph编译的核心函数。
def compile(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any):
if self._captured:
# A fx graph just be captured once now.
return
import torch_npu
# warm up before capture
with record_function("acl_graph_warm_up"):
torch_npu.npu.synchronize()
for _ in range(self.num_warmup_iters):
outs = self.fx_graph(*args, **kwargs)
torch_npu.npu.synchronize()
# start capture aclgraph
self._captured = True
self._capture_inputs.extend(args)
logger.debug('Start to capture fx graph[id: %s] for AclGraph[id: %s].', id(self.fx_graph), id(self.graph))
with record_function("acl_graph_capture"):
self.capture(*args, **kwargs)
logger.info('Success to capture fx graph[id: %s] and start to run AclGraph[id: %s].',
id(self.fx_graph), id(self.graph))
代码中涉及到warm up过程,其中有self.fx_graph,这个self.fx_graph是什么呢?
其设置在_NpuGraphConverter的run方法中。
def run(self, *args, **kwargs):
optimized_fx = _optimize_fx(self.module)
self._graph.save_fx_graph(optimized_fx)
with self._graph.context():
super().run(*args, **kwargs)
return self._graph
流程图如下:

回到warmup阶段。代码中并未标注该warmup过程的作用,不过在前几篇的介绍中提到在图运行前进行warmup操作,可以生成一些缓存,避免在真正运行时候产生的编译时间开销。这里也大概可以这么理解吧。
接下来,进入关键函数
with record_function("acl_graph_capture"):
self.capture(*args, **kwargs)
经常看到record_function,小编这里也给出一个解释。
在 PyTorch 中,torch.profiler 提供了一套工具来帮助开发者分析和优化模型的性能。record_function 是 torch.profiler 模块中的一个上下文管理器(context manager),用于标记代码块以便于在性能分析期间更容易地识别和分析特定部分的行为。
主要作用
标记代码段:通过使用 record_function,可以为你的代码中的一段逻辑添加标签或名称。这对于了解特定函数、模块或自定义操作对整体性能的影响非常有用。
性能分析:当你使用 torch.profiler.profile 来分析你的模型时,record_function 标记的部分会在分析结果中以你指定的名字出现,使得分析报告更易于理解。它允许你聚焦于那些可能需要优化的关键区域。
事件追踪:record_function 可以为你感兴趣的代码块生成跟踪事件,这些事件会被包含在最终的性能分析报告中。这有助于深入理解各个部分执行的时间消耗情况以及它们之间的相互关系。
使用示例
以下是一个简单的例子,展示了如何使用 record_function:import torch from torch.profiler import profile, record_function, ProfilerActivity # 创建一个简单的模型和输入张量作为示例 model = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10) x = torch.randn(10) with profile(activities=[ProfilerActivity.CPU], record_shapes=True) as prof: with record_function("my_function"): y = model(x) print(prof.key_averages().table(sort_by="cpu_time_total")) # 输出将包括标记为 "my_function" 的部分的性能数据 在这个例子中,我们使用 record_function 来标记调用 model(x) 这一过程,并命名为 "my_function"。当我们打印出性能分析的结果时,可以看到关于 "my_function" 的详细信息,包括其CPU时间等,从而帮助我们了解这部分代码的性能特征。 总之,record_function 是一个非常有用的工具,可以帮助开发者更好地理解和优化他们的PyTorch模型,通过明确地标记代码的不同部分来进行细致的性能监控和分析。
2.3 capture函数
给出capture函数的调用图,如下:

还是得吐槽下,torchair中的代码注释太少了,太少了。看代码有点费劲。
def capture(self, *args: Any, **kwargs: Any):
from torchair._acl_concrete_graph.acl_graph import UpdatedNodeCaptureInterp, CapturedGraphUpdateAndReplay
captured_interpreter = UpdatedNodeCaptureInterp(self.fx_graph, self._meta_inputs)
updated_input_func = captured_interpreter.process_need_updated_ops()
import torch_npu
with torch_npu.npu.graph(self.graph, pool=self.pool, stream=self.stream,
capture_error_mode=self.capture_error_mode):
self._capture_outputs = captured_interpreter.run(*args, **kwargs)
