SVN supports several protocols for network access: SVN, SVN+SSH, HTTP, HTTPS. If you are behind a firewall, HTTP-based Subversion is advantageous since SVN traffic will go through the firewall without any additional firewall rule setting. In this tutorial, I will describe how to set up an HTTP-based Subversion server on CentOS or Fedora platform.
First, install Subversion, as well as Subversion module for Apache HTTP server as follows. This will also install Apache HTTP server as a dependency if it is installed.
Next, create a local SVN repository which will store code
$ sudo svnadmin create /svnrepos
Make the SVN repository readable and writable by the same user as the one which Apache HTTP server runs as. On CentOS or Fedora platforms, this user is "apache".
Edit Apache HTTP server configuration as follows.
LoadModule dav_svn_module modules/mod_dav_svn.so LoadModule authz_svn_module modules/mod_authz_svn.so <Location /svnrepos> DAV svn SVNPath /svnrepos AuthType Basic AuthName "Subversion repositories" AuthUserFile /etc/svn-auth-users Require valid-user </Location>
Next, add Subversion users who are authorized to access the SVN server. Here I use basic authentication provided by Apache HTTP server. For that, usehtpasswd command which creates usernames and password for authenticated HTTP users.
The first time you run htpasswd command, use "-c" option, which will create an initial SVN password file. For subsequent runs ofhtpasswd command, do not use "-c" option.
New password: Re-type new password: Adding password for user user1
$ sudo htpasswd -m /etc/svn-auth-users user3
. . .
Now restart Apache HTTP server.
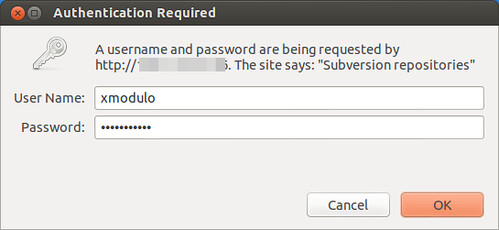
At this point, the SVN server should be accessible via HTTP. Go to: "http://<ip-address-svn-server>/svnrepos" to browse the SVN repository via web interface. As shown below, you will be prompted to enter username and password to proceed.
Also, when you try to access the SVN server from SVN client software, you will also be required to authenticate yourself.




 本文详细介绍如何在CentOS或Fedora平台上配置基于HTTP的Subversion(SVN)服务器。包括安装Subversion及其Apache模块、创建本地SVN仓库、设置权限、配置Apache服务器以及添加授权用户等步骤。
本文详细介绍如何在CentOS或Fedora平台上配置基于HTTP的Subversion(SVN)服务器。包括安装Subversion及其Apache模块、创建本地SVN仓库、设置权限、配置Apache服务器以及添加授权用户等步骤。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








