1、739. 每日温度
单调栈的思想是存储单调增加/减小的下标,这里存储下标是因为题目一般会用到索引信息。
自己想的有些复杂,想着存储递增的可以在栈中得到索引,但存储递减的话也是能得到的,当前存储的时候的i就是在栈中比它小的那些索引对应的数值。
想问题还是有些太直接了。
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
Stack<Integer> st= new Stack<>();
int len = temperatures.length;
int[] res = new int[len];
st.push(len-1);
int i= len - 2;
while(i >= 0){
if(st.empty()){
st.push(i);
i --;
continue;
}
else if(temperatures[st.peek()] > temperatures[i]){
res[i] = st.peek() - i ;
st.push(i);
i --;
continue;
}
while(!st.empty() &&temperatures[st.peek()] <= temperatures[i]){
st.pop();
}
}
return res;
}
}2、496.下一个更大元素 I
理解错题意了。。
这个题目不难。
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Stack<Integer> temp = new Stack<>();
int[] res = new int[nums1.length];
Arrays.fill(res,-1);
HashMap<Integer, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0 ; i< nums1.length ; i++){
hashMap.put(nums1[i],i);
}
temp.add(0);
for (int i = 1; i < nums2.length; i++) {
if (nums2[i] <= nums2[temp.peek()]) {
temp.add(i);
} else {
while (!temp.isEmpty() && nums2[temp.peek()] < nums2[i]) {
if (hashMap.containsKey(nums2[temp.peek()])){
Integer index = hashMap.get(nums2[temp.peek()]);
res[index] = nums2[i];
}
temp.pop();
}
temp.add(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}3、503.下一个更大元素II
这个题比较典型吧,这是加了一个循环,多了一轮的处理。
注意while循环,,这个容易忘记。
class Solution {
public int[] nextGreaterElements(int[] nums) {
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<>();
st.push(0);
Arrays.fill(res, -1);
for(int i=1 ; i< nums.length * 2 ; i++){
while(!st.empty() && nums[st.peek()] < nums[i % nums.length]){
res[st.pop()] = nums[i % nums.length];
}
st.push(i % nums.length);
}
return res;
}
}4、42. 接雨水
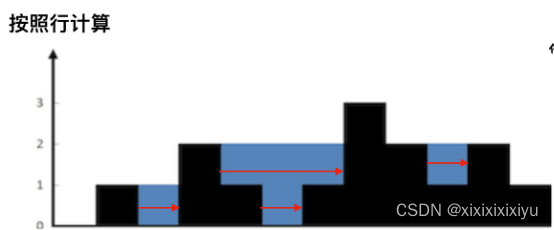
用单调栈的方法需要一行一行算,而不是一列。
列不行的原因是无法通过当前状态就确定这个列的数值应该是多少,也无法通过叠加的方式得到。
掌握这个思路就好写多了。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height){
int size = height.length;
if (size <= 2) return 0;
// in the stack, we push the index of array
// using height[] to access the real height
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
stack.push(0);
int sum = 0;
for (int index = 1; index < size; index++){
int stackTop = stack.peek();
if (height[index] < height[stackTop]){
stack.push(index);
}else if (height[index] == height[stackTop]){
// 因为相等的相邻墙,左边一个是不可能存放雨水的,所以pop左边的index, push当前的index
stack.pop();
stack.push(index);
}else{
//pop up all lower value
int heightAtIdx = height[index];
while (!stack.isEmpty() && (heightAtIdx > height[stackTop])){
int mid = stack.pop();
if (!stack.isEmpty()){
int left = stack.peek();
int h = Math.min(height[left], height[index]) - height[mid];
int w = index - left - 1;
int hold = h * w;
if (hold > 0) sum += hold;
stackTop = stack.peek();
}
}
stack.push(index);
}
}
return sum;
}
}5、84.柱状图中最大的矩形
算的是局部和,当出现两边低中间高的情况就开始计算。至于为什么这么算,主要在于求面积的高就是当前在栈顶处且当前遍历的元素小于他,并且宽是从栈顶到当前遍历的元素。
另外因为栈是升序,所以会栈顶第二个位置的元素跟栈顶元素之间的元素是大于他们的。
很巧妙。
class Solution {
int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
Stack<Integer> st = new Stack<Integer>();
// 数组扩容,在头和尾各加入一个元素
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
newHeights[0] = 0;
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
}
heights = newHeights;
st.push(0);
int result = 0;
// 第一个元素已经入栈,从下标1开始
for (int i = 1; i < heights.length; i++) {
// 注意heights[i] 是和heights[st.top()] 比较 ,st.top()是下标
if (heights[i] > heights[st.peek()]) {
st.push(i);
} else if (heights[i] == heights[st.peek()]) {
st.pop(); // 这个可以加,可以不加,效果一样,思路不同
st.push(i);
} else {
while (heights[i] < heights[st.peek()]) { // 注意是while
int mid = st.peek();
st.pop();
int left = st.peek();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
result = Math.max(result, w * h);
}
st.push(i);
}
}
return result;
}
}






















 1358
1358

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