updated_node_infos = captured_interpreter.captured_node_infos
logger.debug('In graph {%s}, the updated node num is {%s}.', id(self.fx_graph), len(updated_node_infos))
# gen run func
self._replay_func = CapturedGraphUpdateAndReplay(self.graph, updated_input_func, updated_node_infos)
logger.debug('In graph {%s}, all the non parameter tensor input index list is: {%s}.',
id(self.fx_graph), self._user_inputs_list)
process_need_updated_ops中主要是根据定义的_REPLACE_FUNC_MAP对象,对out_operator:torch.ops.npu.npu_fused_infer_attention_score.out进行替换。
_REPLACE_FUNC_MAP = {
torch.ops.npu.npu_fused_infer_attention_score.default: StaticWorkspaceReplaceFunc(
get_workspace=torch.ops.npu._npu_fused_infer_attention_score_get_max_workspace.default,
out_operator=torch.ops.npu.npu_fused_infer_attention_score.out,
workspace_keys=["workspace"],
output_keys=["attention_out", "softmax_lse"],
updated_param_keys=["actual_seq_lengths", "actual_seq_lengths_kv", "actual_shared_prefix_len"],
),
}
接下来就是主要部分:captured_interpreter.run。
with torch_npu.npu.graph(self.graph, pool=self.pool, stream=self.stream,
capture_error_mode=self.capture_error_mode):
self._capture_outputs = captured_interpreter.run(*args, **kwargs)
torch_npu.npu.graph是在torch_npu中定义的。torch_npu代码仓中的注释还是蛮清晰的,点赞。
class graph:
r"""Context-manager that captures NPU work into a :class:`torch.npu.NPUGraph` object for later replay.
See :ref:`CUDA Graphs <cuda-graph-semantics>` for a general introduction,
detailed use, and constraints.
Arguments:
npu_graph (torch.npu.NPUGraph): Graph object used for capture.
pool (optional): Opaque token (returned by a call to :func:`~torch.npu.graph_pool_handle()` or
:meth:`other_Graph_instance.pool()<torch.npu.NPUGraph.pool>`) hinting this graph's capture
may share memory from the specified pool. See :ref:`Graph memory management<graph-memory-management>`.
stream (torch.npu.Stream, optional): If supplied, will be set as the current stream in the context.
If not supplied, ``graph`` sets its own internal side stream as the current stream in the context.
capture_error_mode (str, optional): specifies the aclmdlRICaptureMode for the graph capture stream.
Can be "global", "thread_local" or "relaxed". During npu graph capture, some actions, such as npuMalloc,
may be unsafe. "global" will error on actions in other threads, "thread_local" will only error for
actions in the current thread, and "relaxed" will not error on actions. Do NOT change this setting
unless you're familiar with `aclmdlRICaptureMode`_
.. note::
For effective memory sharing, if you pass a ``pool`` used by a previous capture and the previous capture
used an explicit ``stream`` argument, you should pass the same ``stream`` argument to this capture.
.. warning::
This API is in beta and may change in future releases.
""" # noqa: B950
default_capture_stream: typing.Optional["torch.npu.Stream"] = None
def __init__(
self,
npu_graph,
pool=None,
stream=None,
capture_error_mode: str = "global",
):
