我们这里讨论的图是图论中的图,主要是研究如何将图显示在一个2D的平面上。首先举一个例子,考虑一个随机图:
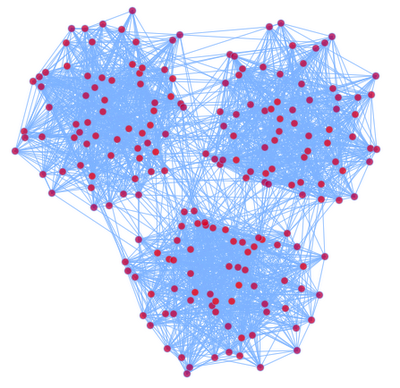
我们定义3n个顶点,分成3个团(Group),我们定义:
p(vi,vj)为vi和vj有边的概率,如果vi,vj属于同一个团,我们去比较大的概率,否则取比较小的概率。这样我们定义了一个有3个Group的随机图。
如果我们想把这个图在2D平面上显示出来,我们希望显示出来的图也能够显示出这种Group的结构。下面就是我们根据一定算法画出来的图:
对于画图的问题,我们可以如下定义:
给定一个图G{V,E},我们的任务是为每个顶点选择2D坐标vi(x,y),以最小化一个我们定义的能量函数E(V,E)。
首先我们考虑最小化的算法,我们可以用经典的梯度下降法,算法如下:
1. 对顶点vi,i=1,2,......,|V|,随机生成每个顶点的坐标。
2. for t = 1 to T:
for i = 1 to |V|:
计算E相对于vi的梯度下降方向ei,并产生vi的下一个位置 vi(t+1) = vi(t) + alpha * e,alpha是步长
这就是梯度下降法的步骤,当然还可以用很多优化算法,比如共轭梯度法,或者进化计算的方法。下面我们主要考虑如何设计能量函数E,E的设计我们将得到分子结构的启发。
我们定义3n个顶点,分成3个团(Group),我们定义:
p(vi,vj)为vi和vj有边的概率,如果vi,vj属于同一个团,我们去比较大的概率,否则取比较小的概率。这样我们定义了一个有3个Group的随机图。
如果我们想把这个图在2D平面上显示出来,我们希望显示出来的图也能够显示出这种Group的结构。下面就是我们根据一定算法画出来的图:

对于画图的问题,我们可以如下定义:
给定一个图G{V,E},我们的任务是为每个顶点选择2D坐标vi(x,y),以最小化一个我们定义的能量函数E(V,E)。
首先我们考虑最小化的算法,我们可以用经典的梯度下降法,算法如下:
1. 对顶点vi,i=1,2,......,|V|,随机生成每个顶点的坐标。
2. for t = 1 to T:
for i = 1 to |V|:
计算E相对于vi的梯度下降方向ei,并产生vi的下一个位置 vi(t+1) = vi(t) + alpha * e,alpha是步长
这就是梯度下降法的步骤,当然还可以用很多优化算法,比如共轭梯度法,或者进化计算的方法。下面我们主要考虑如何设计能量函数E,E的设计我们将得到分子结构的启发。







 本文探讨了如何在二维平面上展示图论中的图,并强调了如何通过算法保持图中Group的结构。介绍了一种使用梯度下降法来最小化能量函数的方法,以确定顶点的最佳坐标。
本文探讨了如何在二维平面上展示图论中的图,并强调了如何通过算法保持图中Group的结构。介绍了一种使用梯度下降法来最小化能量函数的方法,以确定顶点的最佳坐标。
















 2044
2044