# Lazy-init of default_capture_stream helps avoid circular-import errors.
# Not thread safe, but graphs already have the general (explicitly documented)
# restriction that only one capture may be underway at a time in the process.
if self.__class__.default_capture_stream is None:
self.__class__.default_capture_stream = torch.npu.Stream()
self.pool = () if pool is None else (pool,)
self.capture_stream = (
stream if stream is not None else self.__class__.default_capture_stream
)
if self.capture_stream is None:
raise RuntimeError("capture stream is None")
self.stream_ctx = torch.npu.stream(self.capture_stream)
self.npu_graph = npu_graph
self.capture_error_mode = capture_error_mode
def __enter__(self):
# Free as much memory as we can for the graph
torch.npu.synchronize()
gc.collect()
torch.npu.empty_cache()
# Stackoverflow seems comfortable with this pattern
self.stream_ctx.__enter__()
self.npu_graph.capture_begin(
*self.pool, capture_error_mode=self.capture_error_mode
)
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_value, traceback):
self.npu_graph.capture_end()
self.stream_ctx.__exit__(exc_type, exc_value, traceback)
# returning None should propagate exceptions from either capture_end or stream_ctx.__exit__()
graph的定义了__enter__和__exit__,对应了上面with语句的调用。这里也呼应了前面对capture_begin和capture_end的注释,不用手动对这2个接口进行调用。
到这里,也就是知道了capture_begin和capture_end这2个函数调用的位置。
大概调用关系图如下
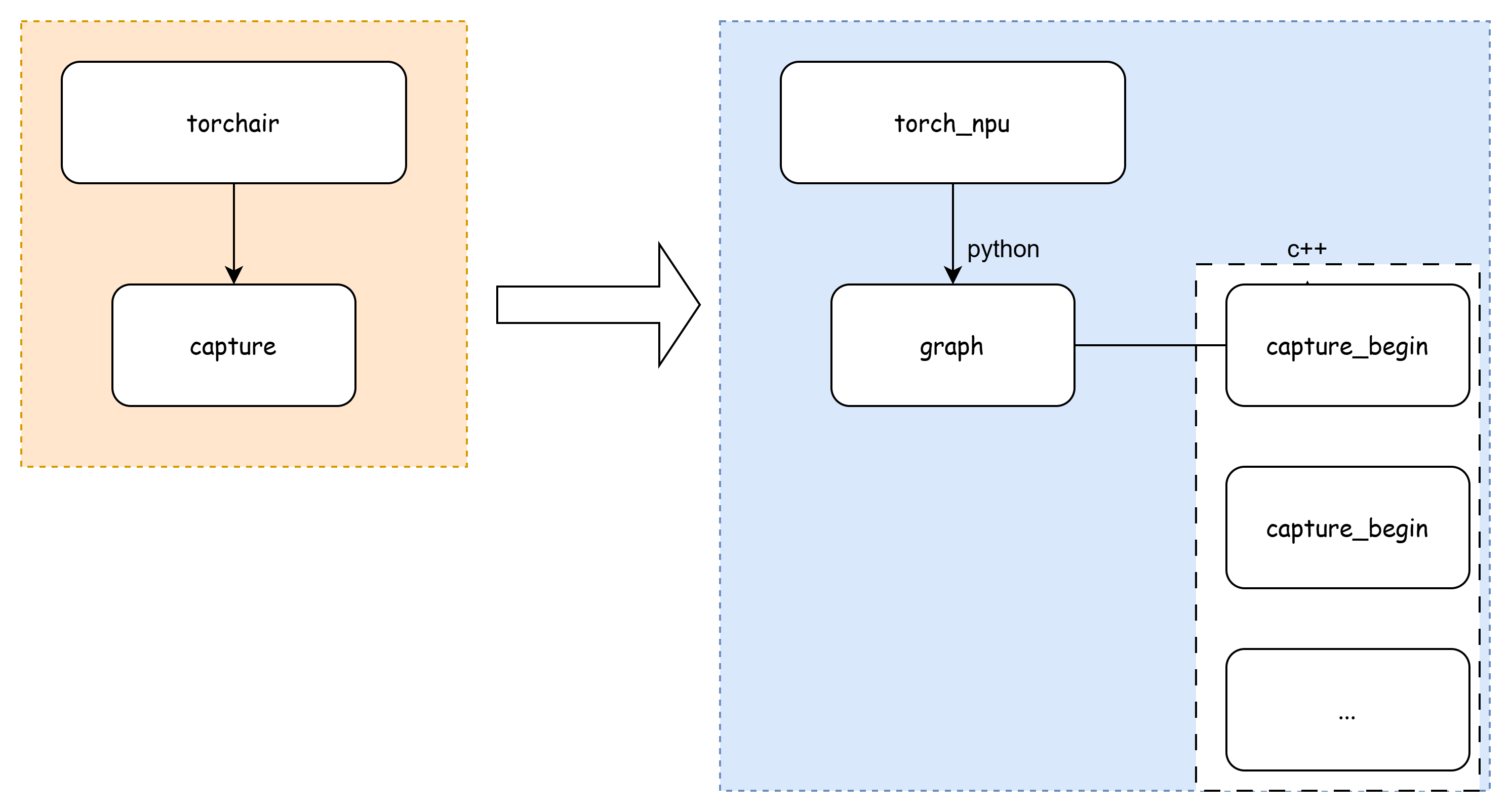
注意到,在capture_begin和capture_end中间还调用了captured_interpreter.run,继续对齐打开看下。
class UpdatedNodeCaptureInterp(fx.Interpreter):
UpdatedNodeCaptureInterp是继承fx.Interpreter,调用的是原始fx.Interpreter的run方法。
2.4 fx.Interpreter
fx.Interpreter 是 PyTorch 的 torch.fx 包中的一个类,它用于解释执行由 torch.fx.Tracer 生成的计算图(Graph)。torch.fx 是 PyTorch 提供的一个工具集,旨在支持模型变换、分析以及自动微分等功能。通过将模型转换为一种中间表示(即计算图),torch.fx 允许用户以编程方式操作和优化这些模型。
Interpreter 类
Interpreter 主要用于逐节点地解释执行计算图。这意味着它可以遍历计算图中的每一个节点,并根据该节点所代表的操作来执行相应的函数或方法。这对于调试、变换计算图或者实现自定义的执行逻辑特别有用。
run 方法
run 方法是 Interpreter 类中的一个重要方法,它的主要作用是从计算图的起点开始执行整个计算图直至结束。当你调用 run 方法时,Interpreter 会按照计算图中节点的拓扑顺序依次解释并执行每个节点对应的操作。
参数:通常情况下,run 方法接受与原始模型前向传播相匹配的输入参数。
返回值:最终返回计算图执行的结果,这通常是与模型输出相对应的数据。
示例代码
以下是一个简化的示例,展示了如何使用 Interpreter 及其 run 方法:
import torch
import torch.fx as fx
# 定义一个简单的模型
class MyModel(torch.nn.Module):
def forward(self, x):
return torch.relu(x)
# 实例化模型并创建其计算图
model = MyModel()
traced = fx.symbolic_trace(model)
# 创建 Interpreter 并运行计算图
interpreter = fx.Interpreter(traced)
output = interpreter.run(torch.tensor([-1.0, 2.0, -3.0]))
print(output) # 输出将会是 [0., 2., 0.]
在这个例子中,我们首先定义了一个简单的模型 MyModel,然后使用 fx.symbolic_trace 来生成这个模型的计算图。接着,我们创建了一个 Interpreter 实例,并通过调用 run 方法执行了这个计算图,传入了一些输入数据。最后,打印出经过 ReLU 激活函数处理后的输出结果。
总之,fx.Interpreter 的 run 方法提供了一种直接且灵活的方式来执行 torch.fx 计算图,使得开发者可以更容易地进行模型调试、变换及优化。
3 小结
整体梳理下来,aclgraph成图,最开始的来源还是torch.compile中的FX graph,这其实与cudagraph的图来源是一样的。只是, 当前在torchair中对图进行了一些修改(也可认为是算子适配,或者算子替换),以便支持npu上的运行。
在torchair代码中也看到了一些问题,比如节点替换的时候,会遍历整个图中的节点,这个再图比较大的时候,其实也是有时间开销的,可以考虑下下如何优化。另外,代码基本没有注释。
下一篇章,将对capture_begin和capture_end展开分析。






















 2994
2994

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








